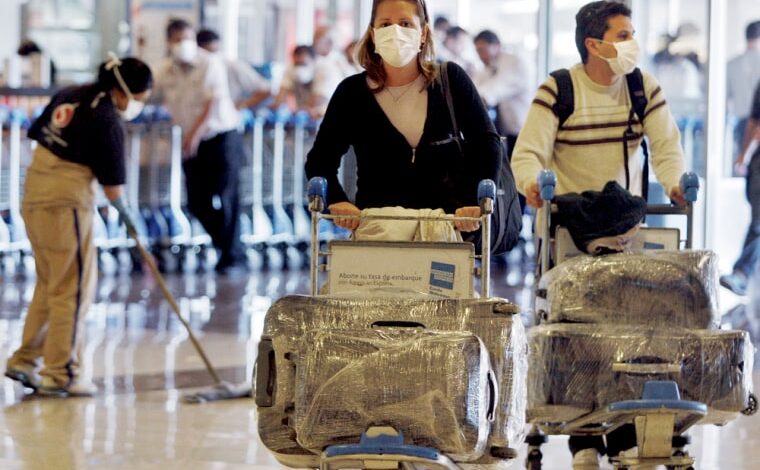

Caribbean Nations Swine Flu Precautions
Caribbean nations take swine flu precautions to protect their populations from outbreaks. This proactive approach involves various measures, from strengthening public health infrastructure to educating the public about prevention strategies. Understanding the potential impact on tourism and the importance of international cooperation is also crucial in the face of a global health concern.
This article explores the specifics of swine flu preparedness in Caribbean nations, examining the preventative measures in place, the potential impact on the tourism industry, and the role of international collaboration in combating the spread of this illness.
Overview of Swine Flu
Swine flu, or influenza A(H1N1), is a viral respiratory illness that can affect pigs and humans. Understanding its various forms, transmission pathways, and historical impact is crucial for effective preventative measures. While not always severe, the potential for pandemic outbreaks necessitates ongoing vigilance and preparedness.This overview delves into the different aspects of swine flu, from its historical context to the current global understanding, highlighting the importance of staying informed about this viral threat.
Types of Swine Flu
Swine influenza viruses are categorized into various subtypes based on their hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins. The most common types affecting humans are those that have combined swine, avian, and human influenza genes, creating a hybrid virus capable of infecting people. The specific strain and its genetic makeup can significantly influence the virus’s transmissibility and severity.
Transmission Methods
Swine flu, like other influenza viruses, is primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets. This occurs when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, releasing tiny particles containing the virus into the air. These particles can be inhaled by others in close proximity, leading to infection. Direct contact with contaminated surfaces can also contribute to transmission, though to a lesser extent.
The virus’s transmissibility varies among different strains and can be influenced by factors like humidity and temperature.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of swine flu can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, headache, fatigue, and sometimes, diarrhea or vomiting. The severity of symptoms can differ depending on individual factors and the specific strain of the virus. Early detection and treatment are essential to mitigate potential complications.
Historical Context of Outbreaks
Several significant swine flu outbreaks have occurred throughout history. The 2009 pandemic, caused by the H1N1 strain, was a global event with a considerable impact on public health systems worldwide. Understanding past outbreaks provides valuable insights into the virus’s behavior and the effectiveness of preventative measures. Historical data underscores the need for ongoing research and preparedness strategies.
Differences Between Strains
Different strains of swine flu viruses can vary in their virulence and transmissibility. Some strains may cause only mild symptoms, while others can lead to severe illness, hospitalization, and even death. The severity of a particular outbreak is influenced by the specific strain’s genetic composition and the overall health of the population. Factors such as pre-existing conditions play a role in the impact of the virus.
Current Understanding of Global Distribution
The global distribution of swine flu viruses is constantly monitored by public health organizations. Tracking cases and outbreaks helps understand the virus’s spread and the effectiveness of public health interventions. International collaborations play a vital role in coordinating surveillance and response efforts to contain the spread of any potential outbreak.
