Mexicos Wine Capital Unveiling the Best
Capital of mexican wine – Mexico’s Wine Capital: Unveiling the Best. Mexico’s burgeoning wine industry is a fascinating tapestry woven with history, terroir, and tradition. This journey delves into the heart of Mexican wine, exploring the factors that shape its character and potential. We’ll investigate the regions, the grapes, the cultural significance, and the exciting future of this remarkable beverage.
From the sun-drenched vineyards to the bustling wine festivals, we’ll uncover the region that truly deserves the title of Mexico’s wine capital. We’ll consider not just production volume, but also the quality, the experience, and the cultural impact. This investigation will leave you with a deeper understanding of the heart and soul of Mexican wine.
Introduction to Mexican Wine
Mexico’s wine industry, though smaller than its counterparts in Europe or South America, boasts a rich history and a growing reputation. From the rugged vineyards of Baja California to the fertile valleys of the central highlands, Mexican winemakers are crafting unique and flavorful expressions. This burgeoning industry reflects a dedication to quality and a passion for cultivating excellence within a diverse landscape.The history of winemaking in Mexico stretches back to the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors.
While Mexico City might be the cultural capital, the true heart of Mexican wine production lies elsewhere. Think of the relationships between winemakers and distributors, or even farmers and vineyards, as “allies but not pals” – sometimes collaborating, sometimes competing. This complex dynamic definitely shapes the landscape of Mexican wine, a landscape that’s still evolving and worth exploring.
Early vineyards were established in the colonial era, primarily in the cooler mountainous regions, and focused on producing wines for local consumption and religious ceremonies. Over time, the industry experienced periods of decline and resurgence, reflecting the country’s broader economic and social shifts. Modern Mexican winemaking, however, is characterized by a renewed emphasis on quality and innovation, resulting in wines that increasingly command international attention.
Major Wine-Producing Regions
Mexican wine production is concentrated in several key regions, each with its own unique terroir. These regions exhibit variations in climate, soil composition, and grape varieties, leading to diverse and distinctive wine styles. The specific conditions within each region shape the character of the wines, creating a tapestry of flavors and aromas that reflect the country’s rich agricultural heritage.
- Baja California: Known for its Mediterranean climate, Baja California produces a significant portion of Mexico’s wine. The region’s warm days and cool nights, coupled with well-drained soils, create ideal conditions for various grape varieties, particularly those with high acidity. The vineyards here are often situated along the coast, offering a distinct microclimate influenced by the Pacific Ocean.
- Central Highlands: High altitudes and cooler temperatures in the central highlands offer a different terroir. The mountainous terrain and volcanic soils contribute to a more complex wine profile. These regions are known for producing wines with a focus on structure and elegance, often showcasing the full potential of specific grape varieties.
- Michoacán: This region boasts a rich agricultural history, and wine production has a long tradition. The climate in Michoacán, influenced by the surrounding mountains and valleys, contributes to a unique character in the wines. This region’s vineyards benefit from a distinct microclimate, offering a chance to experiment with unique varietals and vintages.
Common Grape Varieties
Mexico’s winemakers utilize a range of grape varieties, both indigenous and internationally recognized. The choice of grape depends on the specific region and the desired wine style. Careful selection and cultivation are crucial in achieving the best possible results. The grape varieties themselves play a crucial role in shaping the final product.
While the capital of Mexican wine might surprise some, it’s actually a region known for its vibrant vineyards. With blue sky tours predicting sunny days in its 30th year , it’s the perfect time to explore the wineries and savor the delicious local varietals. After all, a beautiful backdrop to a great wine tasting experience is key to any good trip.
- Cabernet Sauvignon: A popular choice, known for its full-bodied structure and often showing characteristics of black fruit and cedar.
- Merlot: Often complements Cabernet Sauvignon in blends, offering a softer structure and fruity flavors.
- Tempranillo: A grape variety known for its rich tannins and dark fruit profiles, often producing wines with a structured and elegant character.
- Malbec: This variety is well-suited to certain Mexican regions, exhibiting a range of flavors from black fruit to earthy notes.
