
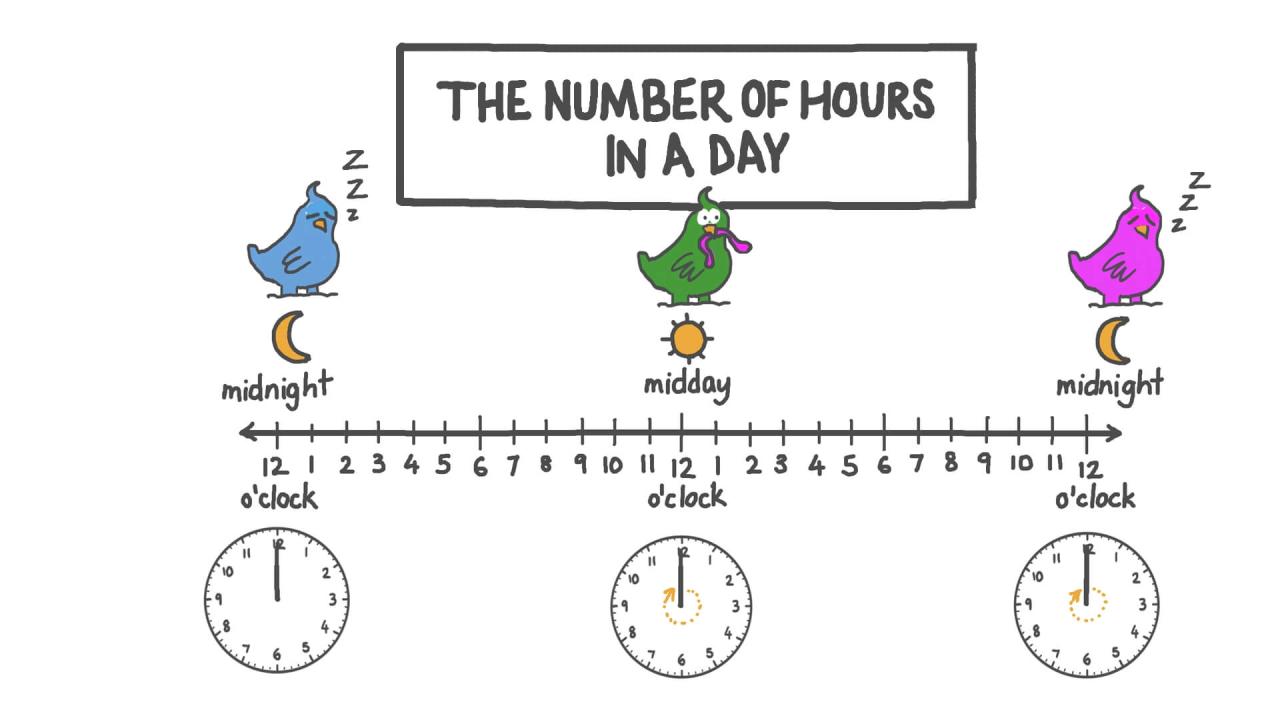
A 24-Hour Day Our Time-Bound World
A 24 hour day – A 24-hour day sets the stage for our entire existence, dictating our routines, shaping our global interactions, and influencing everything from our sleep cycles to international trade. This deep dive explores the intricacies of this fundamental unit of time, examining its historical context, scientific underpinnings, cultural impact, and even its surprising variations.
From the precise definition of a day, to its impact on daily life and societal structures, we’ll uncover the fascinating relationship between a 24-hour day and our world. We’ll also delve into the ways different cultures perceive and utilize this time frame, highlighting the diverse approaches to daily living.
Defining a 24-Hour Day
A 24-hour day is a fundamental unit of time, deeply ingrained in our daily lives and crucial for organizing schedules and activities. Understanding its precise definition, historical development, and the units that compose it provides a fascinating insight into how we measure and perceive time. This understanding also sheds light on the intricate relationship between Earth’s rotation and our perception of time.A 24-hour day is precisely defined as the time it takes for Earth to complete one full rotation on its axis relative to the Sun.
