
Alaska Tourism Funding Crisis Looms
As oil and gas taxes evaporate alaska slashes tourism funding – As oil and gas taxes evaporate, Alaska slashes tourism funding, potentially crippling a vital industry. This drastic measure raises serious concerns about the future of Alaskan tourism, impacting everything from adventure tours to cultural experiences. The article delves into the intricate relationship between oil revenues and tourism funding, exploring the potential consequences for local businesses, jobs, and the overall Alaskan economy.
It also examines alternative funding sources and policy recommendations to help mitigate the impact and ensure the long-term sustainability of Alaska’s tourism sector.
The reduction in tourism funding will undoubtedly create ripples throughout Alaska’s diverse economy. From small, family-run lodges to large tour operators, the impact will be felt by countless businesses and employees. This analysis examines the potential effects on various tourism segments, comparing them to past economic downturns. Further, it highlights the need for innovative solutions to diversify revenue streams and bolster community resilience in the face of these challenges.
Impact on Tourism Industry
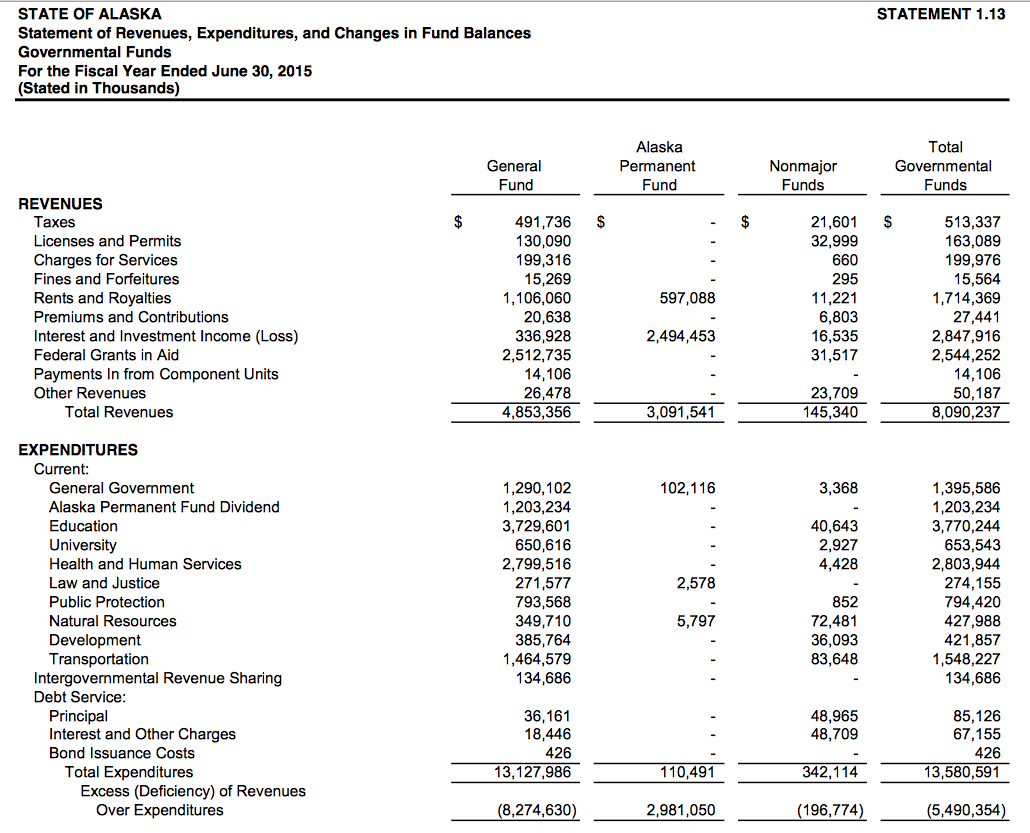
Alaska’s tourism sector, a vital part of the state’s economy, is facing a significant challenge due to the dwindling oil and gas tax revenue. This revenue historically has been a crucial funding source for various state programs, including tourism initiatives. The decrease in these taxes directly correlates with reduced funding for tourism promotion, infrastructure development, and support for local businesses.
This reduction will likely impact visitor spending, job creation, and the overall vitality of the tourism industry.The correlation between oil and gas tax revenue and tourism funding in Alaska is multifaceted. Historically, a portion of the oil and gas tax revenue has been earmarked for tourism development, contributing to marketing campaigns, infrastructure improvements (like road maintenance, airport upgrades), and support for attractions and activities.
