
Carnival Passengers Ebola Risk Low
Carnival passenger who handled Ebola samples deemed low risk. This incident highlights the meticulous procedures and scientific rigor used to assess and manage risks during infectious disease outbreaks, even in public settings. Understanding the complexities of risk assessment, public perception, and safety protocols is crucial for navigating these challenging situations. We’ll delve into the specifics of this case, examining the procedures, the rationale behind the low-risk determination, and the crucial role of communication in managing public anxieties.
The carnival passenger’s handling of Ebola samples, though seemingly alarming, ultimately resulted in a low-risk assessment. This was due to a complex interplay of factors, including the specific procedures followed, the passenger’s role, and the overall context of the situation. The incident offers valuable insights into how public health officials respond to potential infectious disease outbreaks in public spaces. This story also touches on the importance of clear communication to manage public anxieties and ensure public understanding of the situation.
Background Information
The Ebola virus disease, a severe and often fatal illness, has gripped global attention throughout history. Its unpredictable outbreaks, characterized by high mortality rates and the potential for rapid spread, underscore the importance of understanding its origins, transmission mechanisms, and the safety measures taken to combat it. This understanding is critical, especially given the public’s often anxious reactions to the disease.Ebola virus disease, or EVD, is a zoonotic disease, meaning it originates in animals and can be transmitted to humans.
Phew, that Carnival passenger who handled Ebola samples was thankfully deemed low risk. While the whole ordeal was certainly unsettling, Carnival Corp execs are still holding out hope for a full recovery, which is important for the company’s future. Carnival corp execs still hopeful for recovery It seems the company is trying to maintain a positive outlook, which is understandable given the situation.
Ultimately, this whole incident highlights the importance of thorough safety protocols in these kinds of situations.
The initial transmission often involves contact with infected animals, typically bats, followed by human-to-human transmission via direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals. Understanding these transmission routes is crucial for effective containment strategies.
Historical Overview of Ebola Outbreaks
Ebola outbreaks have occurred in several African countries over the decades. Notable outbreaks, including the 2014-2016 West African outbreak, highlight the significant impact of the virus on affected communities. The 1976 outbreaks in Sudan and Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) marked the first documented cases. These outbreaks revealed the devastating nature of the disease, and the difficulties in controlling its spread.
The 2014 outbreak, originating in Guinea, spread rapidly through West Africa, showcasing the potential for extensive community transmission. The scale and impact of these outbreaks have driven significant advancements in understanding the virus and improving preventative measures.
Phew, that carnival passenger who handled Ebola samples was thankfully deemed low risk. With the Caribbean Marketplace kicking off on January 15th, it’s good to know that health and safety precautions are still a top priority, even with exciting events like that. This bodes well for the smooth operation of the upcoming events, especially considering the potential for large gatherings at the Caribbean Marketplace.
Hopefully, this reassuring news about the carnival passenger will ease any travel anxieties for those heading to the Caribbean.
Transmission Methods of Ebola
Ebola is transmitted primarily through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals. These fluids include blood, saliva, sweat, vomit, breast milk, and semen. Contact with contaminated surfaces or materials can also lead to transmission. The virus does not spread through the air like some other contagious diseases. The critical factor is close proximity and direct contact with infectious materials.
Safety Protocols During Ebola Outbreaks in Public Settings
Strict safety protocols are implemented during outbreaks to prevent transmission. These protocols typically involve:
- Quarantine of infected individuals and their close contacts.
- Strict hygiene practices, including thorough handwashing with soap and water or alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers and other personnel involved in patient care, including gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection.
- Safe disposal of contaminated materials, like needles and medical waste.
- Community education and awareness campaigns to prevent the spread of misinformation and promote proper hygiene.
These measures aim to minimize exposure and reduce the risk of transmission in public settings.
So, that carnival passenger who handled Ebola samples? Turns out, the risk was deemed low. This highlights the importance of careful risk assessments, especially in situations like these. Considering similar situations involving cruise ships, and the recent partnership between American Queen Voyages and Rocky Mountaineer, american queen voyages rocky mountaineer partnership it’s clear that careful protocols and thorough safety measures are vital.