Comparison of Swine Flu Symptoms with Other Respiratory Illnesses
| Symptom | Swine Flu | Common Cold | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Often present | Sometimes present | Usually present |
| Cough | Common | Common | Common, often severe |
| Sore Throat | Common | Common | Possible |
| Muscle Aches | Common | Rare | Possible |
| Headache | Common | Possible | Possible |
| Fatigue | Common | Possible | Possible |
| Diarrhea/Vomiting | Possible | Rare | Possible |
This table provides a basic comparison of symptoms. A doctor’s evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Caribbean Nations’ Preparedness
The Caribbean, with its unique blend of geography, population density, and existing health infrastructure, presents a complex landscape for swine flu preparedness. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and strengths of individual nations is crucial for effective response strategies. Different islands and countries face varying degrees of risk, influenced by factors like tourism, travel patterns, and the capacity of their healthcare systems.
Assessing these elements allows for targeted interventions and resource allocation.Existing public health systems in the Caribbean vary considerably. Some nations have well-established epidemiological surveillance networks and robust laboratory capabilities, while others may face limitations in terms of resources and trained personnel. This disparity in infrastructure necessitates tailored approaches to preparedness, considering the specific needs and constraints of each nation.
Specific Caribbean Nations at Risk
Several Caribbean nations are particularly vulnerable to swine flu outbreaks due to their high population density, tourism-dependent economies, and proximity to other countries. These nations, often with smaller healthcare systems, are more susceptible to rapid disease transmission. Examples include the Bahamas, Barbados, Jamaica, and some of the smaller islands in the Lesser Antilles. The density of population in certain areas and the constant influx of tourists amplify the potential for outbreaks.
Predicting specific outbreaks is difficult, as it depends on various factors including viral strains, transmission rates, and the overall health status of the population.
Existing Public Health Infrastructure
The public health infrastructure within the Caribbean nations varies greatly. Some countries have well-developed systems for disease surveillance, including robust laboratory capabilities for rapid diagnosis. However, other nations may lack the same level of infrastructure and resources. This disparity necessitates a coordinated effort to strengthen public health systems across the region. For instance, nations with robust systems can share resources and expertise with those lacking them.
Caribbean nations are understandably taking precautions against swine flu, boosting health protocols across the region. This is especially important now that Aruba has accepted JetBlue’s CommonPass health passport program, a move that will likely influence other islands in their approach to travel safety. The initiative could streamline travel procedures and reduce the spread of illness by allowing for quicker, verified health checks, ultimately helping Caribbean nations maintain visitor safety and tourism as swine flu concerns remain.
Preventative Measures Implemented
Caribbean nations are taking proactive steps to mitigate the risk of swine flu outbreaks. These include strengthening surveillance systems, promoting hand hygiene, providing information to the public about preventative measures, and stockpiling necessary medical supplies. The World Health Organization (WHO) and regional health organizations offer guidance and support to Caribbean nations in implementing these measures. Each nation’s implementation will vary based on its resources and priorities.
Comparison of Preparedness Levels
Comparing the preparedness levels of Caribbean nations requires a multi-faceted assessment. Factors such as the number of trained healthcare workers, availability of diagnostic equipment, and the capacity for rapid response need to be evaluated. Nations with more developed healthcare systems and better funding may be better equipped to handle an outbreak compared to those with limited resources. For example, larger islands often have more extensive infrastructure, while smaller islands may have limited resources and personnel.
Resources and Personnel for Swine Flu Response, Caribbean nations take swine flu precautions
| Nation | Available Personnel (Doctors, Nurses, etc.) | Diagnostic Capacity | Medical Supplies (Ventilators, etc.) | Emergency Response Teams |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahamas | Moderate | Good | Limited | Adequate |
| Barbados | High | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Jamaica | High | Good | Moderate | Adequate |
| Dominica | Low | Limited | Very Limited | Limited |
This table provides a general overview of available resources and personnel for swine flu response. The specific numbers and capacities may vary depending on the particular situation and the resources available at the time of an outbreak. It’s crucial to remember that these figures are estimates and may not reflect the full extent of available resources.