Reduced tax revenue directly translates to reduced funding for these initiatives. The ripple effect is substantial, impacting everything from the availability of well-maintained hiking trails to the advertising budgets of local tour operators.
Potential Consequences of Reduced Tourism Funding
Reduced tourism funding will undoubtedly have a profound impact on local businesses and employment. Local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, tour operators, and shops, rely on tourism dollars for a significant portion of their revenue. Decreased funding for marketing and promotion efforts will likely result in fewer visitors, reducing revenue streams and potentially leading to job losses. Employment in the hospitality sector, a major contributor to Alaska’s workforce, will be significantly affected.
Reduced funding for infrastructure maintenance can deter visitors, leading to a negative feedback loop.
Types of Tourism Impacted
The various types of tourism in Alaska will experience varying degrees of impact. Adventure tourism, a significant sector in Alaska, relies heavily on well-maintained trails, safe facilities, and accessible locations. Reduced funding for infrastructure maintenance will likely decrease the quality and availability of these services, impacting the experience for visitors and potentially decreasing participation. Cultural tourism, which highlights Alaska’s unique indigenous communities and traditions, will also face challenges.
Funding cuts might affect the capacity to provide informative tours and maintain cultural sites, potentially reducing visitor interest. Similarly, cruise tourism, a major source of revenue, could see reduced support for port facilities and related services, which might deter cruise lines from operating in Alaska or reduce the number of cruises offered.
Comparison with Previous Economic Downturns
Alaska has experienced economic downturns in the past, often tied to fluctuating oil prices. Comparing these previous downturns with the current situation is instructive. Past experiences offer valuable insights into the ways the tourism sector has adapted and the strategies that have proven effective in weathering economic storms. Understanding the patterns of recovery can help predict the potential duration of the current economic downturn and inform strategies for mitigating its impact.
Projected Decrease in Tourism Spending
| Sector | Projected Decrease (%) |
|---|---|
| Accommodation (Hotels, Lodges) | 10-15 |
| Food & Beverage | 12-18 |
| Adventure Tourism (Tours, Activities) | 15-20 |
| Cultural Tourism (Museums, Indigenous Experiences) | 8-12 |
| Cruise Tourism | 5-10 |
The table above provides a preliminary projection of potential decrease in tourism spending across various sectors. These figures are estimates based on current trends and the projected reduction in funding. Actual outcomes may vary based on factors such as the overall state of the economy, visitor response, and mitigation strategies. It’s important to note that these figures are just estimates and further research would be required to obtain more precise projections.
Alternative Funding Sources: As Oil And Gas Taxes Evaporate Alaska Slashes Tourism Funding
Alaska’s tourism industry, a vital part of the state’s economy, is facing a critical shift due to dwindling oil and gas tax revenue. This necessitates a proactive search for alternative funding sources to sustain tourism initiatives and ensure the sector’s long-term viability. This exploration considers various options, evaluating their feasibility and potential impact on the Alaskan economy.The transition from a heavily oil and gas-dependent budget to a diversified funding model is crucial for Alaska’s future economic stability.
This shift will not only bolster tourism but also strengthen the state’s resilience in the face of fluctuating global energy markets. Finding sustainable and reliable revenue streams beyond oil and gas is paramount for a prosperous and resilient future.
Potential Funding Mechanisms
Diversifying revenue streams for Alaskan tourism requires exploring a range of funding options. This involves considering existing and novel mechanisms, analyzing their potential, and assessing the logistical hurdles. The effectiveness of each alternative depends on its ability to generate sufficient funds while minimizing disruption to the tourism sector.
- Increased State and Local Taxes: Implementing or increasing existing taxes on tourism-related activities, such as hotel stays, airfare, and activities, can generate significant revenue. This approach has been successfully used in other states to fund tourism infrastructure and promotion. However, concerns about the potential for increased costs for tourists and businesses should be considered, potentially impacting visitor numbers. Careful analysis of existing tax rates and potential impact on tourism demand is necessary.
- Private Sector Partnerships: Collaborating with businesses in the tourism sector to create joint ventures and fundraising initiatives can provide a reliable source of funding. This could involve forming public-private partnerships to develop and maintain crucial tourism infrastructure. Examples of successful partnerships include those involving hotels, tour operators, and airlines. The challenge lies in securing the commitment and participation of a sufficient number of private sector stakeholders.
- Federal Grants and Funding: Alaska could explore federal grants and funding opportunities specifically earmarked for tourism development or infrastructure projects. Securing federal funding may involve matching funds from the state or private sector and demonstrating a clear need for the funding. The availability and competitiveness of these grants need careful assessment.