- Zinfandel: A popular variety that thrives in warmer climates, producing wines with vibrant flavors and often showcasing a significant alcohol content.
Comparative Analysis of Mexican Wine Regions
The following table provides a concise comparison of Mexican wine regions, highlighting key factors that influence wine production. Differences in climate, soil composition, and grape varieties contribute to the unique characteristics of wines from each region.
| Region | Climate | Soil | Grape Varieties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baja California | Mediterranean, warm days, cool nights | Well-drained, often sandy | Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc |
| Central Highlands | Cooler temperatures, mountainous | Volcanic, varied | Cabernet Franc, Tempranillo, Pinot Noir |
| Michoacán | Influenced by mountains and valleys | Varied, often fertile | Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Syrah |
Identifying the Capital of Mexican Wine
Declaring a single “capital” of Mexican wine is tricky, as the country boasts diverse and excellent wine regions. Instead of a single epicenter, Mexico’s wine scene thrives on the contributions of various areas, each with its unique terroir and winemaking traditions. The quality and volume of production vary significantly across the regions, making a simple designation challenging. Instead, a comprehensive understanding of the leading regions and their characteristics is more informative.Identifying the most important wine region hinges on a combination of factors.
Production volume, the quality of the wines produced, and the economic significance of the industry within a specific region are key indicators. This multifaceted approach allows for a nuanced appreciation of Mexico’s wine landscape.
Criteria for Determining the “Capital”, Capital of mexican wine
Several factors contribute to a region’s prominence in the Mexican wine industry. Production volume, measured in tons of grapes or bottles produced annually, is a crucial metric. However, quality is equally important, as a high volume of mediocre wine does not necessarily equate to a strong wine region. The reputation of wines from a particular region, often built on critical acclaim and consumer preference, is also a significant factor.
Finally, the economic impact of the wine industry on the region, including job creation and overall economic growth, provides valuable context.
While the capital of Mexican wine might surprise some, it’s actually the city of Aguascalientes. But if you’re looking for an adventurous trip, consider checking out aqua expeditions to operate Mekong cruises , offering incredible river experiences. Regardless of your travel style, Aguascalientes remains a fantastic destination for wine lovers.
Leading Wine Regions
Mexico’s wine regions display considerable variation in their wine production and quality. Baja California, located in northwestern Mexico, is renowned for its cooler climate and high-quality Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay. Other significant regions include Valle de Guadalupe, known for its dramatic vineyards and international-quality wines. The state of Jalisco also produces notable wines, while the regions of Guanajuato and Aguascalientes contribute to the country’s wine production.
Quality and Reputation Comparisons
The quality of wines varies considerably across Mexican regions. Baja California, with its established vineyards and cooler climate, often produces wines with higher acidity and complexity. The wines from Valle de Guadalupe, while known for their quality, may differ in style and flavor profiles, owing to the variations in soil and grape varieties. Similarly, other regions have their own distinctive qualities, impacting the overall reputation of the wines produced there.
Further investigation into specific vineyards and winemakers within each region provides a more granular view of the quality and reputation of Mexican wines.
Economic Significance of the Wine Industry
The wine industry plays a crucial role in the economies of various regions. In Baja California, for example, the wine industry provides employment opportunities, boosts tourism, and contributes significantly to the local economy. Similarly, the Valle de Guadalupe, with its numerous wineries and related businesses, exemplifies the economic importance of the wine industry. The economic impact extends beyond direct employment, as it fuels supporting industries, like restaurants, lodging, and related services.
Top 5 Wine Regions and Their Characteristics
| Region | State | Key Characteristics | Production Volume (Approximate) | Wine Quality Reputation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valle de Guadalupe | Baja California | Dramatic landscapes, international-quality wines, Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay | High | High |
| Baja California | Baja California | Established vineyards, cooler climate, higher acidity, Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay | High | High |
| Jalisco | Jalisco | Varied terroirs, distinctive styles, potential for growth | Medium | Moderate to High |
| Guanajuato | Guanajuato | Unique terroir, experimentation with diverse varietals | Low | Moderate |
| Aguascalientes | Aguascalientes | Emerging region, potential for growth | Low | Low |
Note: Production volume is a rough estimate and can vary significantly based on year and vineyard yields. Quality reputation is a subjective evaluation based on critical reviews, awards, and consumer feedback.