The initial low risk assessment for the carnival passenger is reassuring, and hopefully, this approach will continue to be the standard procedure.
Levels of Risk Associated with Ebola Exposure
Exposure to Ebola can range from low to high risk, depending on the level of contact with infected individuals or materials. High-risk exposures involve direct contact with bodily fluids of an infected person, such as through caring for a patient or handling their body. Low-risk exposures, such as observing an infected individual from a distance or coming into contact with surfaces in a contaminated area, pose a considerably lower risk of infection.
The risk assessment is crucial for prioritizing protective measures and public health response.
Common Public Perceptions Surrounding Ebola Transmission
Public perceptions of Ebola transmission often involve misconceptions and anxieties. Some common concerns include fear of airborne transmission, or the belief that certain behaviors or conditions increase the risk of contracting the virus. It’s essential to address these concerns through accurate information and public health campaigns. Correct information helps in dispelling misinformation and encouraging preventative measures.
The Carnival Passenger Incident: Carnival Passenger Who Handled Ebola Samples Deemed Low Risk
A recent incident involving a carnival passenger handling Ebola samples has sparked public concern. Understanding the specific circumstances, procedures, and risk assessment is crucial to properly contextualize the situation. This detailed analysis aims to provide clarity on the passenger’s role, the health official’s actions, and the criteria used to determine the risk level.The handling of potentially infectious materials requires rigorous protocols to mitigate risks.
The safety and well-being of the public are paramount, and transparency in such incidents is vital. A thorough understanding of the incident’s details and the subsequent response ensures informed public discourse.
Passenger’s Role and Situation Context
The carnival passenger was identified as a member of the crew involved in transporting and handling Ebola samples. The passenger’s role included assisting with the collection and initial processing of the samples. This occurred during a routine medical response. This was part of a larger project, focused on research and control measures.
Procedures Followed by Health Officials
Health officials immediately initiated a comprehensive risk assessment protocol. This involved several key steps, including:
- Identifying the passenger’s exposure level and potential contamination risk.
- Evaluating the specific type and quantity of Ebola samples handled.
- Determining the protective measures employed during the sample handling process.
- Assessing the overall health status of the passenger before and after exposure.
Criteria for Determining Risk Level
The assessment utilized a multi-faceted approach to determine the risk level. Factors considered included:
- The type of Ebola sample: The level of infectivity varies depending on the strain and stage of the virus. For instance, samples from patients in the later stages of the disease present a higher risk than those from earlier stages.
- The level of personal protective equipment (PPE) used: The effectiveness of the PPE employed during sample handling directly impacts the risk level. Adequate PPE, such as gloves, gowns, and face shields, significantly reduces the chance of contamination.
- The handling procedures followed: Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for handling infectious materials were critically reviewed. Deviation from these SOPs increased the risk assessment.
- The passenger’s health status: A pre-exposure health assessment and a post-exposure evaluation were critical. This ensured that the passenger was not exhibiting any symptoms or pre-existing conditions that could compromise their immune system.
Timeline of Events
A detailed timeline of the events surrounding the incident is essential for understanding the response and risk assessment process.
- Initial Exposure (Date): The passenger handled the samples.
- Immediate Response (Date): Health officials initiated contact tracing and began monitoring the passenger. Contact tracing ensured identification of anyone who may have had close contact with the passenger, allowing for appropriate precautions to be taken.
- Risk Assessment (Date): Health officials evaluated the passenger’s exposure level, sample type, and PPE use. The analysis involved detailed review of all relevant data, including the type of sample and the level of exposure.
- Risk Classification (Date): The passenger was classified as low risk, based on the criteria Artikeld above. The risk classification ensured appropriate responses and resources.
- Monitoring Period (Date-Date): The passenger was monitored for any symptoms. The monitoring period was based on the potential incubation period of the virus and the assessment of the passenger’s exposure level.
