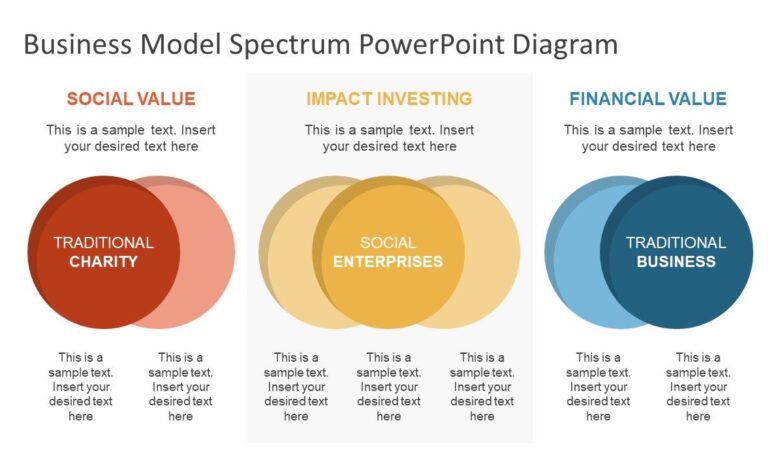
A Stripped-Down Business Model Simplified Success
A stripped down business model – A stripped-down business model, a streamlined approach to entrepreneurship, focuses on maximizing efficiency and minimizing overhead. This model offers a unique path to success, especially for startups and small businesses, by prioritizing core functions and eliminating non-essential elements. It’s about concentrating on the fundamentals, from defining the core offering to crafting an effective marketing strategy, all while keeping costs under control.
This in-depth exploration dives into the intricacies of a stripped-down business model, covering everything from defining its core characteristics to illustrating its successful implementation across various industries. We’ll examine its benefits, drawbacks, and the crucial elements that underpin its success. We’ll also look at how to adapt this model to market changes, highlighting real-world examples and case studies.
Defining a Stripped-Down Business Model
A stripped-down business model is a lean and focused approach to creating and delivering value, prioritizing efficiency and minimizing overhead. It contrasts sharply with traditional models that often incorporate complex structures and extensive resources. This approach is becoming increasingly popular, especially for startups and small businesses, as it enables rapid scaling and flexibility.This model focuses on core competencies and eliminates non-essential functions, creating a streamlined structure for quick market entry and adaptation.
It’s about identifying the absolute minimum necessary to achieve profitability and growth. Key differentiators from traditional models are evident in resource allocation, operational procedures, and the overall strategic direction.
Core Characteristics of a Stripped-Down Model
A stripped-down model prioritizes essential functions, drastically reducing reliance on extensive infrastructure and overhead. This often translates to a smaller team, limited physical space, and a leaner marketing strategy. The focus is solely on generating revenue and profit with minimal wasted resources.
Key Components Distinguishing it from Traditional Models
Traditional business models often involve elaborate supply chains, extensive marketing campaigns, and large physical footprints. Stripped-down models, in contrast, rely on streamlined processes, strategic partnerships, and efficient technology to maximize return on investment. These models prioritize agility and scalability over complexity and rigidity.
- Reduced Infrastructure: Stripped-down models often utilize cloud-based services, virtual offices, and shared resources to minimize the need for physical infrastructure. This results in significant cost savings and quicker scalability.
- Strategic Partnerships: Outsourcing non-core functions to external providers allows businesses to concentrate on their core competencies and maintain operational efficiency.
- Minimal Marketing: A lean marketing strategy, focusing on targeted customer segments and digital channels, can effectively generate leads and convert them into paying customers without extravagant expenditures.
- Agile Processes: Adaptability and responsiveness to market changes are crucial elements of a stripped-down model. This is often achieved through flexible workflows, quick decision-making, and continuous improvement.
Motivations Behind Adopting a Stripped-Down Model
Several factors motivate businesses to adopt a stripped-down model. These factors often involve financial constraints, a desire for rapid growth, or the need for operational flexibility.
- Financial Constraints: Limited capital and resources are common drivers for adopting a stripped-down model. It allows businesses to maximize the return on limited investment by minimizing overhead.
- Rapid Growth: The ability to quickly scale operations and adapt to market changes is often a key motivation. Stripped-down models can facilitate this by minimizing the bureaucratic hurdles associated with larger organizations.