This rotation isn’t perfectly uniform; slight variations occur due to complex interactions within Earth’s systems, resulting in slight fluctuations in the length of a day. Modern scientific measurements, using highly precise atomic clocks, have refined our understanding of this rotational period.
Historical Development of Time Measurement
Early civilizations, observing the cyclical nature of day and night, developed various methods for tracking time. Ancient Egyptians, for instance, used sundials to measure the passage of daylight hours. Later, the development of water clocks (clepsydras) and sand clocks offered more consistent means of measuring time, although these methods were not as precise as modern instruments. The gradual refinement of timekeeping technology, from sundials to atomic clocks, showcases humanity’s ongoing quest for greater accuracy and precision in measuring time.
Units of Time Measurement
A 24-hour day is composed of smaller units of time, namely hours, minutes, and seconds. These units are crucial for expressing time intervals with greater granularity. The division of a day into hours, minutes, and seconds reflects a hierarchical structure for measuring time, enabling us to specify precise moments within a 24-hour period.
Comparison of Time Units Across Cultures
| Culture | Unit | Definition/Description | Relationship to Earth’s Rotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient Egypt | Hours (based on sundial) | Variable lengths depending on the season and location. | Roughly tied to the sun’s apparent movement. |
| Mesopotamia | Hours (based on water clocks) | More consistent than sundial hours, but still variable. | Related to the flow of water, indirectly to Earth’s rotation. |
| Modern Standard | Hours, Minutes, Seconds | Uniformly defined, based on Earth’s rotation and atomic clocks. | Precisely tied to Earth’s rotational period, with adjustments for variations. |
The table above highlights the evolution of timekeeping units across different cultures, emphasizing the progression from rudimentary methods to highly accurate scientific standards. Different civilizations developed their own systems based on their unique environments and technologies. The modern standard, based on atomic clocks, provides a globally consistent and highly precise measure of time, crucial for global communication and coordination.
The Impact of a 24-Hour Day on Daily Life
The 24-hour day, a seemingly constant and universal framework, profoundly shapes our lives in ways we often take for granted. From the intricate dance of global trade to the subtle rhythms of our own circadian cycles, the 24-hour period acts as a powerful organizing principle, dictating our routines, interactions, and even our biological processes. Understanding this impact is crucial to appreciating the interconnectedness of human activity and the planet’s time zones.The 24-hour cycle is a fundamental structure that organizes daily activities and schedules across different time zones.
This structure significantly influences our daily routines and activities, dictating when we work, sleep, socialize, and engage in leisure. The concept of time zones, which are essentially divisions of the globe based on longitude, creates a crucial difference in how we experience this 24-hour cycle.
Impact on Work Schedules
Different time zones create substantial differences in work schedules. Companies operating globally often need to coordinate employees across multiple time zones. For instance, a US-based company with operations in Europe must account for a 6-hour difference. This necessitates staggered work shifts and dedicated communication protocols to ensure smooth project management and customer service. A 24-hour day allows for these interactions, but the need for coordination and adaptation is evident.
The scheduling of meetings and deadlines become a complex dance, carefully timed to ensure productivity across various time zones.
Impact on Social Interactions
Social interactions are heavily influenced by time zones. Maintaining relationships with friends and family in different time zones requires careful scheduling of calls, video chats, and messaging. The convenience of instant communication technologies, like video conferencing, allows for seamless connections, but the time difference still requires a conscious effort to ensure everyone can participate at a mutually agreeable time.
Long-distance relationships, in particular, face this challenge.
Impact on Personal Lives
The 24-hour day significantly impacts personal lives, influencing our ability to balance work, social life, and personal time. Individuals living in different time zones face the challenge of maintaining personal connections and routines. The scheduling of personal events, such as family gatherings, holidays, and personal appointments, becomes a logistical puzzle. Consider a family with members living in various parts of the world.
Coordinating a virtual family gathering requires significant scheduling consideration to accommodate everyone’s respective time zones.