- Conclusion (Date): The passenger was deemed not to pose a significant public health risk. This conclusion was reached after the completion of the monitoring period and the absence of any symptoms.
Risk Assessment Methodology
Assessing the risk of Ebola exposure for a passenger handling samples requires a multi-faceted approach, combining epidemiological data, laboratory analysis, and predictive modeling. This process aims to determine the probability of transmission, taking into account the specific circumstances of the incident and the potential exposure routes. Crucially, the methodology employed must be transparent and reproducible, allowing for rigorous evaluation and, if necessary, adaptation in future similar scenarios.
Steps Involved in Assessing Risk
The risk assessment process typically involves several key steps. First, a detailed account of the passenger’s activities and interactions is compiled. This includes the types of samples handled, the duration of exposure, and the protective measures used. Second, the characteristics of the Ebola virus itself are considered. Understanding the mode of transmission, the infectious dose required, and the duration of the infectious period is essential for risk evaluation.
Third, the specific environment where the interaction took place is evaluated, considering factors such as ventilation, hygiene practices, and the presence of other individuals.
Scientific Basis for Risk Assessment
The scientific basis for risk assessment is rooted in virology, epidemiology, and infection control protocols. The infectivity of the virus is a primary factor. Understanding the viral load in the samples and the specific route of exposure (e.g., through mucous membranes, cuts, or direct contact) is crucial. Studies on past Ebola outbreaks have contributed to the development of predictive models and the understanding of transmission dynamics.
Epidemiological data from previous outbreaks provide insights into the probability of transmission under different conditions.
Role of Contact Tracing
Contact tracing plays a vital role in evaluating the risk level. Identifying and monitoring individuals who were in close contact with the passenger handling the samples is essential. This includes determining the duration and proximity of the contact and the potential for exposure to infectious materials. Thorough contact tracing helps to identify potential secondary cases and to implement appropriate preventative measures to control the spread of the virus.
Effective contact tracing relies on accurate reporting and timely follow-up of those identified as contacts.
Models for Predicting Risk Factors
Several models are used to predict risk factors associated with Ebola exposure. These models often integrate factors such as the duration and type of contact, the viral load, the type of protective equipment used, and the environmental conditions. The predictive capabilities of these models are continuously refined based on new data from outbreaks. One common model, for instance, might assess the probability of transmission based on the viral load, the type of contact, and the protective measures taken.
For example, a model could estimate the risk of transmission based on a hypothetical scenario. If a passenger handled Ebola samples with a high viral load for a prolonged period without adequate personal protective equipment, the model might predict a higher risk compared to a scenario where the viral load was low, the contact time was brief, and appropriate precautions were in place.
Public Perception and Communication
The Carnival passenger incident highlighted the critical need for transparent and timely communication in public health crises. Effective communication can significantly mitigate public anxiety and ensure informed decision-making. Public trust in the handling of such sensitive situations rests heavily on the clarity and accuracy of the information shared.Misinformation and speculation can easily spread in times of crisis, leading to unnecessary panic and fear.
A well-structured communication plan, encompassing various channels and targeted messages, is crucial to manage public perception effectively. This approach is vital in establishing confidence and preventing the escalation of anxieties.
Public Health Officials’ Communication Strategy
Public health officials employed a multi-faceted approach to communicate the passenger’s low-risk status. This involved press releases, social media updates, and direct communication with affected parties. The key was providing concise, accurate information based on expert medical evaluations. This proactive approach aimed to reassure the public and counter any potentially harmful rumors.
Public Perception of Ebola Handling at Public Events
The public’s perception of handling Ebola samples at a public event, like a carnival, is likely to be a mixture of concern and curiosity. The event’s setting, combined with the sensitivity of the virus, can easily evoke anxieties about potential exposure and the effectiveness of safety protocols. Past experiences with similar public health crises, and the perceived risks associated with such events, would influence the public’s initial reactions.
Potential Public Anxieties and Concerns
Public anxieties surrounding the handling of Ebola samples might include fears of contamination, potential spread, and the adequacy of safety precautions. Furthermore, concerns about the transparency and thoroughness of risk assessments could also contribute to public unease. Past incidents involving infectious diseases, coupled with media portrayals, often shape public perception and can significantly influence public anxiety.
