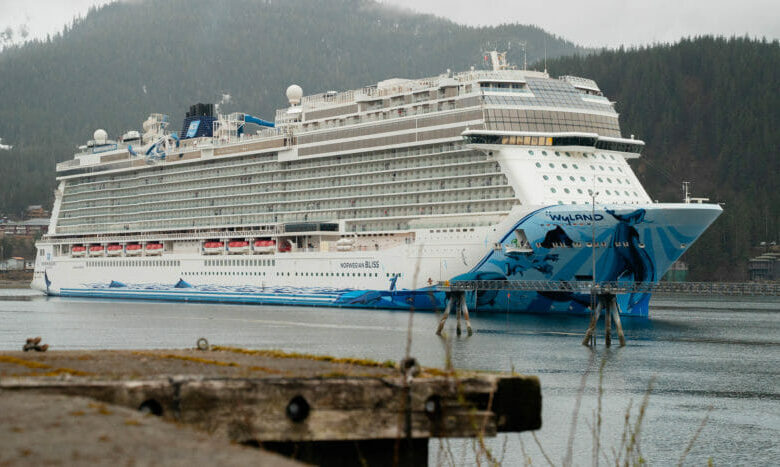
Alaska Scrutinizes Cruise Industry Practices
Alaska scrutinizes cruise industry practices, examining the environmental impact of these massive vessels on Alaskan waters. From historical regulations to current operational practices, this deep dive explores the complexities of the relationship between cruise tourism and the fragile Alaskan ecosystem. The scrutiny reveals both the challenges and opportunities for a sustainable future for the industry in this unique environment.
This analysis delves into the specific regulations, past violations, and the evolving environmental concerns surrounding cruise ships in Alaska. It details the methods Alaska uses to monitor and evaluate compliance, considering the impact on cruise line operations, local communities, and passengers. The discussion also explores potential solutions for improving environmental responsibility and Artikels the potential for innovative technologies to reduce the environmental footprint of these vessels.
Background of Alaskan Cruise Industry Regulations
The Alaskan cruise industry, a significant part of the state’s economy, has a complex history of regulations, evolving in response to environmental concerns and public pressure. Early regulations were often reactive, responding to incidents rather than proactively shaping industry practices. This historical overview explores the development of these regulations, highlighting key legislation and policy changes that have shaped the industry’s environmental footprint.
Historical Overview of Cruise Ship Regulations
Cruise ship regulations in Alaska have evolved significantly since the early days of the industry. Initially, the focus was primarily on safety and navigation, with environmental concerns playing a secondary role. As public awareness of the industry’s impact on Alaska’s pristine ecosystems grew, regulatory bodies were compelled to adapt and strengthen their approach. This evolution reflects the changing understanding of the interconnectedness between human activities and the environment.
Evolution of Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent over time. Early regulations focused primarily on waste disposal, but later ones expanded to include air emissions, noise pollution, and the impact of cruise ship traffic on sensitive marine ecosystems. The industry’s response to these regulations has varied, with some cruise lines adopting more sustainable practices while others have lagged behind.
Examples of Past Violations and Enforcement Actions
Past violations of Alaskan cruise regulations have included instances of exceeding allowable discharge limits, improper waste disposal, and violations of noise pollution standards. Enforcement actions have ranged from fines to warnings, and in some cases, to court settlements. These actions have often served as a catalyst for the development of more comprehensive regulations. A key example is the case of a cruise ship discharging excessive sewage into Alaskan waters, resulting in a significant fine and subsequent changes to waste management protocols.
Timeline of Key Legislation and Policy Changes
- 1970s: Initial legislation focused on ship safety and navigation standards, with minimal environmental provisions. This early stage highlighted the need for a more comprehensive approach.
- 1980s: Growing awareness of the environmental impacts of cruise ships led to the development of regulations concerning waste discharge and pollution control.
- 1990s: Increased pressure from environmental groups and the public spurred the introduction of more stringent regulations, including those related to noise pollution and the protection of marine wildlife.
- 2000s-Present: Ongoing efforts to refine and expand regulations address emerging environmental concerns, such as the effects of climate change on Alaskan waters.