- Operational Flexibility: Adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs is critical. A stripped-down model allows for quicker adjustments to strategies and operations, increasing adaptability.
Examples of Businesses Successfully Implementing the Model
Several businesses have successfully implemented a stripped-down business model to achieve rapid growth and profitability.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies: Many SaaS companies operate with a minimal physical presence, relying heavily on cloud-based services and remote teams. This allows for significant cost savings and rapid expansion.
- E-commerce startups: Online retailers frequently use a stripped-down model by focusing on their core function (selling products online) and leveraging platforms like Shopify or Amazon to handle logistics and other support functions. This allows for rapid scaling and reduced upfront investment.
- Consultancy firms: Consultants often operate with a minimal office footprint, relying on remote work and virtual meetings. This flexibility enables them to respond quickly to client needs and manage resources effectively.
Benefits and Drawbacks
A stripped-down business model, focusing on core functionalities and minimizing overhead, can be a powerful strategy for startups and established companies alike. However, it’s crucial to understand the potential advantages and disadvantages before implementing this approach. This model demands careful consideration of trade-offs and a thorough understanding of the market and customer needs.This section delves into the benefits and drawbacks of a stripped-down business model, comparing it to other models, and outlining the associated trade-offs.
Understanding these aspects is critical for businesses considering this model to make informed decisions.
Potential Advantages
A stripped-down model often allows for rapid market entry and faster time-to-market. By eliminating non-essential features and processes, companies can focus resources on core competencies and customer needs. This can lead to a more agile and responsive business, enabling quicker adaptation to changing market conditions. Furthermore, the lower overhead costs associated with a streamlined model can lead to higher profit margins and greater capital efficiency.
This allows for reinvestment in product development or marketing efforts, or for more rapid expansion.
- Rapid Market Entry: Focusing on core functionalities accelerates development and launch, enabling quicker market penetration compared to models with extensive features.
- Agile and Responsive Operations: Simplified operations enhance adaptability to market changes, allowing quicker pivots and adjustments.
- Lower Overhead Costs: Minimizing non-essential expenses directly translates to higher profit margins and better capital efficiency.
- Increased Capital Efficiency: The reduced capital requirements associated with the stripped-down model enable more rapid reinvestment in growth initiatives.
- Enhanced Customer Focus: Prioritizing core features allows companies to better understand and cater to the fundamental needs of their target market.
Potential Disadvantages
While a stripped-down model offers several advantages, it also presents potential drawbacks. A lack of features can lead to limited customer appeal, particularly if competitors offer more comprehensive solutions. This can affect customer acquisition and retention. Furthermore, the reduced features may limit future scalability and adaptation to evolving market demands. It’s crucial to carefully assess whether the core features adequately meet customer needs and expectations, considering potential future expansion.
A stripped-down business model, focusing on core offerings, is definitely trending. It’s all about efficiency, you know? Take a look at how AK is streamlining operations with their renovated Sanctuary Sun IV resort; ak unveils renovated sanctuary sun iv is a prime example. It highlights how streamlining services can actually boost appeal and value. Ultimately, a leaner approach can often be the most effective way to achieve long-term success.
- Limited Customer Appeal: Stripped-down models might not be attractive to customers seeking comprehensive features, leading to decreased customer acquisition.
- Reduced Scalability: Limited features can hinder future growth and adaptation to evolving customer needs.
- Limited Competitive Advantage: If competitors offer a broader range of features, the stripped-down model might not offer a compelling advantage in the market.
- Customer Acquisition Challenges: Building a customer base with a limited feature set might require more aggressive marketing strategies.
- Potential for Feature Creep: Maintaining the stripped-down approach becomes difficult if customer demands for additional features arise, requiring careful management and decision-making.
Comparison with Other Models
Comparing a stripped-down model with other business models reveals key differences in approach and strategic focus. A traditional business model often includes a wider range of features, aiming to attract a broader customer base. However, this approach often leads to higher costs and a slower time to market. Conversely, a premium model prioritizes high-quality features and a premium price, targeting a specific customer segment.
A hybrid approach often combines elements of different models, allowing for flexibility and adaptability. Each model has its unique trade-offs, and the optimal choice depends on the specific business goals and market conditions.