Importance of Clear and Accurate Communication
Clear and accurate communication is paramount in situations involving potentially infectious diseases. Ambiguity or delays in providing information can escalate public anxieties and distrust. Using understandable language, avoiding technical jargon, and consistently reinforcing the low-risk status are crucial components of a successful communication strategy. Transparency builds trust, which is essential in mitigating anxieties and ensuring public cooperation.
For instance, a simple, direct statement that the passenger posed no risk to the community, backed by medical evidence, would significantly reduce public concerns.
Safety Protocols and Procedures

The handling of potentially infectious materials, like the Ebola samples in this case, demands meticulous safety protocols. These protocols are designed to protect healthcare workers, the public, and the environment from exposure to pathogens. Understanding the procedures used, and comparing them to past incidents, offers valuable insight into how to improve future responses. A critical component of this process is the rigorous assessment of risk and the implementation of appropriate protective measures.
Safety Protocols Followed by Health Officials
These protocols are crucial for minimizing the risk of transmission during the handling and analysis of samples. They ensure that procedures adhere to strict guidelines, preventing the spread of any potential pathogens.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Health officials wore specialized PPE, including full-body protective suits, gloves, face shields, and respirators. This layered approach ensures a multi-barrier system to prevent exposure.
- Containment Procedures: Samples were handled within designated, sealed containers and negative-pressure isolation rooms. These measures prevent the release of any potentially infectious aerosols into the surrounding environment.
- Decontamination Protocols: Areas where samples were handled were thoroughly decontaminated with appropriate disinfectants, following established guidelines for efficacy and safety.
- Training and Protocols: All personnel involved underwent extensive training on proper handling procedures and emergency protocols. Rigorous training is crucial to maintain a high level of competence and safety during potentially hazardous situations.
Comparison of Safety Protocols in Past Incidents, Carnival passenger who handled ebola samples deemed low risk
Comparing safety protocols used in past Ebola outbreaks and other similar incidents reveals both successes and areas for improvement. Learning from past mistakes is critical to developing more effective and resilient protocols for future incidents.
| Incident | Key Safety Protocols | Comparison/Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|
| 2014-2016 West African Ebola Outbreak | Limited access to appropriate PPE, inadequate training for healthcare workers | This highlighted the critical need for comprehensive training and the availability of sufficient PPE. |
| 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic | Rapid implementation of social distancing, mask mandates, and enhanced hygiene protocols | This demonstrated the effectiveness of community-wide measures and the need for rapid adaptation in response to emerging threats. |
| Past Flu Pandemics | Public health campaigns emphasizing hygiene, isolation, and vaccination | The importance of proactive public health measures to mitigate spread was apparent. |
Protective Gear Used and Their Levels of Protection
The type of protective gear used dictates the level of protection afforded to personnel. Different levels of protection are necessary depending on the potential risk level.
Turns out, the carnival passenger who handled Ebola samples was deemed low risk, which is good news. Thinking about all the amazing spa towns in the Czech Republic, like Karlovy Vary, definitely puts things in perspective. A healthy dose of relaxation in these thermal springs might be just the ticket for someone who handled potentially infectious samples. A little bit of peace and quiet, like you’d find in a healthy dose of Czech Republic spa towns , could be exactly what the doctor ordered for all involved.
Hopefully, the passenger is now feeling much better and ready to get back to their normal life.
| Protective Gear | Description | Level of Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Full-body protective suit | Provides comprehensive protection against bodily fluids and aerosols. | High |
| Gloves | Protects hands from contact with potentially contaminated materials. | Moderate to High |
| Face shields/masks | Protects the face and respiratory system from splashes and aerosols. | Moderate to High |
| Respirators | Filters airborne particles and prevents inhalation of pathogens. | High |
Cleaning and Disinfection of Potentially Contaminated Areas
Thorough cleaning and disinfection are essential to prevent the spread of contamination. These procedures must be carefully planned and executed to ensure efficacy.