Factors Influencing the “Capital” Designation: Capital Of Mexican Wine
Declaring a “capital” of Mexican wine is a complex endeavor, not simply a matter of volume or price. The designation is deeply intertwined with the region’s unique character, offering a compelling experience for wine enthusiasts. This “capital” status reflects a convergence of factors, including the quality of wineries, the appeal to tourists, and the overall infrastructure dedicated to supporting wine appreciation.
While the capital of Mexican wine might surprise some, it’s actually a fascinating debate, with experts arguing for different regions. Considering the recent news of an analyst predicting caution in credit card use ( analyst predicting caution in credit card use ), it might be wise to approach wine purchases with a similar level of careful consideration. Ultimately, the best Mexican wines are still out there, just maybe a bit more thought needs to go into the journey of finding them.
The region’s vibrancy as a wine destination is further enhanced by engaging festivals and exceptional tasting experiences.Beyond the basic production of fine wines, a true “capital” of Mexican wine must offer a rich experience that encompasses tourism, accessibility, and a sense of place. This necessitates a thriving wine scene supported by both the industry and the local community, making it a destination that transcends the simple consumption of wine and becomes a part of the cultural tapestry.
Role of Tourism and Wine Tourism
The success of a wine region as a “capital” is heavily influenced by its appeal to tourists. Regions that actively promote wine tourism, offering structured tours, immersive experiences, and well-marked routes for wine lovers, often attract a broader audience. This includes showcasing the history and culture of the region alongside the wine production process. Such initiatives not only benefit the local economy but also contribute to the region’s overall reputation as a must-visit destination for wine enthusiasts.
For instance, regions with well-established wine trails and designated routes for wine tasting attract more tourists, who, in turn, contribute significantly to the local economy.
Availability of High-Quality Wineries and Vineyards
A critical factor in the “capital” designation is the quality and quantity of wineries and vineyards. The presence of numerous renowned wineries, producing exceptional wines with unique characteristics and recognized quality, elevates the region’s reputation. A concentration of top-tier producers demonstrates a strong winemaking tradition and a commitment to excellence, drawing in both local and international consumers. The sheer number of high-quality wineries within a specific region significantly impacts its status as a wine “capital”.
Presence of Wine Festivals and Events
Wine festivals and events are vital for establishing a region as a “capital”. These events provide a platform for showcasing local wines, hosting renowned winemakers, and attracting both local and international visitors. The frequency and quality of such events, coupled with their promotion and accessibility, significantly contribute to the region’s image as a vibrant wine destination. Events that bring together wine enthusiasts, sommeliers, and winemakers create a dynamic atmosphere, promoting the region as a hub for wine culture.
Accessibility and Infrastructure for Wine Lovers
The accessibility and infrastructure available to wine lovers are crucial. Well-maintained roads, convenient transportation options, and readily available accommodation contribute to a smooth and enjoyable experience. The presence of dedicated wine shops, tasting rooms, and restaurants catering to wine lovers further enhances the region’s appeal. Easy access and adequate infrastructure are essential for a region to be recognized as a wine “capital” for its accessibility.
Quality of Wine-Tasting Experiences
The quality of wine-tasting experiences is a significant indicator of a region’s standing as a wine “capital”. This includes well-designed tasting rooms, knowledgeable staff, and a variety of wines available for tasting. High-quality wine-tasting experiences, offering insights into the wines and the region’s history, contribute to a memorable and enjoyable experience for visitors. These factors collectively establish the region as a desirable destination for wine connoisseurs.