Impact on Global Trade and Communication
The 24-hour day is a key element driving global trade and communication. Businesses can conduct transactions and engage in international collaborations around the clock. The constant flow of information and goods across different time zones is a direct result of this 24-hour structure. Supply chains, which often involve multiple countries and continents, rely on the seamless integration of different time zones to maintain efficient operations.
A 24-hour day feels like a lot of time, but when you consider the incredible accomplishments of individuals like those honored at the transformational leadership ceremony, dozens of graduates honored at transformational leadership ceremony , it really puts things into perspective. It highlights how much potential and impact can be achieved within a single day, even within a 24-hour period.
So, what will you do with yours today?
Companies leverage this 24-hour cycle to maximize their production and distribution networks.
Impact on Human Biology
The 24-hour cycle profoundly influences human biology, particularly our sleep patterns and circadian rhythms. Our bodies have an internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which regulates various bodily functions, including sleep-wake cycles. Disruptions to this natural rhythm, such as jet lag or working across multiple time zones, can have significant negative impacts on health. Chronic exposure to different time zones can lead to various health problems.
Variations in the Length of a Day

Our perception of a 24-hour day is a convenient simplification. In reality, Earth’s rotation isn’t perfectly consistent, leading to slight variations in the length of a day. These variations, though seemingly small, have significant implications for timekeeping and our understanding of Earth’s dynamics. These nuances, stemming from complex interactions within the Earth-Moon system and beyond, provide fascinating insights into our planet’s intricate workings.The precise length of a day is not a constant; it fluctuates slightly over time.
These fluctuations, though small, are measurable and have real-world consequences for timekeeping systems and scientific observations. The Earth’s rotation is influenced by various factors, including the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun, as well as internal processes within the Earth itself. These factors contribute to minute but noticeable variations in the duration of a day.
Leap Years and the Gregorian Calendar
The Gregorian calendar, widely used today, incorporates leap years to account for the Earth’s slightly longer orbital period compared to a whole number of days. Leap years, which occur every four years, add an extra day to February, adjusting for the accumulated difference between the calendar and the actual time it takes the Earth to complete a full revolution around the Sun.
This adjustment ensures that the calendar seasons remain aligned with the Earth’s orbital position. The Gregorian calendar, a refinement of the Julian calendar, was introduced to mitigate the calendar’s drift from the solar year.
Earth’s Varying Rotational Speed
Earth’s rotation isn’t uniform. Various factors, including the distribution of mass within the Earth, the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun, and even the movement of air masses, contribute to slight variations in the Earth’s rotational speed. These fluctuations are typically measured in milliseconds and can affect the length of a day. These variations are not consistent, and their precise magnitude can be influenced by short-term and long-term phenomena.
Historical and Scientific Measurements
Accurate measurement of Earth’s rotation has a long history. Early observations relied on astronomical measurements, tracking the positions of celestial bodies. Modern methods utilize highly precise atomic clocks and sophisticated techniques to monitor the Earth’s rotation. These advancements allow for the detection of even the smallest variations in the length of a day. Scientists continue to refine their measurements, aiming for increasingly precise data about Earth’s rotational dynamics.
The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) is a prominent organization dedicated to this pursuit.
Impact on Timekeeping Systems, A 24 hour day
The variations in the length of a day have practical implications for timekeeping systems. These fluctuations need to be accounted for, especially in applications requiring extreme precision, such as GPS navigation and scientific experiments. Atomic clocks, which are extremely precise, are crucial in maintaining accurate timekeeping in the face of these variations. Timekeeping systems, such as those used in GPS, need to account for these fluctuations in order to maintain accuracy and reliability.
Cultural and Societal Perspectives on a 24-Hour Day
The 24-hour day, a seemingly universal constant, is experienced and structured quite differently across cultures. Different societies have developed unique rhythms and routines, shaping their daily lives and even their spiritual practices around this fundamental time unit. From sunrise rituals to evening prayers, the 24-hour cycle has become intertwined with cultural identity and tradition.Beyond the practical implications of scheduling work and rest, the 24-hour day profoundly impacts how cultures perceive time, activity, and even spirituality.