- Cleaning Solutions: Specific, effective disinfectants are used to eliminate pathogens. These solutions are carefully selected to ensure they are effective against the specific pathogens involved.
- Procedure Steps: A standardized procedure for cleaning and disinfection is followed, ensuring complete coverage of potentially contaminated surfaces. This involves multiple steps, including cleaning, disinfection, and final validation.
- Waste Disposal: Proper waste disposal procedures are critical to prevent secondary contamination. Waste is carefully segregated and disposed of in designated containers to prevent further risk.
Public Health Measures
The handling of potentially infectious materials, like the Ebola samples in the recent Carnival passenger incident, necessitates a robust public health response. Swift and decisive action is critical to mitigating any risk of transmission, while maintaining public trust and confidence in health authorities. Transparency and clear communication are paramount during such events.Effective public health measures encompass a wide range of strategies, from immediate containment protocols to long-term prevention initiatives.
The goal is not just to control the immediate crisis but also to build resilience against future potential outbreaks. These measures aim to minimize the risk of infection spreading, while simultaneously ensuring public safety and well-being.
Implementing Containment Protocols
Immediate containment protocols were crucial in the incident. These protocols likely included rigorous isolation procedures for individuals who may have been exposed, contact tracing to identify and monitor potential secondary cases, and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers. These actions serve to limit the potential for further transmission. Adherence to established safety protocols is essential to prevent the spread of disease.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are indispensable in countering misinformation and fostering a sense of collective responsibility in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Clear and concise communication regarding the situation, alongside the risks and protective measures, is critical. These campaigns should target various demographics, employing multiple channels to ensure maximum reach and impact. For instance, social media campaigns can be combined with community meetings and local media outreach.
While a Carnival passenger handling Ebola samples was deemed low risk, it seems the entire Carnival experience is taking a turn for the worse. The recent news about the Carnival Cougar cruise being a one-and-done deal, as detailed in this article , suggests a broader issue with the company’s operations. Regardless, the low risk assessment for the passenger handling Ebola samples still stands, highlighting a potentially complex situation for the cruise line.
This strategy ensures diverse audiences receive the same accurate information.
Preventative Measures
These measures are critical for containing the spread of infection. The effectiveness of public health measures depends on the cooperation and participation of individuals and communities. Comprehensive strategies are needed to prevent the spread of infection and misinformation.
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation and Quarantine | Separating infected individuals to prevent further transmission. Monitoring those exposed to ensure early detection of potential cases. |
| Contact Tracing | Identifying individuals who have been in contact with infected persons to monitor their health and prevent further spread. |
| Vaccination | Administering appropriate vaccines to individuals at risk or the broader community, if available and recommended by health authorities. |
| Hygiene Practices | Encouraging frequent handwashing, use of hand sanitizers, and appropriate respiratory etiquette (covering coughs and sneezes). |
| Early Detection and Reporting | Promoting awareness of symptoms and encouraging reporting of suspected cases to health authorities. |
Community Engagement Strategies
Community engagement is essential for the success of public health measures. This includes educating communities about preventative measures, addressing their concerns, and empowering them to participate in disease control efforts. These initiatives promote active involvement and ownership of health outcomes. Trust-building measures between the community and health authorities are critical in preventing the spread of misinformation. Examples of these engagement strategies could include community meetings, town hall discussions, and the use of local community leaders to disseminate information.