Precautionary Measures: Caribbean Nations Take Swine Flu Precautions

Caribbean nations, recognizing the potential threat of swine flu, implemented various preventative measures to safeguard public health. These proactive steps, ranging from vaccination campaigns to public health awareness programs, underscore the region’s commitment to mitigating the spread of the virus and protecting its citizens. International cooperation played a crucial role in bolstering these efforts.Effective preventative measures against swine flu involve a multi-faceted approach.
This includes not only individual actions but also coordinated efforts by governments, healthcare providers, and international organizations. By understanding the various strategies employed, Caribbean nations can learn from successes and adapt approaches to best suit their unique circumstances.
Vaccination Programs
Vaccination campaigns are a cornerstone of swine flu prevention. The availability and accessibility of vaccines are critical factors in successful vaccination programs. The Caribbean, like other regions, faced challenges in ensuring equitable vaccine distribution and addressing potential hesitancy among the population. This often necessitates targeted campaigns focusing on specific demographics and addressing concerns directly.
Caribbean nations are taking precautions against swine flu, a smart move given the current global health climate. However, the economic realities of things like american s pay cut are impacting travel budgets and tourism, which could indirectly affect the Caribbean’s economy. This highlights the interconnectedness of global events and how one issue can ripple across borders, making preventative measures like those for swine flu all the more crucial.
Isolation Protocols
Implementing strict isolation protocols is essential for containing the spread of swine flu. These protocols often involve identifying and isolating individuals exhibiting symptoms, tracing contacts, and quarantining potentially infected individuals. The effectiveness of these protocols relies heavily on the prompt identification of cases and the cooperation of the public in adhering to guidelines. Swift and decisive action is crucial to prevent widespread outbreaks.
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns play a pivotal role in educating the public about swine flu prevention. These campaigns often utilize various communication channels, including social media, community gatherings, and traditional media outlets. Effective campaigns provide clear and concise information on how to prevent infection, including hand hygiene, cough etiquette, and seeking medical attention. Clear communication is vital for ensuring the public understands the importance of preventive measures.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the WHO, play a vital role in supporting Caribbean nations’ efforts to prevent swine flu. These organizations provide technical expertise, financial assistance, and logistical support to enhance preparedness and response capabilities. They often share best practices from other regions and facilitate the exchange of knowledge and resources among nations. This collaborative approach is crucial for strengthening public health systems in vulnerable regions.
Examples of Successful Preventative Measures
Successful preventative measures against swine flu have been observed in various regions. For instance, regions with robust surveillance systems and rapid response mechanisms have often been better equipped to contain outbreaks. A combination of swift testing, contact tracing, and isolation has proven effective in preventing widespread transmission.
Comparison of Approaches
Different countries have adopted varying approaches to swine flu prevention. Factors such as economic resources, existing public health infrastructure, and cultural context influence the strategies implemented. Some nations may prioritize vaccination programs, while others may focus on public health campaigns or isolation protocols. The effectiveness of each approach often depends on the specific circumstances and context.
Effectiveness of Preventative Measures
| Preventative Measure | Description | Effectiveness (High/Medium/Low) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccination Programs | Providing vaccines to vulnerable populations | High | High vaccination rates correlated with lower infection rates in some regions. |
| Isolation Protocols | Identifying and isolating individuals exhibiting symptoms | Medium | Swift isolation protocols in some regions limited the spread of the virus. |
| Public Health Campaigns | Educating the public about prevention | Medium | Campaigns promoting hand hygiene and cough etiquette reduced infection rates. |
Impact on Tourism
The Caribbean, a region renowned for its pristine beaches and vibrant culture, heavily relies on tourism for its economic prosperity. A swine flu outbreak, even a contained one, can have a significant and immediate impact on visitor numbers and consequently, the region’s financial well-being. Understanding the potential ramifications and proactive measures to mitigate them is crucial for safeguarding the sector’s resilience.Tourism in the Caribbean is extremely vulnerable to health crises.
