Airline Ground Workers Wage Disparity A Deep Dive
Airline ground workers wage disparity is a critical issue affecting the aviation industry. From baggage handlers to gate agents and customer service representatives, these vital workers often face significant pay discrepancies, impacting their livelihoods and the overall quality of service provided to passengers. This blog post delves into the complexities of this issue, exploring the factors contributing to the wage gap, the impact on workers and communities, and potential solutions for a fairer compensation system.
This in-depth look at airline ground workers wage disparity examines the roles, responsibilities, and working conditions of these essential personnel. We’ll analyze the historical context, the impact of automation, worker rights, and the broader economic and social implications of this issue. Ultimately, we’ll explore actionable solutions to bridge the wage gap and create a more equitable and sustainable system.
Introduction to Airline Ground Workers
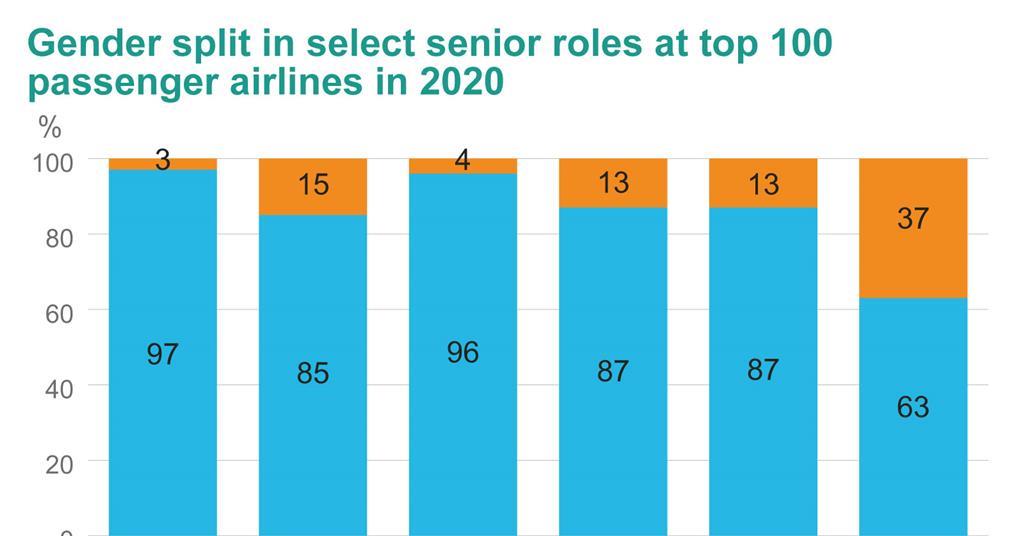
Airline ground workers are the unsung heroes of the aviation industry, quietly ensuring the smooth operation of flights from the moment passengers arrive at the airport until they depart. Their roles are diverse and critical, encompassing everything from baggage handling and gate assistance to customer service and security. Understanding their roles, responsibilities, and working conditions is key to appreciating the complexity of airport operations and the challenges faced by these essential employees.Ground workers play a crucial role in the seamless flow of passengers and cargo through airports.
While the disparity in wages for airline ground workers is a serious issue, planning a trip to Saudi Arabia can be surprisingly straightforward. For example, checking out these 6 key planning tips for travel to Saudi Arabia 6 key planning tips for travel to saudi arabia can help you navigate the cultural nuances and ensure a smooth trip.
Ultimately, fair wages for these essential workers are crucial, regardless of travel plans.
Their responsibilities range from basic tasks to complex procedures, demanding a high level of efficiency and attention to detail. From loading and unloading baggage to managing flight schedules and assisting passengers, these workers are vital cogs in the machine of air travel.
Roles and Responsibilities of Ground Workers
Ground worker positions encompass a wide spectrum of responsibilities, each vital to the smooth functioning of an airport. Baggage handlers, for example, are responsible for the safe and efficient transport of checked baggage, ensuring it reaches the correct flights. Gate agents are the first point of contact for many passengers, providing crucial information and assistance at the gate. Customer service representatives are instrumental in addressing passenger concerns and resolving issues, ensuring a positive travel experience.
Security personnel are crucial in maintaining airport safety and security, adhering to strict protocols to protect passengers and assets.