Illustrative Case Studies
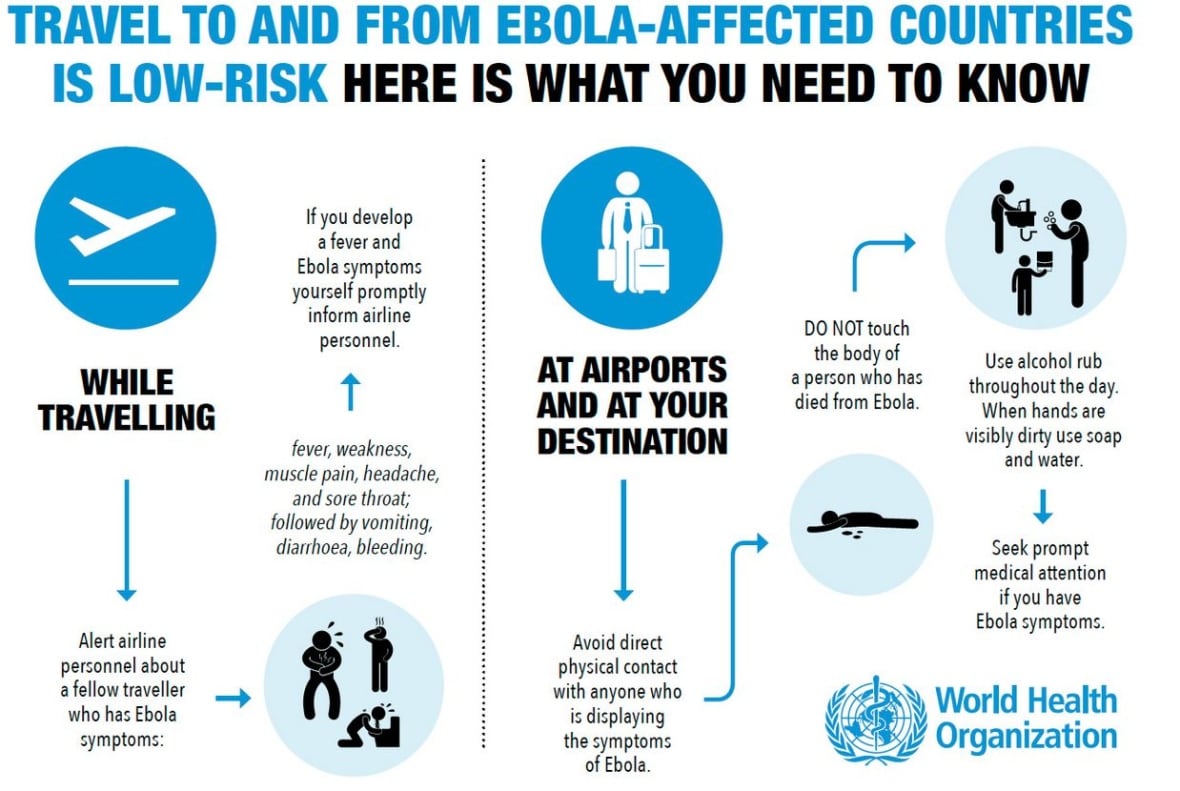
Carnival’s recent Ebola incident, while thankfully low-risk, highlights the critical importance of preparedness and rapid response protocols in handling potential infectious disease outbreaks at large public events. Understanding how similar situations have been managed in the past can provide valuable insights and lessons learned, allowing us to better anticipate and mitigate future risks. This section explores illustrative case studies, analyzing the factors contributing to low-risk assessments and emphasizing the need for robust safety procedures.
Similar Situations at Public Events
Public events, encompassing everything from festivals to sporting events, often attract large crowds, increasing the potential for infectious disease transmission. Historical examples demonstrate that meticulous planning and swift response are crucial for containing any potential outbreaks. These incidents highlight the importance of a proactive approach, from initial risk assessment to ongoing monitoring and containment strategies.
Factors Contributing to Low-Risk Assessments
Several factors often contribute to a low-risk assessment in cases involving the handling of infectious diseases at public events. These include the pre-event risk assessment, which involves detailed evaluation of the situation and the implementation of stringent safety protocols, and the rigorous monitoring and reporting systems in place during the event.
Rapid Response and Preparedness
Rapid response and preparedness are crucial in mitigating potential outbreaks. A well-defined and practiced incident response plan, coupled with the availability of trained personnel and adequate resources, significantly enhances the ability to contain the situation. Early detection, isolation, and appropriate medical interventions are critical components of a successful rapid response strategy.