The very nature of the industry, involving close contact between visitors and locals, makes it highly susceptible to the spread of contagious illnesses. A perceived or actual threat can quickly deter potential travelers, leading to significant financial losses for businesses and governments alike. The swift and decisive actions taken during previous health scares serve as a crucial reminder of the importance of preparedness.
Potential Impact of Swine Flu Outbreaks on Tourism
A swine flu outbreak can lead to a drastic decrease in tourist arrivals. Fear of infection and travel advisories issued by health organizations can effectively close down markets. This decline in tourist numbers directly impacts hotels, restaurants, tour operators, and other businesses dependent on visitor spending. The ripple effect can be felt throughout the entire economy, affecting employment rates and government revenue.
This is particularly damaging to smaller islands that are highly reliant on tourism.
Measures to Mitigate Negative Effects on Tourism
Swift and transparent communication is key. Clear, concise information about the situation, coupled with reassurance about safety measures, can go a long way in reassuring tourists. Effective communication channels, including social media and travel advisories, are vital for reaching target audiences promptly. Government and industry cooperation in managing the situation is essential to maintaining the region’s image as a safe and welcoming destination.
Importance of Effective Communication Strategies During Outbreaks
Effective communication strategies play a pivotal role in managing the impact of a swine flu outbreak on tourism. A well-coordinated communication plan that includes pre-emptive measures, rapid response protocols, and ongoing updates is crucial. Transparency and honesty are paramount. Avoiding misinformation and proactively addressing concerns with factual data builds trust with tourists and fosters a sense of security.
Comparison of Past Swine Flu Outbreaks on Tourism
Past outbreaks of influenza, including H1N1, have demonstrated a direct correlation between perceived or real health threats and the tourism sector’s performance. For instance, the 2009 H1N1 pandemic saw a significant decline in tourist arrivals across several regions. The swift implementation of preventive measures, combined with targeted communication strategies, was essential in helping to restore confidence and eventually, tourism numbers.
The specific impact varied depending on the region’s responsiveness and the intensity of the outbreak.
Caribbean nations are taking proactive steps to prevent swine flu, which is a smart move. With travel on the rise, and considering the recent predictions of beautiful weather from Blue Sky Tours, who are celebrating their 30th year with sunny days guaranteed in their upcoming tours blue sky tours predicts sunny days in its 30th year , it’s essential that people prioritize health precautions.
These precautions will be key to ensuring a safe and enjoyable trip for everyone, particularly during this time.
Potential Economic Losses and Recovery Timelines
| Outbreak Severity | Potential Economic Losses (Estimated) | Recovery Timeline (Estimated) ||—|—|—|| Low | $500 million – $1 billion | 6-12 months || Moderate | $1 billion – $2 billion | 12-18 months || High | Over $2 billion | 18-24 months |The table above illustrates the potential economic ramifications of varying outbreak severities. It is important to note that these figures are estimates and can vary based on factors like the speed of containment, public health responses, and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
Past experiences with similar crises can inform estimations and aid in developing effective recovery plans.
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns play a crucial role in mitigating the spread of infectious diseases like swine flu. Effective campaigns are essential for educating the public about prevention methods and fostering a culture of preparedness. This is particularly important in vulnerable regions like the Caribbean, where proactive measures can significantly reduce the impact of an outbreak.Public health campaigns regarding swine flu, or any pandemic, need to be more than just announcements.
They need to be tailored to the specific needs and cultural contexts of the population being targeted. This includes considering factors such as language barriers, literacy levels, and existing health beliefs. The ultimate goal is to ensure that information is accessible, understandable, and actionable for everyone.