Comparison of Current and Previous Regulations
| Date | Regulation | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | Initial Safety Standards | Basic requirements for ship safety and navigation. | Limited environmental impact; primarily focused on preventing ship accidents. |
| 1990 | Waste Discharge Standards | Limits on the discharge of sewage and other waste. | Improved water quality in some areas; however, enforcement challenges remained. |
| 2000 | Air Emission Regulations | Control on air pollutants from ships’ engines. | Reduced air pollution, but still needed further improvements. |
| 2023 | Comprehensive Environmental Standards | Integrated regulations addressing various environmental impacts (waste, noise, wildlife). | Increased environmental protection and accountability for cruise lines. |
Current Practices of Cruise Lines in Alaska

The Alaskan cruise industry, a vital part of the state’s economy, faces increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental impact. Cruise lines operating in Alaskan waters must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and public concern. This segment examines the current practices of these companies, focusing on their environmental impact assessments, waste management strategies, and overall environmental responsibility.Cruise lines operating in Alaska employ a variety of practices, aiming to balance the economic benefits of tourism with the preservation of the fragile Alaskan environment.
These practices are often influenced by regulatory requirements and public pressure to minimize their ecological footprint.
Common Practices of Cruise Lines
Cruise lines typically employ a range of measures to address their environmental footprint. These include implementing waste management plans, reducing water usage, and adopting energy-efficient technologies. These initiatives aim to minimize the environmental impact of their operations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Cruise lines are required to conduct environmental impact assessments before embarking on voyages. These assessments typically evaluate the potential impact of the cruise ship’s activities on the Alaskan ecosystem. The assessments often include analyses of noise pollution, water discharge, and potential habitat disruption. The quality and comprehensiveness of these assessments vary significantly among cruise lines, with some providing more detailed information than others.
Waste Disposal and Pollution Mitigation
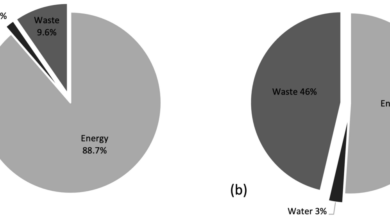
Cruise ships generate significant amounts of waste, including sewage, garbage, and graywater. To mitigate the environmental impact of waste disposal, cruise lines implement various measures. These measures include the use of advanced wastewater treatment systems, the implementation of strict waste segregation protocols, and the careful management of garbage disposal procedures. The effectiveness of these measures can vary significantly depending on the specific cruise line and the level of adherence to regulations.
Environmental Responsibility Statements
Cruise lines often publish environmental responsibility statements outlining their commitment to sustainable practices. These statements frequently address waste reduction, water conservation, and energy efficiency. However, the specifics and depth of these statements vary among different companies, creating inconsistencies in their reported environmental performance.
Waste, Water, and Energy Management Examples
Different cruise lines employ varying strategies for managing their waste, water usage, and energy consumption. Some lines may prioritize advanced wastewater treatment technologies, while others may focus on reducing water usage through efficient plumbing systems and water-saving fixtures. Examples of energy conservation measures include the use of alternative energy sources or the implementation of energy-efficient engines.
Environmental Policies of Cruise Lines
| Company Name | Policy Description | Specific Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cruise Line A | Focuses on reducing overall environmental impact by implementing advanced wastewater treatment, reducing water usage, and optimizing energy consumption. | Investment in cutting-edge wastewater treatment plants, use of water-efficient fixtures, and implementation of alternative energy sources. |
| Cruise Line B | Emphasizes waste reduction through strict segregation protocols, responsible garbage disposal procedures, and minimizing plastic usage. | Implementation of a comprehensive waste management system, promotion of reusable materials, and establishment of recycling programs. |
| Cruise Line C | Prioritizes compliance with environmental regulations and aims to minimize noise pollution and habitat disruption. | Adherence to noise pollution regulations, implementation of marine mammal viewing protocols, and use of low-noise engine technology. |
Alaska’s Scrutiny of Cruise Industry Practices
Alaska’s pristine landscapes and vibrant wildlife attract millions of cruise passengers annually. However, the potential environmental and social impacts of this industry necessitate rigorous oversight. This scrutiny ensures responsible tourism practices and protects Alaska’s unique ecosystems. The state’s approach to monitoring and regulating cruise activities is multifaceted, encompassing a variety of methods and stakeholders.Alaska’s commitment to responsible tourism involves careful evaluation of cruise line practices against environmental standards and public safety protocols.
This proactive approach seeks to mitigate potential negative consequences while maximizing the economic benefits of the cruise industry. The state’s scrutiny is not solely focused on the cruise lines but also extends to the broader ecosystem, including the role of environmental organizations and advocacy groups.