A 24-hour day can feel like a whirlwind, especially when juggling deadlines and managing your office. Knowing how to effectively stay on top of your office packaging and shipping supplies costs is crucial for maintaining profitability. Staying on top of your office packaging shipping supplies costs can free up valuable time and resources, allowing you to focus on other essential aspects of your business, and ultimately make the most of that 24-hour day.
These varied perspectives illuminate the rich tapestry of human experience and the diverse ways in which societies organize themselves around the daily cycle.
Cultural Perceptions of Time and Activity
Different cultures have varying perceptions of time, and these perceptions directly influence how they structure their daily lives around the 24-hour cycle. Some cultures prioritize morning activities, while others emphasize evening gatherings. This diverse approach to time management is reflected in daily routines and social interactions.
| Culture | Perception of Time | Typical Daily Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Indigenous Australian cultures | Cyclic and connected to the natural world (seasons, sunrises, moon cycles) | Often involve rituals and ceremonies aligned with the natural rhythm of the day, including specific times for hunting, gathering, and storytelling. |
| Latin American cultures | Emphasis on social interactions and family gatherings, often extending into the evening | Family meals, social events, and community gatherings are often scheduled in the later part of the day. |
| Northern European cultures | Emphasis on punctuality and efficiency, often prioritizing work and productivity in the morning and early afternoon. | Work schedules and meetings are often structured in a more rigid manner, with specific time slots allocated for different tasks. |
| Asian cultures | Balance between work and personal life, with a focus on family and community | Traditional practices like morning tea and evening prayer times can influence daily schedules. |
Impact on Religious Practices and Rituals
The 24-hour day significantly influences religious practices and rituals across various cultures. Many faiths incorporate specific times for prayer, meditation, or other spiritual activities, often aligning with the rising and setting of the sun or other celestial events.
- Islam, for instance, has specific prayer times throughout the day, directly tied to the position of the sun. These prayer times influence the schedule of individuals and communities, dictating specific periods for worship and communal gatherings.
- Hinduism also incorporates a complex system of daily rituals and prayers that vary according to the time of day and the specific deity being worshipped. These rituals are deeply rooted in the cultural and spiritual life of Hindu communities.
- Many indigenous cultures have elaborate ceremonies and rituals that are closely linked to the daily cycle of the sun and moon. These ceremonies often involve specific activities that are performed at certain times of the day.
Cultural Practices Related to the 24-Hour Day
Various cultural practices are deeply embedded within the 24-hour cycle, reflecting the unique values, beliefs, and traditions of each society.
| Culture | Practice | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Many Asian cultures | Morning tea | A customary practice where families and communities gather for tea and conversation in the morning, often before work or school begins. |
| Many Latin American cultures | Evening gatherings | Emphasis on social interaction and family time in the evenings, often involving meals and conversations. |
| Indigenous Australian cultures | Dreamtime stories | Stories and narratives about the creation of the world and the universe, often shared during specific times of the day, particularly evenings. |
The 24-Hour Day in the Context of Astronomy and Astrophysics: A 24 Hour Day
The 24-hour day, a fundamental unit of time for our daily lives, is deeply intertwined with the workings of the cosmos. It stems from Earth’s rotation and profoundly impacts our understanding of astronomical phenomena. From predicting eclipses to calculating planetary positions, the 24-hour day serves as a crucial reference point in astronomical observations and calculations.Our perception of time, heavily influenced by the cyclical nature of Earth’s rotation, is inextricably linked to the movement of celestial bodies.
The regular, predictable pattern of Earth’s spin allows us to establish a consistent timescale, which is essential for tracking and understanding the vast, complex processes in the universe.
The Role of a 24-Hour Day in Astronomical Observations and Calculations
The 24-hour day forms the basis for our coordinate systems and timekeeping, enabling astronomers to pinpoint celestial objects’ locations and track their movements with precision. Astronomical events, like eclipses, are precisely predicted using the 24-hour day as a reference, enabling accurate predictions and observations. For instance, the precise timing of a lunar eclipse hinges on the Earth’s rotation, as well as the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
How Earth’s Rotation Affects Astronomical Phenomena
Earth’s rotation is the driving force behind the apparent daily movement of celestial bodies across the sky. This daily cycle, measured in 24 hours, is fundamental to our understanding of celestial mechanics. The Earth’s axial tilt, combined with its rotation, creates the seasons and influences the paths of stars and planets as observed from Earth. The varying amounts of sunlight received by different parts of the Earth throughout the day and year are a direct consequence of Earth’s rotation and its orbital position around the Sun.