Content and Methods of Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns about swine flu prevention should include clear and concise information about transmission, symptoms, and prevention strategies. These campaigns should be comprehensive, covering various aspects such as hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms develop. Visual aids, such as posters, infographics, and videos, are often used to reinforce key messages.
Community engagement is also vital, involving local leaders, health workers, and community organizations to deliver the information directly to the people.
Examples of Effective Public Health Campaigns
Several regions have implemented successful public health campaigns for various diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States, for instance, has a long history of successful campaigns related to influenza prevention. These campaigns often employ a multi-pronged approach, using various media platforms to disseminate information, including social media, television, radio, and print. The effectiveness of these campaigns is often measured by changes in public behavior, such as increased handwashing rates or higher vaccination rates.
Similarly, campaigns in other parts of the world, like the World Health Organization’s (WHO) initiatives, have also effectively communicated vital health information during outbreaks.
Importance of Clear and Concise Communication
Clear and concise communication is paramount in public health campaigns. Ambiguous or overly technical language can hinder understanding and lead to misinterpretation of critical information. Public health messages should be presented in plain language, avoiding jargon and using easily understandable visuals. The use of culturally relevant examples and relatable scenarios can enhance comprehension and impact.
Caribbean nations are taking precautions against swine flu, which is a smart move. Meanwhile, it’s great to see beaches resorts getting certification for autism sensitivity training, like the ones offered at beaches resorts get certification for autism sensitivity training. This demonstrates a growing awareness of inclusivity and will likely lead to safer and more enjoyable vacations for everyone, even for travelers concerned about swine flu.
Role of Social Media in Disseminating Information
Social media platforms have become powerful tools for disseminating information during public health emergencies. Their ability to reach a large audience quickly and efficiently makes them invaluable for spreading critical information about swine flu prevention. However, it’s crucial to ensure that information shared on social media is accurate and verified by reliable sources. Misinformation can easily spread through social media, so it is imperative to identify and address false or misleading claims promptly.
Sample Public Service Announcement
“Swine flu can be dangerous. Protect yourself and your loved ones. Cover your coughs and sneezes, wash your hands frequently, and seek medical attention if you experience symptoms. Stay informed. Reliable sources of information are crucial to fighting this. For more details, visit the Ministry of Health website.”
International Cooperation
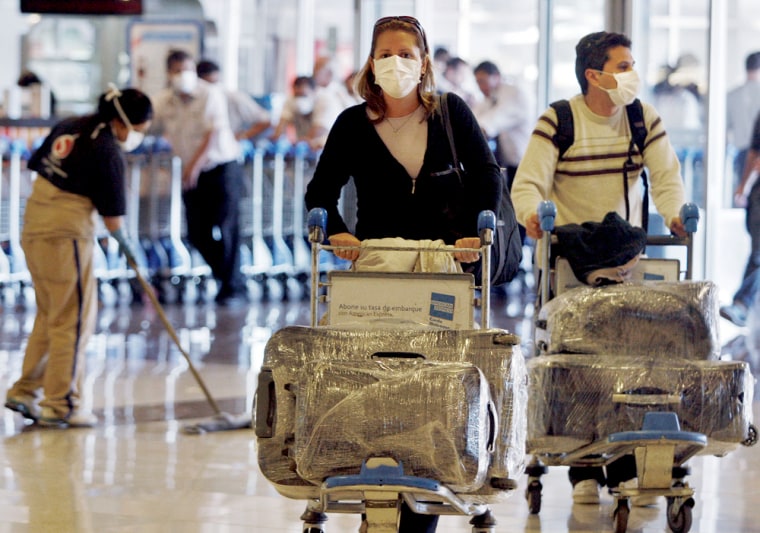

The Caribbean’s vulnerability to infectious disease outbreaks, like swine flu, necessitates strong international partnerships. International organizations possess crucial resources and expertise that can significantly bolster the region’s response capacity. Effective collaboration is paramount to mitigating the impact of such events and safeguarding public health.International collaborations are vital in swiftly responding to and containing infectious disease outbreaks. Sharing information, resources, and best practices across borders can significantly enhance preparedness and response strategies.