Methods of Scrutiny
Alaska employs a comprehensive strategy for evaluating cruise industry compliance. These methods aim to ensure that cruise ships adhere to environmental regulations and safety protocols. This approach is essential to maintain the delicate balance between economic activity and environmental protection.
Alaska’s scrutiny of cruise industry practices is definitely raising some eyebrows. It’s a fascinating contrast to the current travel landscape, where, as Jamaica is confidently expecting a winter arrivals boost, airlift a priority as Jamaica confident of winter arrivals boost , highlighting a different set of challenges and opportunities. Ultimately, the focus on sustainable tourism practices, both in Alaska and other destinations, will be key to the future of travel.
- Inspections and Audits: Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation (ADEC) and other relevant agencies conduct regular inspections of cruise ships to verify compliance with regulations concerning waste disposal, air emissions, and ballast water discharge. These inspections assess whether cruise lines adhere to permits and licenses. Failure to comply can result in fines or other penalties.
- Data Collection and Monitoring: Alaska utilizes various data collection methods, such as sensors on ships and shore-based monitoring stations, to track emissions, waste discharge, and other relevant factors. These data points are critical for identifying trends and patterns that might indicate violations or environmental damage.
- Public Reporting and Transparency: Cruise lines are required to submit reports detailing their environmental performance, waste management, and safety protocols. These reports are publicly accessible, fostering transparency and accountability.
- Collaboration with Environmental Organizations: Alaska actively engages with environmental organizations, such as the Alaska SeaLife Center and the Alaska Ocean Conservation Coalition, to gather data, identify potential problems, and provide input on regulations. This collaboration ensures a wider range of perspectives and expertise are considered in the evaluation process.
Criteria for Evaluating Compliance
The criteria for evaluating cruise line compliance are multifaceted and encompass environmental protection, public safety, and community impact. Compliance is evaluated based on a set of clearly defined standards and guidelines.
- Environmental Impact: Cruise lines are assessed based on their waste management procedures, air emission levels, and adherence to ballast water regulations. These factors determine their impact on marine ecosystems and wildlife.
- Safety Standards: Compliance is evaluated based on ship maintenance, crew training, and emergency response plans. This ensures the safety of passengers and crew, and the protection of the vessel.
- Community Impact: Alaska considers the economic benefits and potential social impacts of cruise activities. Compliance includes adherence to local regulations and community guidelines.
Role of Environmental Organizations
Environmental advocacy groups play a crucial role in monitoring cruise activities and advocating for stronger environmental protections. Their independent oversight is vital to ensuring that cruise lines comply with environmental regulations.
- Data Gathering and Analysis: Environmental groups gather data on cruise ship activities and compare it with established standards. This helps identify any deviations from regulatory requirements.
- Public Awareness and Advocacy: These organizations raise public awareness about the environmental impacts of cruise ships and advocate for stricter regulations. They use public forums and media to disseminate information and promote awareness.
- Expert Advice and Recommendations: Environmental organizations provide expert advice to Alaskan authorities, offering insights into best practices and potential areas of improvement.
Effectiveness of Monitoring Strategies
The effectiveness of different monitoring strategies employed by Alaska varies. Some methods, like public reporting, offer greater transparency, while others, like inspections, provide direct evidence of compliance or non-compliance.
Data Collection and Investigations
Alaska employs a combination of methods to collect data and conduct investigations. These methods ensure that cruise lines operate in a manner that respects the state’s environmental regulations.
| Method of Scrutiny | Organizations Involved | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Inspections | ADEC, Coast Guard | Verify compliance with regulations, issue citations for violations. |
| Data Collection | ADEC, Environmental Groups, Sensors on Ships | Monitor emissions, waste discharge, and other factors. |
| Public Reporting | Cruise Lines | Provide transparency regarding environmental performance. |
| Collaboration | ADEC, Environmental Groups | Share information, provide input, and identify potential problems. |
Potential Impacts of Increased Scrutiny
Alaska’s heightened scrutiny of cruise industry practices is poised to significantly reshape the Alaskan cruise experience and the industry itself. This increased oversight, driven by concerns about environmental impact, community relations, and operational efficiency, will likely trigger a series of adjustments, impacting everything from cruise itineraries to the financial health of various companies. The consequences will ripple through the local economies and the cruise experience itself, demanding adaptation and innovation from all stakeholders.The potential ramifications extend beyond the immediate effects on cruise lines, impacting local communities, and ultimately, the passenger experience.