Accessibility Comparison of Regions
| Region | Accessibility (Ease of Tourist Arrival) | Infrastructure (Wine Tourism Facilities) | Quality of Wineries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region A | High (Excellent transportation, well-connected) | High (Well-established trails, numerous tasting rooms) | Medium (Good quality, but not the highest) |
| Region B | Medium (Good transportation, but some limitations) | Medium (Adequate facilities, but fewer choices) | High (Many renowned wineries, highly recognized) |
| Region C | Low (Limited transportation options, less developed) | Low (Few tasting rooms, underdeveloped infrastructure) | Medium (Varied quality, but some excellent wineries) |
This table illustrates the varying degrees of accessibility and infrastructure among different regions. While Region A scores high in both accessibility and infrastructure, Region B stands out for the quality of its wineries. Region C, despite potentially having excellent wineries, faces challenges in attracting tourists due to limited accessibility and infrastructure.
Cultural Significance of Mexican Wine

Mexican wine, while perhaps not as globally recognized as wines from other regions, holds a significant place in Mexican culture. It’s more than just a beverage; it’s woven into the fabric of celebrations, meals, and traditions, reflecting the country’s diverse heritage and culinary richness. From the vineyards of Baja California to the bustling markets of Mexico City, wine plays a vital role in daily life and national identity.Mexican wine has a deep-rooted history, intertwined with the country’s agricultural and cultural development.
The cultivation of grapes and the production of wine have evolved over centuries, shaping social customs and creating a rich tapestry of experiences. Its presence at family gatherings, festive occasions, and special meals highlights the importance of sharing and celebrating life’s moments.
Role of Mexican Wine in Local Culture
Mexican wine plays a crucial role in local culture, particularly during celebrations and special occasions. It’s a staple at weddings, baptisms, graduations, and other family gatherings. The act of sharing a bottle of wine with loved ones often symbolizes unity, friendship, and the celebration of life’s milestones. Furthermore, Mexican wines are increasingly recognized for their quality and are featured in fine dining establishments and upscale events.
Wine Pairings with Local Cuisine
Mexican cuisine is known for its vibrant flavors and diverse ingredients. Wine pairings with Mexican dishes are as varied as the cuisine itself. The use of fresh herbs, spices, and bold flavors in Mexican dishes often requires wines that can stand up to these tastes.
- Traditional Mexican dishes like mole poblano, featuring rich chocolate and chili notes, often benefit from full-bodied red wines with some fruitiness, such as a Cabernet Sauvignon or a Tempranillo. These wines can complement the complex layers of flavor without overpowering them.
- For dishes with citrus flavors, like ceviche or some seafood preparations, a crisp white wine like Sauvignon Blanc or a light-bodied rosé can enhance the freshness and acidity.
- Tacos with various fillings can pair well with both red and white wines, depending on the specific ingredients. A light-bodied red like a Pinot Noir or a medium-bodied white like a Chardonnay can offer a delightful balance.
Historical Connections Between Wine and Mexican Traditions
The history of wine in Mexico dates back to the Spanish colonization. The introduction of European grape varieties and winemaking techniques transformed the local landscape and culture. The blending of indigenous ingredients and techniques with the Spanish traditions of winemaking has led to a unique Mexican wine style. For example, the introduction of specific grape varietals, like Cabernet Sauvignon, has created a distinctive signature to Mexican wine.
Social Aspects of Wine Consumption in Mexico
Wine consumption in Mexico is deeply rooted in social interactions. Sharing a bottle of wine, especially during gatherings and celebrations, strengthens bonds and fosters camaraderie. The ritual of opening a bottle, pouring it, and raising a glass often carries symbolic meaning, creating a special moment that enhances the experience. Wine is often an integral part of social events, where people gather to celebrate and enjoy each other’s company.
Cultural Impact of Mexican Wine on National Identity
Mexican wine plays a significant role in shaping the country’s national identity. The wine industry, particularly in areas like Baja California, has contributed significantly to the local economy, providing employment and economic growth. The production and appreciation of Mexican wines reflect the country’s agricultural heritage and dedication to quality. The evolution of the wine industry, from its historical roots to its contemporary status, contributes to a sense of national pride and cultural continuity.