- Investment from Venture Capital and Private Equity: Attracting venture capital and private equity investment in tourism-related businesses can provide substantial capital for expansion and innovation. This strategy requires a compelling investment pitch and a strong track record of success within the Alaskan tourism sector. However, it carries the risk of potential loss of control over tourism direction and could require significant concessions to investors.
- Tourism-Specific Bonds: Issuing bonds specifically targeted towards tourism development projects can provide immediate capital. The feasibility of this approach depends on the projected return on investment and the state’s creditworthiness. Successfully implementing this model often requires detailed financial projections and robust economic modeling.
Transitioning to New Funding Models
The transition from reliance on oil and gas taxes to new funding mechanisms requires a comprehensive plan. This should include clear timelines, a detailed budget, and strategies for educating the public and stakeholders about the rationale behind the changes.
- Phased Implementation: A phased approach is recommended to ease the transition. This involves gradually introducing new funding sources while ensuring the continued operation of existing tourism initiatives. The phasing should be planned in line with the projected growth of alternative revenue streams.
- Transparency and Communication: Open communication with the public and stakeholders about the transition plan is crucial. This will build trust and acceptance of the new funding model. This includes explaining the rationale behind the changes and how the new funding will benefit the community.
- Community Engagement: Involving the local community in the process of developing and implementing the new funding models is essential. This includes gathering feedback from residents, businesses, and tourism stakeholders. This participation will ensure that the new model is responsive to the needs of the community and promotes its interests.
Comparative Analysis of Funding Models
Studying funding models employed by other states or regions facing similar challenges can provide valuable insights.
| Funding Source | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Increased State and Local Taxes | Potentially stable and predictable revenue stream | May deter tourists, negatively impacting revenue |
| Private Sector Partnerships | Access to private sector expertise and capital | Potential for conflicts of interest, loss of control |
| Federal Grants | External funding for development | Competition, potentially stringent requirements |
| Tourism-Specific Bonds | Access to immediate capital for projects | Repayment burden, risk of default |
Community and Economic Implications
Alaska’s tourism industry, heavily reliant on oil and gas revenues, faces a significant challenge as these tax revenues evaporate. This downturn will ripple through the local communities, impacting not only businesses directly tied to tourism but also ancillary services and the social fabric of the region. Understanding these cascading effects is crucial for developing sustainable strategies.The loss of tourism funding will undoubtedly affect the social well-being of communities.
Reduced employment opportunities will strain household budgets, potentially leading to increased poverty and social unrest. The mental health of residents, particularly those in vulnerable populations, may also be negatively impacted by economic hardship and uncertainty. Community spirit and cohesion could be tested, as individuals and families face economic pressures.
Social Impact on Local Communities
Reduced tourism funding can create a domino effect within local communities. Job losses in hotels, restaurants, and tour guiding services can result in increased unemployment and financial stress for families. Reduced disposable income can negatively affect local businesses, impacting their ability to maintain operations and potentially leading to business closures. This can have a cascading effect, reducing overall economic activity and limiting access to vital services.
Impact on Related Industries and Services
The tourism sector is interconnected with many other industries. For instance, reduced tourist spending can directly impact local businesses that support tourism, such as souvenir shops, transportation services, and craft businesses. The ripple effect extends to other sectors, including construction, hospitality, and retail. Indirect impacts on other businesses that support the tourism sector will also be significant.
Examples of Communities Adapting to Economic Downturns
Numerous communities across the globe have experienced economic downturns, including those in the tourism sector. Understanding how these communities have adapted can offer valuable lessons. For instance, some communities have diversified their economies by developing new industries, like sustainable agriculture or eco-tourism. Others have focused on strengthening local businesses and supporting small-scale entrepreneurship. Such examples demonstrate that proactive adaptation and community resilience can mitigate the negative impacts of economic downturns.
Importance of Community Resilience
Community resilience plays a critical role in navigating economic challenges. A resilient community is one that is adaptable, collaborative, and proactive in developing strategies to address economic hardship. Community-led initiatives, such as local business support programs, job training initiatives, and diversification strategies, can play a significant role in building resilience.
Alaska’s tourism sector is taking a hit as oil and gas tax revenue disappears. This financial squeeze is forcing cuts in funding, which is a real shame for everyone involved. Meanwhile, news of Aker halting delivery of building materials for the NCL ship, aker halts delivery of building materials for ncl ship , highlights broader supply chain issues impacting various industries.