The economic and social consequences of these changes are complex and will depend on the specific nature and extent of the regulatory actions taken. This analysis explores the potential impacts across various facets of the industry, considering the financial, operational, and reputational implications.
Potential Impacts on Cruise Line Operations in Alaska
Cruise lines will face pressure to implement more sustainable practices. This includes reducing emissions, optimizing waste management, and improving their interactions with local communities. The industry may see a shift toward smaller, more agile vessels, capable of navigating restricted waterways more efficiently and minimizing environmental footprint. Examples include adjustments to docking procedures, implementing shore power systems, and promoting alternative fuels.
Alaska’s scrutiny of cruise ship practices is definitely a hot topic right now. While they’re digging into the details of the industry’s environmental impact, it’s interesting to see how this contrasts with the vibrant artistic scene in Hawaii, where the academy kicks off 58th artists of hawaii exhibit is underway. Ultimately, both issues highlight the complex interplay between tourism, environmental responsibility, and cultural preservation.
Alaska’s investigation into cruise lines is a crucial step towards finding a sustainable balance.
Some lines might face higher compliance costs due to stricter regulations, potentially affecting their profitability and pricing strategies.
Economic Consequences for the Industry and Local Communities
Increased scrutiny could impact the financial health of cruise lines in various ways. Higher operational costs due to compliance with new regulations could lead to price increases for passengers. Additionally, reduced passenger numbers, due to itinerary changes or stricter environmental regulations, could lead to significant revenue losses. Local communities reliant on cruise tourism may experience decreased economic activity if the number of cruise ship visits declines or the duration of visits is shortened.
Conversely, more sustainable practices could attract environmentally conscious tourists, fostering new revenue streams.
Examples of Potential Changes in Cruise Itineraries or Ship Operations
Cruise itineraries may shift to focus on less sensitive areas, prioritizing environmental concerns and community engagement. The number of days spent in port might decrease to minimize environmental impact and reduce congestion. The deployment of smaller vessels or the modification of existing vessels to adhere to new standards will likely become more common. Examples include implementing more stringent waste disposal regulations, and limiting the number of passengers on shore excursions.
Comparison of Potential Financial Impacts on Different Cruise Lines
The financial impact of increased scrutiny will vary based on the size, fleet composition, and existing sustainability measures of individual cruise lines. Larger companies with extensive fleets might face more significant challenges in adapting to stringent regulations compared to smaller, more agile operators. Cruise lines that have already integrated sustainability practices into their operations may be better positioned to absorb the cost of adjustments and maintain competitiveness.
Potential Changes in the Cruise Experience for Passengers
Passengers might experience changes in the duration of port calls, or the number of excursions available. The cruise experience might be less focused on large-scale activities and more on smaller, community-based interactions. Passengers concerned about environmental impact may find this scrutiny to be a positive development, as it suggests a greater focus on sustainability.
Alaska’s ongoing scrutiny of cruise industry practices is definitely raising some eyebrows. It’s a complex issue, and recent events, like Aker halting delivery of building materials for an NCL ship ( aker halts delivery of building materials for ncl ship ), highlight potential underlying problems within the industry. Ultimately, Alaska’s investigation seems crucial to ensuring responsible practices for the future of cruising in the region.
Potential Impacts on the Cruise Industry’s Reputation
Increased scrutiny, if handled effectively, could enhance the industry’s reputation. Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and community engagement can attract environmentally conscious travelers. Conversely, a lack of proactive response to these concerns could damage the industry’s reputation and deter potential passengers.
Table of Potential Impacts
| Stakeholder | Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Cruise Lines | Enhanced reputation, potential for attracting environmentally conscious travelers, adaptation to evolving market demands. | Increased operational costs, potential revenue losses, challenges in adapting to stricter regulations. |
| Passengers | More sustainable practices, potentially enhanced community engagement, focus on smaller-scale activities. | Potential for reduced options, itinerary changes, increased prices. |
| Local Communities | Economic opportunities through sustainable tourism, enhanced community engagement. | Reduced cruise ship visits, potential for decreased economic activity. |
Potential Solutions and Future Directions
The Alaskan cruise industry faces a crucial juncture. Increasing scrutiny necessitates a proactive approach to environmental responsibility and compliance. This involves not only meeting current regulations but also anticipating future needs and embracing innovative solutions. Moving forward requires a collaborative effort between cruise lines, regulatory bodies, and the wider community.Addressing environmental concerns and improving compliance requires a multifaceted strategy.