Levels of Ground Worker Positions
Airline ground worker positions are structured into various levels, each with increasing responsibilities and skill requirements. Entry-level positions typically involve basic tasks such as baggage handling or assisting passengers. More senior positions, such as supervisors or team leaders, entail overseeing and coordinating the work of other ground workers, as well as handling more complex tasks and responsibilities.
Working Conditions and Environments
The working conditions and environments for ground workers at different airports vary significantly. Factors like airport size, passenger volume, and the types of flights handled can significantly influence the working conditions. For instance, large international hubs typically experience higher passenger volumes, leading to more demanding and fast-paced work environments. Ground workers often face long hours, especially during peak travel seasons, and may be exposed to challenging weather conditions or high-stress situations.
Historical Context of Ground Worker Employment
The history of ground worker employment in the airline industry reflects a complex evolution of labor relations and industry demands. Initially, ground worker roles were often performed by smaller, independent companies or even airline employees themselves, but the growth of the industry and the need for specialized labor led to the establishment of dedicated ground handling companies. The historical context underscores the need for fair labor practices and competitive compensation structures, ensuring that ground workers are properly recognized for their contributions.
Impact of Automation and Technology
The airline industry, like many others, is rapidly embracing automation and technology. This shift is transforming the landscape of ground worker jobs, presenting both opportunities and challenges. From baggage handling to gate assistance, technological advancements are reshaping the way airports operate, and consequently, the roles of those who support these operations.
Automation Affecting Ground Worker Tasks
Automation is altering the nature of ground worker tasks. Previously manual processes are being replaced by automated systems. For example, automated baggage handling systems are becoming increasingly common in airports, reducing the need for manual sorting and loading. Similarly, automated gate assistance systems are streamlining passenger check-in and boarding procedures. This shift is impacting the skills and responsibilities required of ground workers.
Potential Displacement of Ground Workers
The implementation of automated systems raises concerns about potential job displacement among ground workers. While automation can increase efficiency and reduce costs for airlines, it can also lead to job losses. As tasks are taken over by machines, the need for human workers in certain roles might decrease. This is a critical factor to consider when evaluating the long-term impact on ground worker employment.
Impact on Ground Worker Job Security
Technological advancements have a significant impact on the job security of ground workers. While automation can increase efficiency, it can also create uncertainty about future employment opportunities. Workers need to adapt to the changing demands of the job market and acquire new skills to remain competitive. Training programs and reskilling initiatives are crucial to ensuring that ground workers can adapt to the evolving technological landscape.
The disparity in wages for airline ground workers is a significant issue, impacting their livelihoods. While the details of their work often get overlooked, it’s worth considering the impact of their roles, especially when you look at the updated features of Norwegian Joy after its China sojourn, like in this recent blog post about after china sojourn norwegian joy updated for alaska.
Ultimately, fair compensation for ground crew is crucial for a smooth and well-functioning travel industry, just as it is for the smooth running of any business.
Examples of Automated Systems in Airports
Automated baggage handling systems, like conveyor belts and robotic arms, are common in many major airports. These systems automate the process of sorting, weighing, and loading baggage, reducing manual labor. Automated gate assistance systems are also emerging, offering self-service kiosks and automated check-in procedures. These systems can significantly reduce the workload on human ground workers.
Comparison of Tasks Before and After Automation
| Task | Pre-automation Method | Post-automation Method | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baggage Handling | Manual sorting, loading, and unloading of baggage onto carts and planes. | Automated conveyor belts, robotic arms, and sorting systems. | Reduced manual labor, increased efficiency, potential job displacement in manual roles. |
| Passenger Check-in | Manual check-in at counters, processing documents, and issuing boarding passes. | Self-service kiosks, automated check-in systems, mobile check-in. | Reduced wait times, increased speed, potential job displacement in traditional check-in roles. |
| Gate Assistance | Manual assistance with baggage, boarding passes, and directions. | Automated gate assistance systems, digital displays, and self-service information. | Streamlined procedures, reduced direct human interaction, potential job displacement in specific gate assistance roles. |
Worker Rights and Labor Relations
Airline ground workers, often overlooked, play a crucial role in the smooth operation of airports. Their work, ranging from baggage handling to gate assistance, is essential for the travel experience. However, these workers frequently face challenges in asserting their rights and securing fair compensation, often due to the complex and sometimes adversarial nature of labor relations in the industry.