Traditional Mexican Cuisine Pairings with Specific Wine Types
| Dish | Wine Type | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Mole Poblano | Cabernet Sauvignon or Tempranillo | The rich flavors and spices of mole poblano complement the full body and fruitiness of these red wines. |
| Ceviche | Sauvignon Blanc or Rosé | The freshness and acidity of these white wines enhance the citrus and seafood flavors of ceviche. |
| Tacos al Pastor | Pinot Noir or Chardonnay | The balanced flavors of tacos al pastor, with its combination of spices and meat, are well-suited to the moderate body of these wines. |
| Pozole | Pinot Noir or Tempranillo | The hearty flavors of pozole, often with pork and hominy, pair well with the earthy tones of these wines. |
Future of Mexican Wine

The Mexican wine industry is poised for significant growth, fueled by increasing domestic demand, evolving consumer preferences, and a burgeoning interest in wine tourism. This burgeoning sector presents both exciting opportunities and noteworthy challenges. The future hinges on addressing these challenges while capitalizing on the unique potential of Mexican terroirs and innovative approaches to production.The industry’s trajectory is complex, shaped by factors ranging from the adoption of sustainable practices to the internationalization of Mexican wines.
While the capital of Mexican wine might surprise some, it’s actually a fascinating topic! Thinking about the rich history and production of Mexican wine, it’s interesting to note that the recent opening of a second Alamo location in Waikiki, Hawaii, alamo opens second waikiki location , provides a great contrast. It highlights the diverse experiences of wine regions around the world, and reminds us that the capital of Mexican wine is a region steeped in unique terroir and traditions.
The success of Mexican wineries in the years to come will depend on their ability to adapt to these changing circumstances and navigate the intricacies of the global wine market.
Potential for Growth in the Mexican Wine Industry
The burgeoning interest in Mexican wines, particularly in the domestic market, creates a significant opportunity for expansion. As Mexican consumers become more sophisticated and explore diverse palates, demand for high-quality, indigenous wines is likely to increase. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of wine tourism presents an additional avenue for growth.
Emerging Trends in Mexican Wine Production
Mexican winemakers are embracing innovative approaches to production, including the exploration of indigenous grape varietals and the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices. These initiatives are enhancing the quality and appeal of Mexican wines, attracting both local and international attention. The growing focus on terroir and meticulous winemaking techniques further underscores the rising standards in the industry.
Projections for the Future of Wine Tourism in Mexico
Wine tourism is projected to flourish in Mexico, with wineries offering visitors opportunities to explore vineyards, attend wine tastings, and immerse themselves in the local culture. The development of wine routes and the integration of wineries into the wider tourism landscape are key elements in this growth. The potential for connecting wine experiences with cultural attractions and historical sites in Mexico offers a compelling draw.
Challenges Facing the Mexican Wine Industry
Despite the promising outlook, the Mexican wine industry faces challenges. Competition from established wine-producing regions remains a key factor. Moreover, establishing a strong international presence and navigating complex export regulations can be formidable obstacles. The development of a robust infrastructure to support the industry’s growth is also crucial.