Trade-offs
The stripped-down model necessitates careful consideration of the trade-offs between features, cost, and customer satisfaction. Businesses must meticulously evaluate whether the core features satisfy customer needs and anticipate future requirements. A thorough market analysis is essential to ensure the stripped-down approach aligns with the target market’s expectations and future needs. A balanced approach considers the value proposition of the core features in relation to the potential limitations of the stripped-down model.
Core Elements of a Stripped-Down Business Model
A stripped-down business model prioritizes efficiency and focuses on delivering core value propositions with minimal overhead. This approach is particularly valuable for startups, small businesses, or established companies seeking to optimize operations and reduce costs. It hinges on the careful selection and execution of essential elements, while minimizing non-essential features or processes.This approach allows for faster adaptation to market changes, greater agility, and often, a lower barrier to entry.
By concentrating on the fundamental building blocks of a business, stripped-down models can streamline operations, optimize resources, and enhance profitability.
Key Components of a Stripped-Down Model
The success of a stripped-down business model relies on strategically choosing and implementing core components. These components must align with the overall value proposition and target market, fostering a streamlined and focused operation.
| Core Element | Typical Characteristics | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Value Proposition | Clearly defined, focused on a specific customer need, and delivered efficiently. It emphasizes core benefits, avoiding unnecessary extras. | A subscription box service specializing in organic dog treats, offering a limited selection of premium ingredients. |
| Customer Segment | A highly defined, niche market segment. This segmentation reduces marketing costs and allows for targeted communication. | A freelance graphic design service targeting small businesses in the food industry. |
| Channels | Direct and cost-effective channels are prioritized. This could involve online platforms, direct sales, or strategic partnerships. | A local artisan coffee shop relying heavily on its social media presence and in-person customer engagement for sales. |
| Customer Relationships | Building relationships with customers through a simple and consistent approach. Focus is on providing exceptional service and value. | A mobile repair service that prioritizes quick and reliable repairs with excellent customer communication. |
| Revenue Streams | Clear and predictable revenue streams that align with the core value proposition. Often, this involves a single or a few primary revenue sources. | A software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform charging a subscription fee based on user access levels. |
| Key Activities | Essential activities that directly support the value proposition. This focuses on the most impactful actions that deliver value to the customer. | A photography studio specializing in product photography for online retailers. |
| Key Resources | Essential resources that support the core activities and value proposition. These resources are strategically selected and optimized. | A local printing shop using specialized equipment for high-quality print jobs. |
| Key Partnerships | Strategic partnerships that support the business model’s core activities and enhance its value proposition. Partnerships should add value without adding significant complexity. | A food truck that partners with local farmers for fresh produce, thereby reducing sourcing costs and ensuring high-quality ingredients. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Stripped-down models can be found across diverse industries. For instance, a successful online tutoring service might focus solely on providing live, one-on-one sessions for math tutoring, for example, instead of offering various supplementary materials. This concentration on a specific need and delivery method results in a leaner operation, optimized for maximum efficiency and profit.
A stripped-down business model is all the rage these days, and for good reason. It’s about focusing on core competencies and cutting out the fluff. This is clearly demonstrated by how airlines and cruise lines are adjusting their plans due to Sandy, as reported in airlines cruise lines alter plans due to sandy. By streamlining operations and prioritizing essential services, they’re adapting to the situation and minimizing losses.
This highlights the adaptability and resilience of a leaner, more agile business model in the face of unexpected challenges.
Application in Different Industries
A stripped-down business model isn’t confined to a single industry; its adaptable core principles can be applied across diverse sectors. From tech startups to established retail giants, the strategy of streamlining operations and focusing on core competencies offers distinct advantages. This flexibility allows businesses to allocate resources effectively, prioritize customer needs, and maintain competitive edge.This adaptability stems from the stripped-down model’s core tenets: a clear focus on the essential value proposition, minimal overhead, and a lean organizational structure.
By removing non-essential elements, businesses can accelerate their growth trajectory, improve profitability, and enhance agility in response to market fluctuations.
Technology Industry
In the dynamic technology sector, a stripped-down model empowers companies to rapidly innovate and respond to evolving customer demands. By prioritizing core technology and focusing on a limited product line, startups can achieve rapid market penetration with a smaller initial investment. For example, a software company focusing solely on a specific niche market can allocate resources to develop cutting-edge solutions without being bogged down by extraneous features.