This section will delve into the obstacles ground workers encounter in advocating for their rights, the role of unions in improving their conditions, and the specifics of collective bargaining in the airline sector.
Challenges in Advocating for Worker Rights
Ground workers frequently face challenges in advocating for their rights due to factors like precarious employment situations, a dispersed workforce, and a sometimes hostile environment. The nature of their work, often involving physically demanding tasks in fast-paced environments, can create an atmosphere where expressing concerns or pursuing grievances may seem risky. Moreover, the hierarchical structure within the airline industry can create an imbalance of power, making it difficult for ground workers to voice their needs effectively.
The lack of a strong, unified voice can also hamper their ability to negotiate better terms.
Role of Labor Unions
Labor unions are instrumental in advocating for better wages, benefits, and working conditions for ground workers. Unions provide a collective voice, enabling workers to negotiate as a group, rather than individually, with employers. This collective bargaining power is critical in achieving improvements in compensation and benefits that individual workers might not be able to secure on their own. Unions provide support and representation for their members in disciplinary actions, grievances, and other employment-related issues.
They are often essential for securing fair treatment and ensuring that workers are not exploited.
Collective Bargaining Processes in the Airline Industry
Collective bargaining in the airline industry is a complex process involving negotiations between labor unions and airline management. These negotiations often cover crucial aspects of employment, such as wages, benefits, working hours, safety protocols, and grievance procedures. The outcome of these negotiations significantly impacts the livelihoods of ground workers, influencing their job security, compensation, and overall working conditions.
The specifics of the bargaining process vary depending on the specific airline and union, but typically involve several stages, from initial proposals to formal agreements. Successful negotiations depend on effective communication, a shared understanding of the issues, and a willingness to compromise.
Examples of Successful Union Campaigns
Numerous union campaigns have led to significant improvements in ground worker compensation. One notable example is a campaign that resulted in increased wages and improved health insurance coverage for baggage handlers. Another campaign focused on establishing clearer grievance procedures and reducing instances of workplace harassment. These examples highlight the positive impact that unionization can have on workers’ rights and overall job satisfaction.
Successful campaigns often involve building a strong coalition of workers, meticulously preparing arguments, and employing effective strategies to put pressure on management.
Key Labor Laws and Regulations Affecting Ground Workers
The following table Artikels some key labor laws and regulations impacting ground workers in the airline industry. These laws vary by jurisdiction, so it’s crucial to consult specific legal resources for comprehensive details. Compliance with these regulations is critical to ensure fair and equitable treatment of ground workers.
| Law/Regulation | Key Provisions |
|---|---|
| National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) | Guarantees the right of employees to organize and bargain collectively, prohibits employer interference with union activities. |
| Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) | Establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, and record-keeping requirements for employees. |
| Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) | Sets standards and guidelines to ensure a safe and healthy work environment. |
| Specific State and Local Laws | May have additional provisions related to employment, wages, and working conditions. |
Economic and Social Implications
The widening wage gap between airline ground workers and their counterparts in other industries, exacerbated by automation and technological advancements, has significant economic and social ramifications. This disparity not only affects the livelihoods of ground workers and their families but also impacts the communities surrounding airports and the overall profitability of the airline industry. Understanding these interconnected effects is crucial for creating sustainable and equitable practices within the aviation sector.The economic consequences of this wage disparity extend beyond the individual ground worker.
Lower wages often translate to reduced spending power within local communities surrounding airports. This, in turn, impacts local businesses and services, potentially creating a downward economic spiral.
Economic Consequences for Ground Workers and Families
Lower wages for ground workers directly impact their ability to afford basic necessities. This can lead to financial instability, reduced access to healthcare, and diminished educational opportunities for their children. The strain on household budgets can also result in increased stress and decreased quality of life. A significant portion of ground workers are likely to rely on government assistance programs due to low wages.
This burden on social safety nets is a further consequence of the wage gap.