This collaborative approach is crucial, especially in regions with limited resources, like many Caribbean nations. The ability to leverage the expertise and resources of international organizations can significantly reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks.
Caribbean nations are understandably taking precautions against swine flu, especially given the recent travel advisories. With cruise ships like the Allure of the Seas undergoing a major refurbishment allure of the seas refurbishment , it’s likely that heightened hygiene standards are already in place, contributing to a safer environment for all passengers. These precautions, along with increased monitoring, are key to ensuring a healthy and enjoyable experience for everyone visiting the region.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations play a pivotal role in supporting Caribbean nations during health crises. Their expertise, funding, and logistical support can significantly enhance local capacities for disease surveillance, prevention, and treatment. These organizations provide crucial assistance, including the provision of medical supplies, training programs for healthcare professionals, and technical expertise to bolster local infrastructure.
Examples of International Collaborations
Numerous examples demonstrate the importance of international cooperation in managing infectious disease outbreaks. The World Health Organization (WHO) has been instrumental in coordinating global responses to various outbreaks, including past influenza pandemics. Regional organizations, such as the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), actively support Caribbean nations in strengthening their public health infrastructure. Their collaborative efforts often involve providing technical assistance, sharing data, and coordinating vaccination campaigns.
Importance of Data and Best Practices Sharing
The sharing of data and best practices between nations is essential for effective outbreak management. This collaborative approach enables the rapid identification of emerging trends, the development of evidence-based strategies, and the adaptation of effective interventions. Sharing information on disease surveillance systems, infection control measures, and public health campaigns fosters a more coordinated and effective response. This process allows for learning from other experiences, which is critical for developing tailored strategies for specific regions.
Challenges in International Cooperation
Despite the importance of international cooperation, challenges remain. These include differing levels of resources and infrastructure among nations, communication barriers, and the need for rapid decision-making in crisis situations. Building trust and fostering strong relationships between international organizations and local authorities are crucial to overcome these hurdles. Furthermore, bureaucratic processes and coordination challenges can sometimes hinder the swift delivery of crucial resources.
Table: Contributions of International Organizations
| Organization | Key Contributions |
|---|---|
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Global coordination, technical guidance, resource mobilization, and setting global standards. |
| Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) | Regional support, technical assistance, capacity building, and epidemiological surveillance. |
| United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) | Support for vulnerable populations, especially children, through vaccination campaigns and health education. |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF) | Financial assistance and policy support for countries impacted by the health crisis, considering the potential economic repercussions. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, Caribbean nations are taking significant steps to address the threat of swine flu. Their preparedness levels vary, but the region is working to mitigate risks through robust public health campaigns, preventative measures, and international cooperation. Tourism plays a vital role in the Caribbean economy, and the potential impact of an outbreak necessitates careful planning and communication strategies.
The future health and economic stability of the Caribbean depend on continued vigilance and collaborative efforts.
Q&A
What are the most common symptoms of swine flu?
Common symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Some cases may also present with nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
How can I protect myself from swine flu?
Vaccination, hand hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are crucial preventative measures. Following public health guidelines and practicing good respiratory etiquette can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
What is the role of international organizations in supporting Caribbean nations?
International organizations provide resources, expertise, and technical assistance to Caribbean nations in strengthening their public health infrastructure and response capabilities. This often involves sharing best practices and facilitating collaboration among nations.
How might swine flu outbreaks impact the Caribbean tourism industry?
Outbreaks can negatively affect tourism due to travel restrictions, cancellations, and reduced consumer confidence. Effective communication strategies and proactive measures are essential to mitigate potential economic losses.