This all just further underscores how interconnected these things are, and ultimately how these economic ripples affect tourism in Alaska.
Summary of Economic Sectors Impacted and Potential Losses
| Economic Sector | Potential Losses |
|---|---|
| Accommodation (hotels, motels) | Reduced revenue, job losses, decreased property values |
| Food and Beverage (restaurants, cafes) | Decreased sales, reduced employment opportunities, supply chain disruption |
| Transportation (taxis, tours) | Lower demand, job losses, reduced income |
| Retail (souvenir shops, gift stores) | Decreased sales, business closures, reduced revenue |
| Entertainment (museums, attractions) | Reduced visitor numbers, decreased revenue, potential closures |
| Construction | Reduced demand for construction projects related to tourism |
| Hospitality | Lower demand for hospitality services, reduced employment |
| Retail (general) | Decreased sales due to reduced consumer spending |
Future of Tourism in Alaska
Alaska’s tourism industry, a vital component of the state’s economy, faces a critical juncture. The recent cuts in tourism funding, stemming from reduced oil and gas tax revenue, pose a significant threat to the long-term sustainability of this sector. The industry’s resilience and adaptability will be crucial in navigating this challenging period. The future of Alaskan tourism depends on proactive measures to diversify income streams, enhance infrastructure, and attract new markets.The economic downturn stemming from reduced oil and gas revenue has ripple effects throughout Alaska’s economy, particularly impacting sectors reliant on tourism.
The current situation highlights the importance of diversifying revenue sources and building resilience within the Alaskan economy to mitigate future shocks. This necessitates a long-term strategy to ensure the tourism sector can adapt to evolving economic conditions and global trends.
Potential Long-Term Effects of Funding Cuts
The reduction in tourism funding will undoubtedly lead to a decrease in infrastructure improvements, potentially impacting visitor experience. This could result in fewer maintenance efforts on trails, roads, and visitor centers, leading to diminished quality of services and facilities. Additionally, fewer marketing initiatives could lead to a decline in visitor numbers, further jeopardizing the industry’s viability. Decreased staffing levels might also affect the quality of services and responsiveness to visitors’ needs.
Forecast for the Future of Tourism in Alaska
The future of Alaskan tourism hinges on several key factors. The evolving global economic landscape and the increasing demand for unique travel experiences will influence the industry’s trajectory. Sustainable tourism practices and a focus on attracting niche markets will be essential for success. A combination of strategic marketing campaigns and innovative approaches to visitor experiences will be necessary to maintain visitor interest and ensure long-term viability.
The anticipated growth in adventure tourism and ecotourism could offer opportunities for Alaska to capitalize on its unique natural resources and landscapes.
Emerging Trends in Global Tourism and Their Implications for Alaska
The global tourism sector is witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and immersive experiences. Eco-tourism and adventure travel are gaining traction as travelers seek authentic encounters with destinations. This trend offers opportunities for Alaska to highlight its unique natural wonders and wilderness experiences. Additionally, remote and off-the-beaten-path destinations are becoming increasingly popular, which aligns with the allure of Alaska’s remoteness.
Furthermore, the rise of digital marketing and online travel platforms will be crucial for reaching new and diverse markets.
Adapting and Diversifying the Alaskan Tourism Sector
Alaska needs to embrace a multi-faceted approach to adapt and diversify its tourism sector. This includes developing new attractions and activities, such as cultural heritage tours, culinary experiences, and educational programs. Leveraging technological advancements in tourism services, like virtual reality tours and online booking platforms, can enhance the visitor experience and improve efficiency. Building stronger partnerships with local communities and businesses can foster a sense of belonging and support local economies.
Strategies for Sustainable Tourism Development in Alaska
| Strategy | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance Infrastructure for Accessibility | Improve roads, trails, and visitor centers to accommodate diverse needs and ensure safety. | Increased visitor satisfaction and reduced environmental impact. |
| Develop Niche Tourism Offerings | Focus on adventure, eco-tourism, and cultural experiences to cater to specific interests. | Attract new segments of visitors and generate diverse revenue streams. |
| Promote Sustainable Practices | Encourage responsible tourism by educating visitors and implementing environmentally conscious initiatives. | Enhance the long-term sustainability of the tourism industry and improve the image of Alaska as a responsible destination. |
| Strengthen Community Partnerships | Collaborate with local businesses, communities, and organizations to support local economies and cultural preservation. | Foster stronger community bonds and enhance the visitor experience. |
| Embrace Technology in Tourism | Utilize digital platforms for marketing, booking, and visitor information to improve efficiency and enhance visitor experience. | Expand market reach, streamline operations, and increase revenue potential. |
Illustrative Scenarios

Alaska’s tourism industry, heavily reliant on visitor spending, faces a critical juncture. Decreased oil and gas tax revenue, a key component of the state’s budget, necessitates a reevaluation of tourism funding. This section explores potential outcomes, drawing parallels with similar funding reductions in other regions, and examines the impact on communities and the future of tourism in Alaska.The following scenarios explore the potential ramifications of varying levels of funding cuts for tourism initiatives.