Social Impact on Airport Communities
The wage disparity in the airline industry has a tangible impact on the communities surrounding airports. Reduced spending power among ground workers translates to less revenue for local businesses. This can lead to a decline in the quality of services offered in these areas. Moreover, a decline in local economic health can affect the overall quality of life for residents, including access to essential services.
The potential for a decline in the quality of life for residents should not be underestimated.
Airline ground workers often face significant wage disparities, a real issue that needs addressing. Managing your office’s packaging and shipping supply costs can be surprisingly similar, though on a much smaller scale. Keeping a close eye on these expenses, like you would with staying on top of your office packaging shipping supplies costs , can help you understand the importance of fair compensation for those on the front lines of operations.
This principle of cost awareness, though in a different context, speaks to the same need for understanding and addressing inequality, whether it’s in the sky or the office supply closet.
Impact on Airline Industry Profitability
A workforce experiencing wage disparity may lead to increased employee turnover. This is because employees who are underpaid or undervalued will be more likely to seek employment elsewhere, requiring significant retraining costs. This can negatively impact the overall productivity and efficiency of the airline industry, potentially impacting profitability. Furthermore, labor unrest, as discussed later, can also cause significant disruptions in operations.
The wage disparity among airline ground workers is a persistent issue, impacting many across the industry. Recent news about Air China halting its Beijing-Honolulu flights, as reported in this article , highlights the complex web of factors influencing these situations. Ultimately, these disruptions and labor issues will continue to affect the quality and availability of air travel services for everyone, from passengers to ground crews.
Potential for Labor Unrest
A significant wage disparity between ground workers and other professions, combined with feelings of undervaluation and lack of recognition, can foster a climate of resentment and frustration. This resentment can lead to labor unrest, including strikes, protests, and decreased morale, which can disrupt operations and negatively impact the airline industry’s reputation. Historical examples of labor disputes in other industries show that similar scenarios can lead to substantial operational disruptions.
Impact on Passenger Service Quality
Lower wages can negatively impact the quality of service provided to passengers. Ground workers may feel demoralized and undervalued, which can manifest as reduced efficiency and a decline in the overall passenger experience. This can lead to increased delays, lost baggage, and negative reviews, potentially impacting the airline’s reputation and customer loyalty. Reduced motivation and job satisfaction directly translate into potentially subpar service.
Potential Solutions and Recommendations
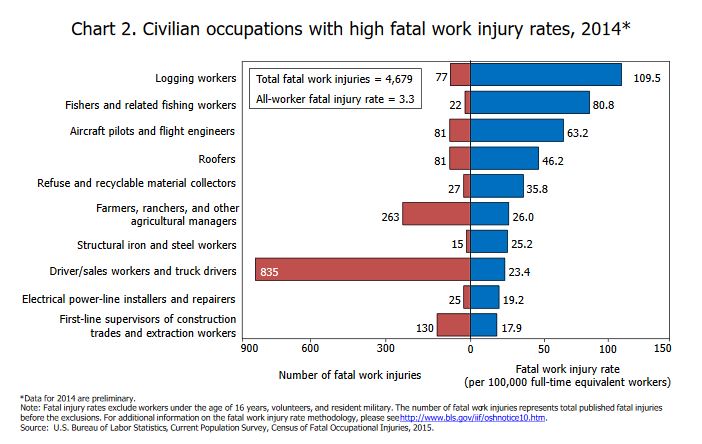
Bridging the wage gap for airline ground workers requires a multifaceted approach that considers the diverse roles and responsibilities within the industry. A fair compensation structure must acknowledge the value each position brings to the overall operation while recognizing the impact of automation and evolving technologies. This necessitates a collaborative effort involving ground workers, management, and industry stakeholders to develop sustainable solutions.Addressing wage disparities necessitates a thorough understanding of the current compensation structure, skill requirements, and the impact of technological advancements on each ground worker role.
This comprehensive analysis forms the foundation for implementing equitable compensation and benefits. Specific strategies for improving ground worker compensation must account for the unique demands and contributions of each position.
Strategies for Bridging the Wage Gap
Various strategies can help bridge the wage gap between different ground worker positions. These strategies need to address the varying skill sets, responsibilities, and working conditions associated with each role. Implementing a comprehensive job evaluation system is crucial for ensuring that all roles are fairly valued. This evaluation should consider the complexity of tasks, required skills, experience, and working conditions.