Steps Involved in Handling Such Incidents
Effective handling of such incidents requires a multi-faceted approach, involving several key steps. These steps typically begin with a pre-event risk assessment, followed by a detailed incident response plan, including communication protocols, and the establishment of a dedicated command center.
Example: The 2009 H1N1 Influenza Pandemic
The 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic underscored the importance of rapid response and preparedness. Public health authorities implemented widespread surveillance and public awareness campaigns, advising preventive measures such as handwashing and vaccination. This proactive approach, along with robust contact tracing, played a vital role in managing the spread of the virus at public events. The experience highlighted the critical need for coordinated efforts between public health agencies and event organizers.
Example: Outbreaks at Sporting Events
Sporting events, due to their large attendance and close proximity, present unique challenges in managing infectious diseases. For example, outbreaks of respiratory illnesses at major sporting events have prompted investigations into ventilation systems and crowd management strategies. These investigations often led to adjustments in protocols, demonstrating the iterative nature of public health measures in managing such situations.
Risk Assessment Methodology Details
Risk assessment methodology involves a systematic evaluation of potential hazards and their likelihood of occurrence. This includes the identification of potential infectious agents, the estimation of exposure risk based on event parameters, and the development of appropriate control measures. A thorough risk assessment, based on epidemiological data and historical precedent, is a critical first step in mitigating potential threats.
A detailed analysis of the specific event, including participant demographics, location, and environmental factors, is essential. For instance, a major outdoor event in a densely populated area might require different mitigation strategies compared to a smaller event in a rural setting.
Public Health Measures in Practice
Public health measures are vital in preventing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases. This includes stringent hygiene practices, like promoting frequent handwashing, and implementing measures to ensure adequate ventilation and sanitation. These measures, along with contact tracing and isolation protocols, can effectively curb the spread of infectious agents. Thorough education of event participants about the importance of these measures is also essential.
This often involves clear communication channels and easily understood guidelines.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
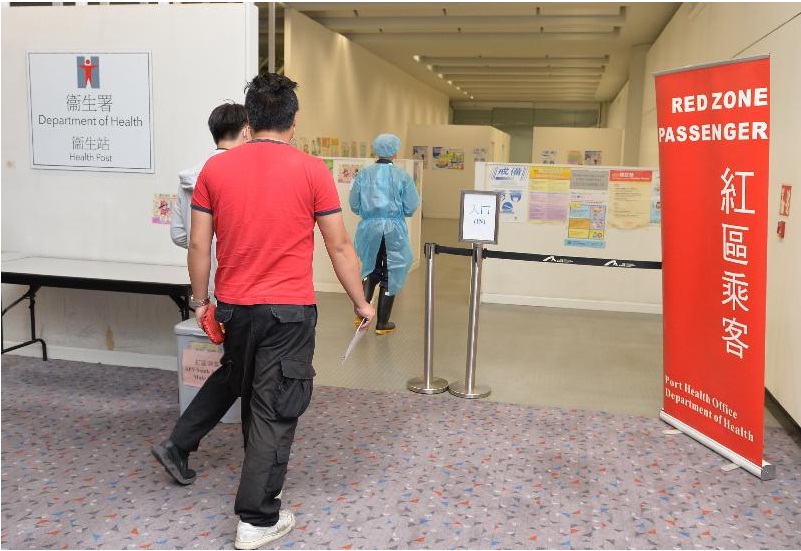

The recent Ebola scare aboard a cruise ship highlights the need for robust risk mitigation strategies in public gatherings. Effective planning and proactive measures are crucial to preventing and managing potential outbreaks, ensuring the safety and well-being of all participants. This requires a multifaceted approach that addresses pre-event assessments, enhanced safety protocols, and clear communication plans.Careful planning and proactive risk assessment are essential to minimizing the chances of disease transmission in crowded environments like cruise ships and large public events.
Effective risk mitigation goes beyond simply reacting to a crisis; it involves anticipating potential issues and implementing preventative measures. By identifying vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards, we can significantly reduce the risk of future incidents.