This includes implementing stricter waste management protocols, encouraging the adoption of eco-friendly technologies, and fostering transparency in operations. Ultimately, the goal is to minimize the industry’s environmental footprint while ensuring continued economic viability for Alaska.
Potential Solutions for Improved Compliance
Crucial to improving compliance is a commitment to rigorous adherence to existing regulations. Cruise lines must invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff, ensuring that everyone understands and adheres to environmental guidelines. This includes implementing robust waste management systems onboard, from efficient recycling programs to effective sewage treatment. Clearer communication with regulatory bodies regarding operations and waste disposal is essential for transparency and accountability.
Environmental Responsibility Initiatives
A significant step towards environmental responsibility involves the adoption of innovative technologies. Hybrid propulsion systems and alternative fuels, like LNG (liquefied natural gas), offer substantial reductions in emissions. The integration of real-time monitoring systems to track emissions and waste discharge allows for more effective management and prompt responses to environmental incidents. Cruise lines should also consider implementing advanced waste processing technologies onboard, converting waste into usable energy or other resources.
Waste Management and Pollution Control Strategies
Effective waste management strategies are crucial. Cruise lines should prioritize waste reduction through source control, promoting reusable materials, and implementing strict protocols for waste disposal at port facilities. This involves collaboration with local authorities to ensure proper waste handling and disposal in designated facilities. Investing in advanced waste treatment technologies, such as on-board composting or anaerobic digestion systems, is another critical step.
Additionally, cruise lines must ensure compliance with discharge regulations, using advanced filtration and treatment systems to reduce the environmental impact of wastewater.
Collaboration Between Cruise Lines, Authorities, and Stakeholders
Collaborative efforts between cruise lines, Alaskan authorities, and local stakeholders are paramount. This includes joint workshops and forums to share best practices and innovative solutions for environmental stewardship. Cruise lines can establish partnerships with local communities to support sustainable tourism initiatives and promote environmentally conscious practices. Developing a comprehensive environmental impact assessment framework for all cruise operations, including specific parameters for waste management and emissions, is essential.
Alaska’s scrutiny of cruise ship practices is definitely raising some eyebrows. While these regulations are important for environmental protection, it got me thinking about a fantastic alternative escape – a healthy dose of Czech Republic spa towns. These charming destinations offer a relaxing retreat, perfect for unwinding after the hustle and bustle of the cruise ship industry. Of course, the focus still remains on the important work of regulating cruise lines, ensuring a responsible and sustainable future for Alaska’s stunning landscapes.
Maybe a post-cruise spa trip to a healthy dose of Czech Republic spa towns would be a welcome respite from the cruise industry’s impact!
Examples of Successful Environmental Initiatives in Other Regions
Successful initiatives in other regions can provide valuable lessons. For instance, the implementation of stricter emission standards in certain European ports has led to a noticeable reduction in pollution. Studies of eco-tourism programs in other regions can provide models for promoting responsible and sustainable tourism in Alaska. Crucially, sharing best practices through international forums and collaborations will foster a global standard of environmental responsibility in the cruise industry.
Proposed Solutions and Potential Impacts
| Proposed Solution | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Implementing hybrid propulsion systems | Reduced emissions, improved fuel efficiency | Higher initial investment costs, potential technological challenges |
| Investing in advanced waste processing technologies | Reduced waste, resource recovery | Higher operational costs, potential technical complexity |
| Strengthening collaboration with local authorities | Improved waste management, enhanced environmental compliance | Potential bureaucratic hurdles, varying local regulations |
Illustrative Examples of Alaskan Cruise Activities
Alaska’s cruise industry, a significant part of the state’s economy, draws millions of visitors annually. However, the industry’s impact on the delicate Alaskan environment and its compliance with regulations are crucial areas of concern. Understanding typical itineraries, environmental consequences of certain practices, and the potential for violations is vital to evaluating the industry’s sustainability.
A Typical Alaskan Cruise Itinerary
A typical Alaskan cruise itinerary usually involves a journey along the Inside Passage, a network of waterways that winds through the state’s fjords and coastal areas. These cruises often last 7 to 10 days, featuring multiple ports of call, allowing passengers to explore various towns and natural wonders. Activities may include wildlife viewing tours, excursions to glaciers, and opportunities to visit historical sites.