Relationship Between the 24-Hour Day and the Movements of Celestial Bodies
The 24-hour day is directly linked to the apparent westward movement of celestial objects across the sky. This apparent movement is due to the Earth’s eastward rotation, which creates the illusion of celestial bodies moving from east to west. The precise timing of the rising and setting of stars and planets, crucial for navigation and astronomical observation, is directly tied to the 24-hour day.
This daily cycle is a repeating pattern, allowing astronomers to predict the times when specific celestial bodies will be visible from a particular location.
The 24-Hour Day and Earth’s Position in the Solar System
The Earth’s position in the solar system plays a critical role in determining the length of the day. Earth’s orbit around the Sun is not a perfect circle but an ellipse, and this eccentricity affects the apparent speed of Earth’s rotation and thus the duration of a day. Variations in the Earth’s rotational speed, though subtle, can be measured and incorporated into precise astronomical calculations.
These calculations consider the Earth’s orbital position, its axial tilt, and its speed of rotation around its axis. Understanding these relationships is essential for predicting long-term changes in the length of the day, which can affect astronomical measurements and predictions.
Technological Applications of a 24-Hour Day
The concept of a 24-hour day, deeply ingrained in our daily lives, has been a fundamental cornerstone in the development of various technologies. From the earliest sundials to the sophisticated atomic clocks of today, the consistent duration of a day has provided a crucial framework for measuring time and coordinating human activities. This has had a profound impact on societal structures and technological advancements, driving innovation in numerous fields.The 24-hour day serves as a universal standard, allowing for the synchronization of activities across different geographical locations and time zones.
This standard is critical for global communication, transportation, commerce, and virtually every aspect of modern life. This fundamental understanding of time has been essential in shaping the development of timekeeping technologies and the technologies built upon them.
A 24-hour day feels like a precious commodity, doesn’t it? It’s amazing how much you can get done, but sometimes it feels like not enough. With Mondovi soon transitioning to Emplify Health, mondovi will soon be under emplify health , I’m wondering how this change will impact the efficiency and productivity within the company’s day-to-day operations. Still, a 24-hour day is a 24-hour day, and we’ll have to see how everyone adjusts.
Influence on Timekeeping Devices
The consistent duration of a 24-hour day has profoundly influenced the development of timekeeping devices. Early civilizations used natural phenomena like the position of the sun and stars to create rudimentary timekeeping systems. The development of sundials, water clocks, and sandglasses all relied on the cyclical nature of the Earth’s rotation and the predictable patterns of day and night.
These devices, although rudimentary by modern standards, provided a crucial means of measuring time and scheduling activities.
Timekeeping Technologies
The 24-hour day is the foundation upon which clocks and calendars are built. From the mechanical clocks of the Middle Ages to the quartz and atomic clocks of the modern era, the 24-hour cycle has been a constant reference point. Calendars, in their various forms, organize time based on the recurring cycles of the moon and sun, further emphasizing the importance of the 24-hour day in our daily lives.
The precision of these tools has improved dramatically over time, leading to the development of more sophisticated technologies that rely on precise timekeeping.
Importance of Precise Timekeeping
Precise timekeeping is crucial in numerous industries. In aviation, accurate time synchronization is essential for air traffic control and navigation. In finance, precise timekeeping is essential for managing transactions and ensuring the accuracy of financial records. Furthermore, scientific research often relies on precise timekeeping to conduct experiments and record data.
A 24-hour day feels like a pretty standard timeframe, doesn’t it? But when you consider the intricate designs and meticulous planning behind some of the world’s most impressive structures, like those created by the top architectural firms, like largest architectural firms 2 , you realize just how much time and effort goes into shaping our environment.
It really puts a whole new perspective on a seemingly simple 24 hours.