- Job Evaluation Systems: Implementing a standardized job evaluation system that objectively assesses the complexity, skill requirements, and responsibilities of each position is crucial. This system should be transparent and regularly reviewed to reflect evolving industry needs and technological advancements. For instance, a system might assign weighting factors to criteria like decision-making authority, physical demands, and required certifications, providing a numerical score that correlates to a fair compensation range.
- Skill-Based Pay: A skill-based pay system can address the value of specialized knowledge and expertise. Ground workers who possess advanced skills, certifications, or training in areas like maintenance or specialized customer service can be rewarded accordingly. This approach encourages continuous learning and skill development within the workforce.
- Industry-Wide Standards: Establishing industry-wide standards for compensation and benefits can promote fairness and equity. This involves setting minimum wage requirements and performance-based incentives that are consistent across different airlines and locations. This would create a benchmark for fair compensation, minimizing the discrepancies that arise from differing compensation policies across organizations.
Fair Compensation for All Ground Worker Roles
Ensuring fair compensation for all ground worker roles is essential for maintaining a motivated and productive workforce. This involves recognizing the value each position contributes to the airline operation, considering the demands and responsibilities of each role, and providing commensurate pay and benefits.
- Transparency and Communication: Transparency in compensation structures and processes is vital. Clear communication about compensation levels, benefits, and performance-based incentives fosters trust and understanding among ground workers. Providing regular updates and addressing concerns through open communication channels can mitigate potential issues.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Implementing regular performance reviews can help identify areas for improvement and recognize exceptional contributions. This can be integrated into the compensation structure by rewarding outstanding performance and skill development. This system should be transparent and regularly audited to avoid bias or favoritism.
- Addressing Working Conditions: Recognizing and addressing the unique working conditions of various ground worker roles is vital. Factors such as shift work, physical demands, and potential exposure to hazardous materials should be considered when evaluating compensation packages.
Recommendations for Improving Ground Worker Compensation and Benefits
Improving ground worker compensation and benefits requires a strategic approach encompassing various elements. These elements include fair wage structures, comprehensive benefits packages, and opportunities for professional development.
- Comprehensive Benefits Packages: Expanding benefits packages to include healthcare, retirement plans, and paid time off can significantly enhance the value proposition for ground workers. Tailoring benefits packages to specific needs and situations, such as families or individuals with significant responsibilities, is also important.
- Employee Recognition Programs: Establishing employee recognition programs can enhance motivation and morale among ground workers. Recognizing outstanding performance and contributions through awards, bonuses, or other incentives can create a positive work environment.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Providing opportunities for professional development, such as training programs and skill enhancement workshops, can enhance the value of ground workers’ contributions and justify their compensation. This fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement, leading to a more skilled and productive workforce.
Role of Industry Stakeholders
Industry stakeholders play a crucial role in addressing wage disparity. This involves a collaborative approach to ensure a fair and equitable compensation structure for all ground workers. Stakeholders include airline companies, labor unions, and government agencies.
Airline ground workers often face significant wage disparities, impacting their livelihoods. This is particularly relevant now, as travel agents are proactively redirecting couples planning babymoons to other destinations due to the Zika virus spreading, as detailed in agents redirect babymooners as zika spreads. The fluctuating travel market and these adjustments highlight the complex economic realities faced by both travel professionals and ground staff, underscoring the need for fair compensation for those who keep the industry moving.
- Collaboration with Unions: Collaboration between airline companies and labor unions is critical. Collective bargaining can ensure fair wages and benefits for ground workers. A collaborative approach that prioritizes the interests of ground workers can lead to a win-win situation for both parties.
- Government Regulations: Government regulations can play a significant role in ensuring fair labor practices and minimum wage standards. Establishing clear guidelines for compensation and benefits can provide a baseline for fairness across the industry.
- Industry Best Practices: Implementing industry best practices for fair compensation and benefits can establish a benchmark for the industry. Sharing successful strategies among stakeholders can contribute to a more equitable compensation structure for ground workers.