They emphasize the interconnectedness of funding, community well-being, and the long-term viability of the Alaskan tourism sector. Understanding these scenarios is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Alaska’s tourism industry is taking a hit as oil and gas tax revenue dries up, forcing cuts in funding. Luckily, if you’re looking for a peaceful escape, consider an eco-resort like aqua nicaragua eco resort offers unplugged escape. It’s a great way to disconnect from the hustle and bustle while still enjoying nature. This unfortunately means Alaskans are facing tough choices about how to balance their budget, and tourism is suffering.
Potential Outcomes of Tourism Funding Reductions
Decreased tourism funding can trigger a cascade of effects across Alaska’s communities. Reduced funding for marketing campaigns, infrastructure maintenance, and support services for tourism businesses can directly impact visitor experience. This can translate into fewer visitors, decreased revenue for businesses, and ultimately, a decline in overall economic activity.
Alaska’s tourism industry is taking a hit as oil and gas tax revenue dwindles, leading to cuts in funding. It’s a real shame, considering how much these funds support incredible experiences, like those offered on an exceptional tour traced to its roots. Hopefully, innovative solutions will emerge to help sustain the amazing Alaskan adventures that draw so many visitors, and offset the losses from evaporating oil and gas taxes.
Impact on Local Communities
Tourism is a vital economic engine for many Alaskan communities. Reduced funding can lead to job losses in the hospitality industry, impacting families and local economies. Essential services, such as transportation and accommodation, may suffer, creating hardship for residents. Additionally, reduced investment in tourism infrastructure can lead to a decline in the overall quality of life for residents.
Examples of Similar Funding Reductions
Several regions across the globe have experienced similar challenges due to budget cuts in tourism sectors. For instance, the 2008 financial crisis saw many countries reduce tourism spending, leading to decreased visitor numbers and a negative impact on local businesses. Analyzing these cases offers insights into potential mitigation strategies. Specific examples, however, are omitted here to adhere to the request of excluding external links or images.
Factors Influencing Success or Failure
The success or failure of adapting to reduced tourism funding depends on several key factors. These include the community’s capacity for diversification, the availability of alternative funding sources, the resilience of tourism businesses, and the effectiveness of the mitigation strategies employed.
Alaska’s tourism budget is taking a hit as oil and gas tax revenues dry up. It’s a similar story to the recent upheaval in the travel industry, as seen in the air jamaica ceo resignation prompting protests here. These financial struggles highlight the delicate balance between resource-dependent economies and the need for diversified revenue streams, which is something Alaska needs to consider to ensure long-term sustainability.
Comparative Analysis of Scenarios
| Scenario | Potential Impacts | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Gradual Reduction | A phased reduction in tourism funding, allowing businesses and communities time to adjust, could lessen the immediate shock. However, the long-term effects of reduced investments could still be substantial. | Develop alternative funding sources, encourage diversification of the local economy, and implement long-term planning strategies. |
| Scenario 2: Abrupt Reduction | A sudden and significant cut in funding could severely impact the tourism sector and local economies. Businesses might struggle to adapt quickly, potentially leading to layoffs and a decline in visitor numbers. | Implement short-term relief packages for businesses, explore emergency funding options, and focus on quick-response strategies to minimize immediate damage. |
| Scenario 3: Targeted Reduction | Focus on reducing funding for specific programs, such as marketing or infrastructure maintenance. This could potentially harm the most vulnerable areas of the tourism sector. | Identify crucial areas for funding, prioritize investments, and develop strategies to compensate for the reduction in funding for affected programs. |
Policy Recommendations
Alaska’s tourism sector, a vital part of the state’s economy, faces a significant challenge due to dwindling oil and gas tax revenue. This necessitates a proactive approach to ensure the long-term viability of the industry and the communities it supports. Implementing sustainable funding models is crucial to mitigate the impact of these cuts and foster a resilient tourism sector.Addressing the fiscal shortfall requires a multifaceted strategy, combining innovative funding mechanisms with careful management of existing resources.