This streamlined approach fosters rapid iteration and continuous improvement, crucial for success in a competitive technology landscape.
Retail Industry
The retail industry presents a unique opportunity to leverage a stripped-down model. By focusing on a specific customer segment and streamlined supply chains, retailers can optimize their operational efficiency. A clothing retailer focusing solely on sustainable and ethically sourced products can differentiate itself and attract environmentally conscious consumers. This targeted approach allows the business to build brand loyalty and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Furthermore, an online-only retail store can cut down on the costs associated with physical retail spaces and overhead, allowing for greater flexibility and reduced risks.
Services Industry
The services industry, encompassing everything from consulting to hospitality, also benefits from a stripped-down model. By emphasizing expertise in a particular area and eliminating non-essential services, companies can build a strong reputation for quality and specialization. For example, a consulting firm concentrating solely on financial services can leverage its deep expertise to attract clients seeking specialized advice in that domain.
The streamlined focus on core competencies allows the company to build strong relationships with clients and maintain its competitive edge.
Table of Diverse Industry Applications
| Industry | Core Elements Adaptation | Target Audience | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Focus on core technology, limited product line, agile development | Tech-savvy consumers seeking innovative solutions | A mobile app solely for grocery shopping |
| Retail | Specific customer segment, streamlined supply chain, focus on a particular niche | Consumers with specific needs or preferences | A clothing store specializing in sustainable fashion |
| Services | Expertise in a specific area, eliminating non-essential services, high-quality service delivery | Clients seeking specialized expertise and high-quality services | A consulting firm focused solely on marketing strategy |
Strategies for Implementing a Stripped-Down Business Model
A stripped-down business model, by its very nature, requires a focused and streamlined approach to implementation. This involves a deliberate choice to prioritize essential functions and eliminate non-essential ones. The process demands meticulous planning and execution to ensure success, as every resource is vital and must be deployed strategically. Success hinges on understanding the specific challenges and opportunities inherent in each unique situation.Implementing a stripped-down business model isn’t just about reducing costs; it’s about optimizing resources to achieve maximum impact with minimal expenditure.
This strategy is particularly effective for startups, established businesses seeking to reinvent themselves, or those operating in highly competitive markets. The key lies in a calculated, step-by-step approach.
Defining Key Implementation Steps
A systematic approach to implementation is crucial for a successful stripped-down model. This involves a clear understanding of the target market, careful resource allocation, and a willingness to adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
- Market Analysis and Segmentation: Thoroughly research the target market to identify specific needs and preferences. Segment the market to pinpoint distinct customer groups and tailor offerings accordingly. This ensures resources are directed towards the most profitable segments, maximizing impact.
- Core Function Identification: Identify and prioritize the essential functions that directly contribute to value creation. Analyze the value proposition to pinpoint the most important aspects of the business. Eliminate any functions that don’t directly support core offerings. This sharpens the focus and eliminates unnecessary overhead.
- Resource Optimization: Evaluate and optimize existing resources to meet the needs of the stripped-down model. This could involve renegotiating contracts, outsourcing non-core functions, or acquiring necessary equipment efficiently. Maximize the utilization of available resources for optimal efficiency.
- Technology Integration: Leverage technology to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. Explore and implement tools that can streamline operations, such as CRM systems or project management software. This can greatly improve communication and productivity, especially for smaller teams.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Establish a system for continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs). Regularly review and adjust strategies based on real-time data and market feedback. Adaptability is key; the ability to respond to changing conditions is critical for sustained success.
Adapting Strategies to Specific Circumstances
The effectiveness of a stripped-down model hinges on its adaptability to unique situations. Recognizing the particular dynamics of each industry and context is paramount for success.
- Industry-Specific Considerations: The requirements for a stripped-down model will differ depending on the industry. For instance, a software company might prioritize software development and marketing, while a retail store might focus on inventory management and customer service. This underscores the importance of tailor-making the model to the specific needs of the industry.
- Market Volatility: In dynamic markets, flexibility is critical. The model must be prepared for adjustments based on market trends and competitor actions. Adapting to market fluctuations is essential to stay ahead.