Passengers typically disembark at a designated port and explore the region for a specific amount of time before returning to the ship for the next leg of the journey. A detailed itinerary might include visits to Ketchikan, Juneau, Skagway, and Glacier Bay National Park.
Environmental Impact of Anchoring, Alaska scrutinizes cruise industry practices
Anchoring, a necessary aspect of cruise ship operations, can have significant environmental impacts. Large cruise ships often require extensive anchor deployments in shallow waters, potentially causing damage to sensitive seabed ecosystems. The dragging of anchors across the seabed can disturb benthic organisms, and sediment plumes stirred up by anchors can negatively impact water clarity and aquatic life. Furthermore, the position of the anchor can impact the behavior of marine wildlife, and in some cases, lead to the accidental entanglement of marine animals.
Waste Discharge and Pollution
Cruise ships generate substantial waste, including sewage, graywater, and garbage. Regulations concerning the discharge of these materials vary, and non-compliance can lead to environmental pollution. Sewage, if not properly treated and discharged, can introduce harmful pathogens into the marine environment, negatively affecting the health of aquatic life and potentially impacting human health through consumption of contaminated seafood. Graywater, containing detergents and other contaminants, can also have adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Cruise lines are required to adhere to specific discharge standards, and violations can result in severe penalties.
Hypothetical Cruise Line Violation of Alaskan Regulations
A hypothetical scenario involving a cruise line violating Alaskan regulations might involve the improper disposal of sewage or ballast water. For instance, a cruise ship operating in a protected area may discharge untreated sewage, violating the discharge standards. Such a violation could result in fines, sanctions, and potentially legal action. The severity of the violation would determine the penalties and potential consequences for the cruise line.
Environmental Incident Involving a Cruise Ship
An environmental incident involving a cruise ship could involve an oil spill during a voyage. The spill could contaminate coastal waters and beaches, potentially causing harm to marine wildlife and affecting the ecosystem. Such an incident might result in the closure of fishing areas and the imposition of restrictions on recreational activities in the affected area. The scale and severity of the spill would determine the extent of environmental damage and the subsequent cleanup efforts.
Alaska’s scrutiny of cruise ship practices is definitely raising some eyebrows. While the industry grapples with environmental concerns and potential overtourism, it’s interesting to see a major investment like a 40m investment buys a rebirth at Ritz-Carlton St Thomas being made in tourism. This highlights the ongoing need for balancing the economic benefits of tourism with the environmental and social impacts.
Alaska’s approach to cruise lines is a crucial step towards sustainable tourism.
Case Study of an Alaskan Cruise Company Complying with Environmental Regulations
A case study of a cruise company complying with environmental regulations might involve the use of advanced wastewater treatment systems. Companies that are committed to environmental stewardship invest in cutting-edge wastewater treatment facilities that effectively remove pollutants before discharge. They may also utilize alternative fuel sources or implement energy-efficient technologies to minimize their environmental footprint. This demonstrates a commitment to sustainable practices, minimizing the environmental impact of their operations.
Closure: Alaska Scrutinizes Cruise Industry Practices

In conclusion, Alaska’s scrutiny of cruise industry practices highlights the delicate balance between tourism and environmental protection. The analysis reveals the need for a collaborative approach between cruise lines, authorities, and stakeholders to ensure responsible operations. Ultimately, this process aims to create a more sustainable and respectful relationship between the cruise industry and Alaska’s unique natural resources. The future of cruise tourism in Alaska hinges on the industry’s ability to adapt to evolving regulations and embrace sustainable practices.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are some examples of past violations by cruise lines in Alaskan waters?
Unfortunately, specific examples are not detailed in the Artikel. However, the Artikel indicates that past violations exist and are part of the historical context of regulations.
How are Alaskan authorities collecting data to investigate cruise ship activities?
The Artikel mentions Alaskan authorities collect data and conduct investigations but doesn’t provide specific details. Further research would be needed to understand the methodologies.
What are some potential economic consequences for local communities if cruise ship operations are impacted by increased scrutiny?
The Artikel suggests potential economic consequences, but doesn’t specify details. These might include changes in revenue for local businesses and potential job losses or shifts in the local economy.
What are some innovative technologies that could reduce the environmental impact of cruise ships?
The Artikel notes the potential for innovative technologies but doesn’t list examples. Possible examples include more efficient engines, better waste management systems, and alternative energy sources.