Pre-Event Risk Assessments
Pre-event risk assessments are critical for identifying potential health hazards and implementing preventative measures. These assessments should encompass factors such as the nature of the event, the anticipated attendance, and the potential for exposure to infectious agents. Comprehensive assessments should consider the possibility of infectious disease outbreaks, potential environmental risks, and any other health concerns that might arise.These assessments should consider the specific risks posed by the event location, such as proximity to known disease hotspots or areas with compromised sanitation.
They should also analyze the potential for disease transmission based on the type of event, such as crowded indoor spaces or outdoor gatherings with limited access to hygiene facilities. Furthermore, they should account for any underlying health conditions within the expected attendee population. Historical data on similar events can provide valuable insights for developing and refining risk assessment methodologies.
For example, analyzing data from past events with similar attendee demographics can help predict potential health concerns.
Enhanced Safety Measures at Public Gatherings
Implementing enhanced safety measures at public gatherings is paramount to mitigating risks. These measures should focus on maintaining hygiene standards, providing adequate medical facilities, and establishing clear protocols for potential exposure incidents.
- Improved Hygiene Practices: Public gatherings should have readily available hand sanitizer stations, and promote frequent handwashing. Providing hand sanitizers and encouraging their use at strategic locations throughout the event is vital. Additionally, regular cleaning and disinfection of high-touch surfaces like restrooms and common areas are crucial.
- Enhanced Medical Facilities: Having readily available medical personnel and facilities at public gatherings is essential. This includes providing trained medical personnel who can respond to potential health emergencies and provide first aid. Medical facilities should have the necessary equipment and supplies to manage potential exposure incidents.
- Clear Exposure Protocols: Establishing clear protocols for handling potential exposure incidents is crucial. This includes procedures for reporting suspected cases, isolating individuals, and contacting public health authorities. These protocols should be communicated clearly to all participants and staff involved.
Procedures for Handling Potential Exposure Incidents
A well-defined flowchart outlining the procedures for handling potential exposure incidents is critical. This flowchart should detail the steps to be taken by all stakeholders, from event organizers to medical personnel, in case of a suspected exposure incident.
| Step | Action | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suspected exposure reported | Event attendee or staff |
| 2 | Immediate isolation of suspected case | Event staff, medical personnel |
| 3 | Contact tracing and identification of potential contacts | Public health authorities |
| 4 | Notification of public health authorities | Event staff, medical personnel |
| 5 | Medical evaluation and treatment | Medical personnel |
| 6 | Public health investigation and response | Public health authorities |
These procedures are crucial for limiting the spread of the disease and minimizing the risk to public health. Clear communication and adherence to protocols are vital in managing any potential exposure incident effectively.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the carnival passenger incident, while concerning, underscores the critical importance of meticulous risk assessment, clear communication, and robust safety protocols during potential infectious disease outbreaks in public settings. The incident highlights how a coordinated response, scientific analysis, and effective public communication can successfully manage such events, minimizing public anxieties and ensuring public safety. The detailed protocols and procedures employed illustrate the proactive measures in place to mitigate risks.
Question Bank
What were the specific procedures followed by health officials to assess the risk?
Health officials followed a standardized protocol involving contact tracing, sample analysis, and risk modeling to determine the passenger’s exposure level and assess the risk of transmission. This included identifying and monitoring potential contacts, laboratory analysis of the samples, and evaluating the potential for transmission based on the specific circumstances.
How did public health officials communicate the passenger’s low-risk status to the public?
Public health officials utilized multiple channels, including press releases, social media, and community meetings, to disseminate clear and accurate information about the passenger’s low-risk status. The communication strategy aimed to address public concerns, dispel misinformation, and ensure transparency.
What are some preventative measures that can be taken to mitigate the risk of Ebola transmission in similar events in the future?
Future preventative measures include enhanced pre-event risk assessments, strict adherence to safety protocols, clear communication strategies, and continuous monitoring of potential exposure incidents. This includes protocols for handling potentially infectious materials, and protocols for cleaning and disinfection of potentially contaminated areas.