- Competitive Landscape: Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial. Identifying strengths and weaknesses in comparison to competitors is essential for developing a strategic advantage. Understanding competitors’ moves is critical to strategic positioning.
Potential Challenges During Implementation
Implementing a stripped-down model can present certain obstacles. Anticipating and addressing these challenges proactively is essential for success.
- Resistance to Change: Employees or stakeholders might resist changes to established processes. Effective communication and training are vital to address any concerns.
- Maintaining Quality: Reducing resources can sometimes impact the quality of services or products. It’s important to maintain high standards while streamlining operations. This is critical for retaining customer loyalty.
- Measuring Success: Defining and measuring success in a stripped-down model might require a shift in perspective. Focus on KPIs that align with the streamlined operations. This helps avoid misinterpreting progress.
Implementation Flowchart:
Start | V Market Analysis & Segmentation | V Core Function Identification & Prioritization | V Resource Optimization & Allocation | V Technology Integration & Automation | V Continuous Monitoring & Adaptation | V Success
Key Metrics for Evaluating Success
A stripped-down business model, by its very nature, prioritizes efficiency and lean operations. This necessitates a different approach to measuring success compared to more complex models. Instead of focusing on elaborate metrics, a stripped-down model emphasizes key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly reflect its core objectives. These metrics are crucial for tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and making informed decisions.
Evaluating the success of a stripped-down model is less about grand visions and more about consistently achieving the fundamentals. It’s about ensuring each component of the model performs as expected and contributes to the overall goal. This requires a clear understanding of the specific metrics that will provide the most relevant insights.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), A stripped down business model
Understanding the KPIs is essential for evaluating the performance of a stripped-down business model. They offer a focused lens through which to view the health and progress of the business. Choosing the right metrics is crucial to ensure they accurately reflect the core values and objectives of the model.
A stripped-down business model can be surprisingly effective, focusing on core offerings and minimizing overhead. This approach, exemplified by the innovative approach of Anthem, a good sport with its skydiving simulator ( anthem a good sport with skydiving simulator ), allows for agility and a strong return on investment. Ultimately, a leaner operation often leads to greater flexibility and efficiency.
| KPI | Description | How to Measure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The cost of acquiring a new customer. | Divide total marketing and sales expenses by the number of new customers acquired. | If $10,000 was spent on marketing and 50 new customers were acquired, the CAC is $200. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | The total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with the business. | Estimate the average revenue per customer and the average customer lifespan. | If a customer spends $500 annually and has a 5-year relationship, the CLTV is $2,500. |
| Customer Churn Rate | The rate at which customers stop doing business with the company. | Divide the number of customers lost in a given period by the total number of customers at the beginning of that period. | If 10 out of 100 customers stopped using the service in a month, the churn rate is 10%. |
| Conversion Rate | The percentage of leads that convert into paying customers. | Divide the number of conversions by the number of leads. | If 20 out of 100 leads converted, the conversion rate is 20%. |
| Operating Expenses | The total cost of running the business. | Track all expenses associated with operations, including salaries, rent, utilities, and materials. | If total operating expenses are $5,000 per month, the monthly operating expenses are $5,000. |
| Revenue per Unit | The revenue generated per product or service sold. | Divide total revenue by the number of units sold. | If $10,000 in revenue was generated from selling 100 units, the revenue per unit is $100. |
Using Metrics for Improvement
Regularly tracking and analyzing these KPIs is crucial. This allows for identifying areas needing improvement and making data-driven decisions. A stripped-down model relies heavily on efficiency, and these metrics are the key to ensuring optimal performance. The information gleaned from these metrics can be used to refine processes, optimize marketing strategies, and adjust pricing models.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations: A Stripped Down Business Model
Stripped-down business models, while often associated with lean operations, can be incredibly effective when executed correctly. These models prioritize efficiency and focus, cutting out unnecessary layers and maximizing resource allocation. This approach can be particularly advantageous for startups, established businesses looking to streamline operations, or even large enterprises seeking to pivot into new markets. Examining successful implementations provides valuable insights into the strategies and methods that drive positive results.