Potential Strategy Flowchart
 [Description of flowchart: A flowchart depicting a step-by-step process for implementing improved compensation for ground workers. The flowchart begins with a comprehensive job evaluation, moves to stakeholder consultation and data analysis, and culminates in the implementation of a revised compensation structure and benefits package. Each step includes specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities.]
[Description of flowchart: A flowchart depicting a step-by-step process for implementing improved compensation for ground workers. The flowchart begins with a comprehensive job evaluation, moves to stakeholder consultation and data analysis, and culminates in the implementation of a revised compensation structure and benefits package. Each step includes specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities.]
Global Perspective
The issue of wage disparity for airline ground workers isn’t confined to a single country or region. It’s a global problem with variations in severity and manifestation across different parts of the world. Understanding the global context is crucial to developing effective solutions. Different economic structures, labor laws, and cultural norms all play a role in shaping the compensation and working conditions for ground staff.
Wage Disparities Across Countries, Airline ground workers wage disparity
Significant variations exist in ground worker wages across the globe. Factors such as cost of living, local economic conditions, and national labor laws contribute to these differences. For instance, ground workers in developed nations often earn higher wages compared to their counterparts in developing countries, reflecting the prevailing economic realities in those regions.
Impact of Globalization on Ground Worker Compensation
Globalization has significantly influenced ground worker compensation. Increased competition among airlines, driven by the ease of international travel and trade, often results in downward pressure on wages in some regions. Furthermore, the ability of companies to relocate operations to areas with lower labor costs exacerbates the disparity.
Role of International Labor Standards
International labor organizations play a crucial role in establishing minimum standards for worker compensation and working conditions. However, the enforcement and implementation of these standards vary significantly across countries. Compliance and adherence to these international standards can act as a guideline for fair compensation, but the actual enforcement is a complex process, often reliant on individual country regulations and policies.
Best Practices in Addressing Wage Disparity
Several industries have successfully addressed wage disparity by implementing transparent compensation structures, promoting collective bargaining, and encouraging industry-wide agreements. Examples include the retail sector in some countries where industry-wide minimum wage standards have helped to ensure a fairer distribution of compensation. In the hospitality sector, industry bodies have played a critical role in establishing compensation benchmarks for different roles, which have proven effective in standardizing pay scales.
Comparison of Ground Worker Wages
| Country | Estimated Average Ground Worker Wage (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $25-40 | Dependent on role and experience. Higher in high-cost areas. |
| United Kingdom | $20-35 | Varied by role and experience; impacted by local living costs. |
| India | $5-15 | Significant variations based on location, experience, and company. |
| Brazil | $10-25 | Compensation is influenced by local economic conditions and regulations. |
| China | $8-20 | Wage levels vary considerably based on location and company. |
Note: These are estimated figures and may not reflect the exact compensation for all ground workers in each country. The figures are subject to variation based on numerous factors.
Last Recap

In conclusion, the airline ground workers wage disparity problem is multifaceted and deeply rooted in historical, economic, and technological factors. Addressing this inequality requires a comprehensive approach that considers the needs of workers, the demands of the industry, and the broader social and economic implications. By understanding the complexities and exploring potential solutions, we can strive towards a fairer and more equitable system for all ground workers in the aviation sector.
FAQs: Airline Ground Workers Wage Disparity
What is the typical working environment for ground workers at different airports?
Working conditions vary significantly based on the airport’s size, location, and the specific role. Some roles, like baggage handlers, often involve strenuous physical labor and exposure to varying weather conditions. Gate agents and customer service representatives typically work in controlled environments but face high-pressure situations and long hours.
How does unionization impact ground worker wages?
Unionization can significantly influence ground worker wages and benefits. Unions advocate for fair compensation and better working conditions through collective bargaining, often resulting in improved pay and benefits for their members compared to non-unionized workers.
What are some examples of automated systems used in airports and their impact on ground workers?
Automated baggage handling systems, self-service kiosks, and AI-powered customer service tools are transforming airport operations. While these technologies improve efficiency, they also lead to potential job displacement for ground workers, requiring retraining and adaptation to new roles.
How does globalization impact ground worker compensation?
Globalization affects ground worker compensation by creating competition between workers in different countries. Lower wages in certain regions can pressure airlines to offer lower compensation, impacting workers globally. International labor standards play a role in mitigating this disparity.