Potential Opportunities for Mexican Wine to Expand Internationally
Mexico possesses unique terroirs and grape varietals that could appeal to international markets. Strategic marketing campaigns targeting specific consumer segments and emphasizing the authenticity and distinctiveness of Mexican wines are crucial. Furthermore, collaborations with international wine importers and distributors could help Mexican wineries gain a wider reach and recognition.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Mexican Wine Exports
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Complex export regulations and bureaucratic hurdles | Strategic partnerships with international distributors and importers |
| Limited brand recognition and awareness in international markets | Highlighting unique grape varietals and terroir |
| Competition from established wine-producing regions | Developing targeted marketing campaigns for specific consumer segments |
| Maintaining quality control and consistency across production | Utilizing sustainable agricultural practices and ethical sourcing |
| Difficulties in securing reliable transportation and logistics | Building strong relationships with international wine buyers and importers |
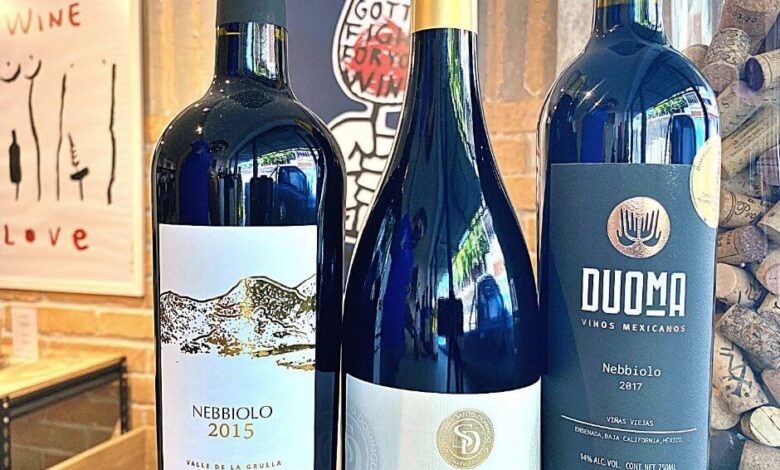
Visual Representation (Illustrations/Images)
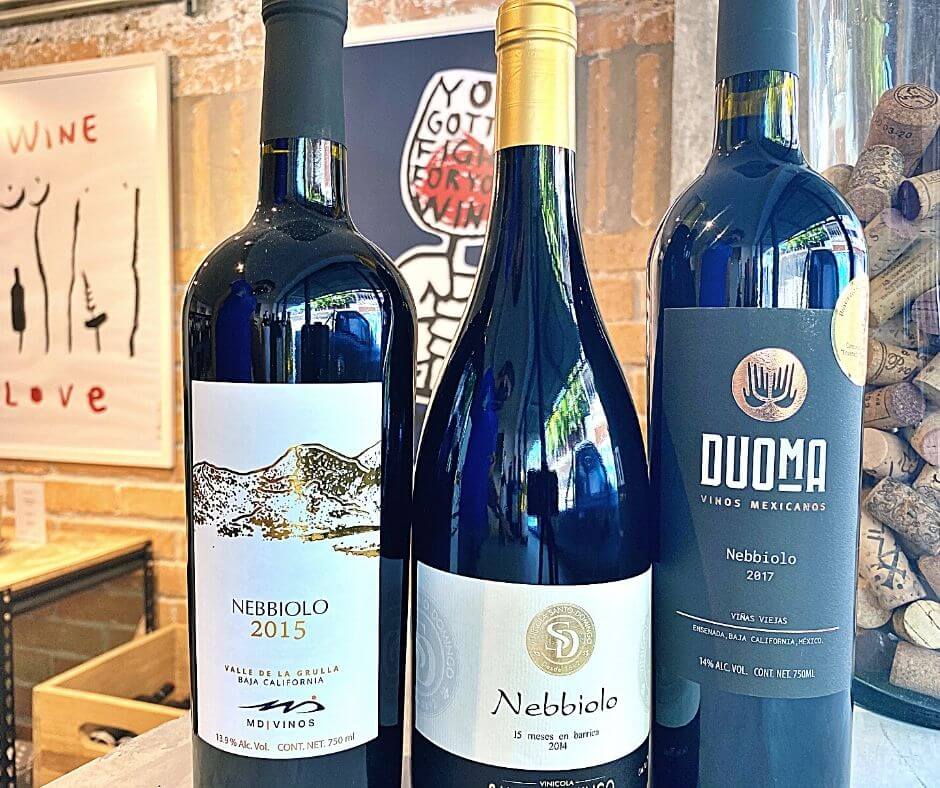

Mexican wine, with its rich history and diverse terroir, deserves a visual representation that captures its essence. From the sun-drenched vineyards to the elegant bottle designs, imagery plays a crucial role in conveying the unique character of Mexican wines. Visuals can evoke emotions, tell stories, and help consumers connect with the product on a deeper level. This section will explore the various visual elements that showcase Mexican wine’s charm.
Vineyards and Wineries
Images of Mexican vineyards should depict the stunning landscapes where these grapes mature. Pictures of rolling hills, covered in emerald vines stretching towards a vibrant sky, are crucial to highlighting the beauty of the terroir. Ideally, these images would include details of traditional farming techniques, such as the meticulous pruning of vines or the careful harvesting process, emphasizing the dedication and skill involved in crafting Mexican wines.