Examples of Successful Stripped-Down Models
Successful implementations of stripped-down business models demonstrate a clear path forward for organizations aiming for streamlined operations and enhanced profitability. The following examples showcase the flexibility and potential of this model across diverse industries.
| Company | Industry | Key Strategies | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Razorpay | Financial Technology (FinTech) | Focused on a core offering (online payments) with minimal overhead. Leveraged technology for automation and scaling. | Rapid growth, market leadership in online payments in India, and significant user base. This company demonstrated how streamlined operations can fuel rapid expansion and dominance in a competitive market. |
| Mailchimp | Marketing Automation | Started with a simple, easy-to-use email marketing platform. Prioritized customer experience over unnecessary features. Built a robust API and automation infrastructure. | Gained a massive customer base, became a leading email marketing provider, and fostered a loyal user community by offering a user-friendly platform. This demonstrates how a simple, focused offering can cultivate a large, satisfied user base. |
| Airbnb | Hospitality | Initially focused on connecting hosts with travelers. Built a robust platform for listing and booking accommodations, with minimal in-house management. Outsourcing critical tasks proved highly efficient. | Revolutionized the hospitality industry by providing a user-friendly platform and fostering a global community. The stripped-down model allowed for rapid expansion and disruption of traditional hotel businesses. |
Key Strategies and Methods
A common thread among these successful implementations is a laser focus on core competencies. By eliminating extraneous functions and concentrating on delivering value, these companies achieved remarkable results. A strong understanding of the target market and customer needs is crucial for defining a focused value proposition.
“A stripped-down business model is not about sacrificing quality; it’s about focusing on delivering maximum value with minimal resources.”
The examples above showcase the efficacy of a stripped-down business model. By concentrating on core competencies, and leveraging technology to automate processes, these companies achieved rapid growth and market leadership. This strategy highlights how streamlining operations can create a competitive advantage.
A stripped-down business model, focusing on core offerings, can be surprisingly effective. Thinking about a trip to Saudi Arabia, you’ll need 6 key planning tips for travel to Saudi Arabia to make the most of your time. 6 key planning tips for travel to Saudi Arabia will help you streamline your trip and avoid common pitfalls.
This kind of strategic simplicity, like a well-planned trip, is key to a successful, lean operation.
Adapting to Market Changes
Stripped-down business models, while offering agility and cost-effectiveness, require a high degree of adaptability. Market shifts, technological advancements, and evolving customer preferences can quickly render a model obsolete if not proactively addressed. This section delves into strategies for successfully adapting a stripped-down model to changing market conditions, emphasizing the crucial balance between minimizing overhead and maintaining competitiveness.
Maintaining a lean structure allows for quicker response times to market fluctuations. This adaptability is a key advantage, allowing companies to swiftly adjust offerings and operations without being weighed down by complex systems and high overhead. Companies utilizing this strategy must develop a deep understanding of market dynamics and proactively seek opportunities for change, keeping a watchful eye on trends and consumer behavior.
Strategies for Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
A key aspect of adapting a stripped-down model is its inherent flexibility. The minimal structure allows for rapid pivots and adjustments in response to evolving demands. Companies employing this model can often quickly introduce new products or services, adjust pricing, and modify their marketing strategies. This agility is a significant competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
A stripped-down business model can be incredibly effective, especially when focusing on core offerings. Take, for example, the recent renovations at Amanyara Turks and Caicos. amanyara turks and caicos renovations highlight a streamlined approach, prioritizing luxury and exclusivity. By eliminating extraneous services and focusing on the core experience, Amanyara’s model demonstrates how a leaner structure can actually enhance the overall guest experience.
This principle can be applied to various industries, proving a stripped-down business model can be surprisingly powerful.