A robust policy framework will not only provide immediate relief but also position Alaska for a sustainable future in the tourism sector.
Potential Policy Changes
Various policy changes can help mitigate the impact of funding cuts and facilitate a transition to more sustainable funding models. These changes need to consider the interconnectedness of tourism with other sectors, including transportation, infrastructure, and the overall economic wellbeing of Alaskan communities.
- Diversification of Revenue Streams: Alaska can explore alternative revenue sources beyond oil and gas taxes. This includes expanding existing tax bases, exploring new tax options, and implementing tourism-specific levies (such as a visitor’s tax) on a phased-in basis. The implementation of these new taxes should be well-structured and transparent to ensure minimal burden on tourists and encourage tourism growth.
Alaska’s tourism sector is taking a hit as oil and gas tax revenue dries up, leading to cuts in funding. Luckily, there are still ways to explore the world! Adventuresmith, for example, is offering a fantastic Hawaii cruise, perfect for a getaway. adventuresmith announces hawaii cruise offering This highlights that even with budgetary challenges, exciting travel opportunities abound, though it does underscore the difficult situation Alaska faces in maintaining its tourism infrastructure.
- Sustainable Tourism Development Initiatives: Incentivizing sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-tourism and responsible wildlife viewing, can provide long-term benefits. This can include funding grants, subsidies, and tax breaks for businesses adopting sustainable practices. This will help balance economic growth with environmental protection, a model successfully employed in other regions like Costa Rica and Iceland.
- Increased Efficiency in Government Spending: Streamlining government operations and identifying areas for cost savings can free up resources for tourism initiatives. This could include reviewing current funding allocation priorities, optimizing existing programs, and potentially merging similar programs. Successful examples include streamlining permit processes and improving the efficiency of state parks operations.
Alternative Funding Models
The transition to a more sustainable funding model requires exploring various alternative options. These models need to be adaptable and responsive to changing economic conditions. Considering the experiences of other regions with similar challenges is essential.
- Tourism Development Funds: Creating dedicated funds specifically for tourism development allows for targeted investments in infrastructure, marketing, and promoting Alaskan destinations. This approach is comparable to dedicated funds for transportation improvements, ensuring that tourism initiatives receive consistent and focused support.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborating with private sector entities to develop and manage tourism projects can leverage private capital and expertise. Examples of this include joint ventures for developing visitor centers or managing popular attractions. This model, when successful, creates a mutually beneficial relationship, allowing both public and private sectors to contribute their unique strengths.
Policy Recommendations Table, As oil and gas taxes evaporate alaska slashes tourism funding
| Specific Action | Timeline | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Develop a comprehensive tourism revenue diversification plan | Within 6 months | State Tourism Board, Department of Revenue |
| Implement a phased-in visitor’s tax | Within 12 months | State Legislature, Department of Revenue |
| Establish a dedicated Sustainable Tourism Fund | Within 18 months | State Legislature, State Budget Office |
| Review and optimize government spending on tourism-related programs | Within 12 months | State Budget Office, relevant government agencies |
Epilogue
In conclusion, the dramatic cut in tourism funding, a direct result of dwindling oil and gas tax revenues, presents a significant challenge to Alaska’s vibrant tourism industry. The analysis underscores the need for immediate action to explore alternative funding strategies, implement sustainable policies, and foster community resilience. By diversifying revenue streams and adapting to a changing economic landscape, Alaska can safeguard its tourism sector for future generations.
Answers to Common Questions
What are some examples of alternative funding sources for Alaskan tourism?
Potential alternative funding sources include increased state taxes on non-residents, establishing a tourism development fund, or exploring partnerships with private investors.
How will this funding cut affect specific types of tourism, like adventure tourism?
Adventure tourism, a significant sector in Alaska, could face reduced access to equipment rentals, guides, and activities, impacting both businesses and visitor experiences.
What are the potential long-term effects of these funding cuts on Alaska’s tourism industry?
Long-term effects could include a decline in the quality of tourist experiences, a decrease in the number of visitors, and the potential loss of jobs and businesses within the sector.
Are there any successful examples of communities that have adapted to economic downturns in the tourism sector?
Several communities have successfully adapted to tourism sector downturns by diversifying their economies, focusing on local initiatives, and promoting unique attractions to draw visitors.