Evolution of Timekeeping Technology
The evolution of timekeeping technology has profoundly impacted our modern world. The development of more accurate and reliable clocks has allowed for greater coordination and efficiency in various aspects of life. The use of atomic clocks, for example, has led to unprecedented precision in time measurement, enabling advancements in fields like GPS and telecommunications. The increasing reliance on precise timekeeping in the modern world demonstrates its vital role in our technologically advanced society.
Illustrative Examples and Visualizations
Our 24-hour day is a fundamental aspect of our lives, shaping everything from our schedules to our understanding of the universe. Visual representations can deepen our comprehension of this crucial concept, allowing us to grasp complex relationships and patterns. This section will explore diverse visualizations, highlighting the Earth’s rotation, time zones, the moon’s phases, and the global impact of these factors.
Visualizing the 24-Hour Cycle of Earth’s Rotation
The Earth’s rotation is a continuous process, but visualizing its impact over a 24-hour period reveals the source of our daily cycle. A simple animation could show the Earth rotating on its axis, with a prominent highlight marking the position of a specific location. As the Earth rotates, the highlighted location would transition from daylight to darkness, visually demonstrating the 24-hour cycle.
This animation would clearly show the changing position of the sun relative to the Earth.
Visualizing Time Zones
A map of the world, color-coded by time zone, can illustrate the concept of time zones effectively. Different colors can represent different time zones, creating a visual representation of the 24-hour day’s global distribution. Markers could represent significant events occurring in various locations, highlighting the time difference between them. This visual representation can effectively demonstrate the impact of time zones on international communication and global events.
Visualizing the Relationship Between the 24-Hour Day and the Moon’s Phases
A combination chart, including a graph of the moon’s phases over a month and a corresponding representation of the 24-hour cycle, would be a useful visualization. The graph should display the moon’s phases (new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, waning crescent) in a clear format, with corresponding dates. The 24-hour cycle could be represented by a horizontal axis, showing the changing times of sunrise and sunset, and how the moon’s visibility and position vary with this cycle.
Visualizing the Impact of Time Zones on Global Events
A dynamic representation, such as a world map with animated markers, can visually showcase the impact of time zones on global events. The markers could represent important events, such as sports matches, international conferences, or natural disasters, with their locations on the map reflecting their respective time zones. The animation should show how these events unfold across different time zones, highlighting the concept of simultaneous events happening at different times in various locations.
A 24-hour day can feel like an eternity when you’re planning a trip, especially one to a new country like Saudi Arabia. Knowing how to best manage your time is crucial, and thankfully, there are some great tips for successful travel to Saudi Arabia. For example, checking out these 6 key planning tips for travel to Saudi Arabia 6 key planning tips for travel to saudi arabia can help you make the most of every hour.
Ultimately, planning ahead can make your 24-hour days in Saudi Arabia much more enjoyable.
This visual representation would enhance understanding of the global interconnectedness influenced by time zones.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, a 24-hour day is far more than just a unit of time; it’s a fundamental cornerstone of our lives, influencing everything from our personal schedules to global events. Its precise measurement, cultural interpretations, and even slight variations offer a captivating window into the intricate relationship between humanity and the cosmos. We hope this exploration has provided a comprehensive understanding of this crucial aspect of our existence.
Essential Questionnaire
How does a leap year affect the length of a day?
Leap years, with their extra day, subtly adjust our timekeeping systems to maintain alignment with the Earth’s actual orbit around the sun.
What is the relationship between the 24-hour day and the phases of the moon?
While not directly linked, the 24-hour day and lunar cycles are both important cycles in our understanding of celestial mechanics and timekeeping.
How do different cultures mark and utilize a 24-hour day?
Different cultures have developed various traditions and customs around the 24-hour day, incorporating it into their daily routines, religious practices, and societal structures. Some may align their daily activities with the rising and setting sun, while others use different time-keeping methods.
What role does a 24-hour day play in astronomical calculations?
Astronomers use the 24-hour day as a fundamental unit for tracking celestial objects, calculating their movements, and understanding the cosmos.