Maintaining Competitiveness with Minimal Overhead
Maintaining competitiveness with limited resources demands strategic decision-making. Companies must prioritize efficiency, focus on core competencies, and optimize operations to maximize output while minimizing costs. Outsourcing non-core functions and adopting technology to automate processes are effective strategies to improve operational efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Successful Adaptations
Several businesses have successfully adapted their stripped-down models to changing market conditions. For example, many online retailers have adopted a lean model, relying heavily on digital platforms and third-party logistics providers to minimize physical infrastructure. This adaptability has allowed them to quickly respond to shifting consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Comparing Adaptation Strategies
| Adaptation Strategy | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Diversification | Expanding product offerings to cater to evolving consumer needs. | Increased market share, reduced reliance on a single product. | Potential for cannibalization of existing products, increased complexity. |
| Pricing Adjustments | Adapting pricing strategies in response to market fluctuations or competitor actions. | Maintaining profitability, responsiveness to market conditions. | Potential for impacting perceived value, loss of customer loyalty if pricing adjustments are significant. |
| Technological Integration | Leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and automate processes. | Improved operational efficiency, cost reduction, increased agility. | Potential for high initial investment costs, need for skilled personnel to manage technology. |
| Partnership Development | Collaborating with other businesses to expand market reach or access resources. | Enhanced resources, wider market reach, shared risks. | Potential conflicts of interest, dependence on partners, possible loss of control. |
Illustrative Examples of a Stripped-Down Model
A stripped-down business model focuses on minimizing overhead and maximizing efficiency to achieve profitability with lean resources. This approach is particularly attractive for startups and businesses seeking rapid growth with limited capital. By eliminating non-essential features and functions, these models can quickly establish a presence in the market and build a customer base.
This section details a hypothetical stripped-down business model for an online subscription service, highlighting its features, pricing, target market, marketing strategies, costs, and revenues. This example demonstrates how a lean model can be highly effective in a competitive market.
Hypothetical Online Subscription Service
This model focuses on a curated selection of high-quality, niche products delivered monthly to subscribers. The service eliminates unnecessary bells and whistles, focusing solely on providing a streamlined experience and delivering value.
Features
- Curated selection of 5-7 products per month, categorized by interest (e.g., sustainable living, art supplies for kids).
- Monthly subscription fee, with no additional charges for shipping or handling within the service area.
- Easy online subscription management and cancellation options.
- Minimalist website design, emphasizing product discovery and order placement.
Pricing
The subscription service offers a single tier: a $29.99 monthly fee for the curated selection. This fixed price removes the complexity of different packages and options, making it easier for customers to understand and choose.
Target Market
The target market is individuals aged 25-45 with an interest in curated experiences and high-quality products. They are digitally savvy, appreciate ease of use, and value a focused, premium product selection.
Marketing Strategies
- Social media marketing: Focus on visual storytelling on platforms like Instagram and Pinterest, highlighting the curated products and subscriber experiences. A strong influencer marketing campaign can also be very effective.
- Content marketing: Create blog posts and social media content around the curated themes. This establishes expertise and drives engagement with the target market.
- Email marketing: Send out newsletters with exclusive offers, product spotlights, and behind-the-scenes content about the curation process. This builds a loyal customer base.
Costs and Revenues
| Cost Category | Estimated Monthly Cost |
|---|---|
| Product Sourcing | $1,500 |
| Website Maintenance | $200 |
| Marketing & Advertising | $500 |
| Shipping (estimated per order) | $5 |
| Total Monthly Costs | $2,200 |
| Revenue Category | Estimated Monthly Revenue |
| Subscription Revenue (100 subscribers) | $2,999 |
The estimated profit margin is $799 per month. This is a simplified calculation; actual results may vary based on factors such as subscriber acquisition costs and market fluctuations.
Last Word
In conclusion, a stripped-down business model provides a compelling alternative to traditional approaches. By focusing on core competencies and minimizing unnecessary expenses, businesses can achieve remarkable efficiency and profitability. The key is to carefully consider the trade-offs, adapt the model to your specific industry and target audience, and constantly monitor performance. This guide provides a roadmap to navigate the complexities of implementing and adapting a stripped-down model, paving the way for sustainable and successful growth.
Helpful Answers
What are the common motivations for choosing a stripped-down business model?
Businesses often opt for a stripped-down model to reduce initial investment, accelerate market entry, and focus on core competencies. It’s particularly attractive to startups with limited resources or those seeking rapid growth.
What are some common pitfalls of a stripped-down model?
Potential drawbacks include a reduced ability to scale, limited resources for future expansion, and challenges in attracting investors who might perceive the model as too risky.
How does a stripped-down business model differ from a franchise model?
A stripped-down model emphasizes internal efficiency and core competency, while a franchise model relies on a pre-existing brand and system. A stripped-down model is more focused on individual innovation, while a franchise model is more focused on scalability through a proven framework.
How can I measure the success of a stripped-down business model?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and revenue per employee are vital in evaluating the model’s effectiveness. Focus on metrics that demonstrate efficiency and profitability within the constrained resources.