They should showcase the unique characteristics of different regions, like the arid landscapes of Baja California or the fertile valleys of the Sierra Madre Occidental. For instance, a picture of a winery nestled in a mountainous region could suggest the cooler climate and elevation influence on the wine’s profile.
Wine Labels
Mexican wine labels are often a reflection of the country’s vibrant culture and artistic expression. The imagery on these labels should be meticulously crafted to represent the wine’s origin, varietal, and style. For example, a label featuring a stylized depiction of a vineyard or a local landmark can instantly connect the consumer with the region’s identity. The use of vibrant colors and symbolic imagery, such as agave plants or traditional Mexican art motifs, can further enhance the visual appeal and tell a story about the wine’s heritage.
Sophisticated typography and artistic elements add to the label’s overall aesthetic.
Regional Characteristics in Imagery
The visual representation of Mexican wine regions should emphasize the diversity of its landscapes and climates. For example, images of Baja California’s vineyards could showcase the arid desert environment, emphasizing the adaptation of vines to harsh conditions. Conversely, images of vineyards in the cooler mountainous regions of the Sierra Madre could highlight the altitude and the impact on the grape’s characteristics.
The use of appropriate color palettes and textures can convey the distinct personality of each region, helping consumers understand the nuances of the wines produced there.
Wine Festivals and Events
Images of Mexican wine festivals and events should capture the lively atmosphere and cultural celebration. Pictures of vibrant crowds, colorful decorations, and traditional music performances can evoke a sense of community and festivity. These visuals can also showcase the importance of wine as a social and cultural element in Mexican society. Images of people enjoying wine tasting sessions or interacting with winemakers further enhance the festival’s atmosphere and the wine’s accessibility.
Wine Bottle Types
| Bottle Type | Description | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Bordeaux | Classic, elegant shape with a slight taper | Often used for premium red wines, showcasing their refined character |
| Traditional Burgundy | Tall, slender bottle | Common for delicate white wines, highlighting their finesse |
| Rivesaltes | Large-bodied bottle with a wider shoulder | Ideal for robust red wines, emphasizing their full-bodied nature |
| Other/Unique | Specific regional or varietal bottles | Showcasing regional or varietal characteristics |
This table illustrates the variety of bottle shapes used in Mexico. Each type carries its own visual identity and suggests specific qualities of the wine inside. The selection of the appropriate bottle shape is an important aspect of the wine’s presentation. Different bottle types can reflect different styles of Mexican wine, such as the traditional elegance of a Bordeaux-style bottle for premium red wines or the distinctive shape of a Rivesaltes bottle for robust reds.
Closure
In conclusion, while definitively naming a single “capital” of Mexican wine is complex, this exploration reveals the incredible diversity and potential within the country’s wine regions. The vibrancy of the industry, from its historical roots to its modern innovations, is truly inspiring. We’ve uncovered the key factors that contribute to a region’s claim to the title, highlighting the role of tourism, quality wineries, festivals, and accessibility.
Ultimately, the “capital” of Mexican wine is not a single point but rather a vibrant, evolving landscape waiting to be discovered.
General Inquiries
What are some of the most important grapes used in Mexican winemaking?
Mexico utilizes a diverse range of grapes, including Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Chardonnay, and Tempranillo. However, the specific varieties and their prominence vary significantly from region to region, reflecting the diverse terroir.
How does the Mexican wine industry compare to other countries?
Mexico’s wine industry is still developing, but it’s showing remarkable growth. While it doesn’t yet match the established giants, Mexican wines are gaining recognition for their unique character and quality.
What are some common pairings for Mexican wines?
Mexican cuisine is renowned for its diverse flavors. Traditional pairings often involve the boldness of Mexican meats with the richness of red wines. For lighter fare, white wines provide a delightful complement. We’ll explore specific pairings in a later section.
What are the biggest challenges facing Mexican wine?
One significant challenge is competing in the global market with well-established wine regions. Another is navigating the complexities of regulations and international trade.