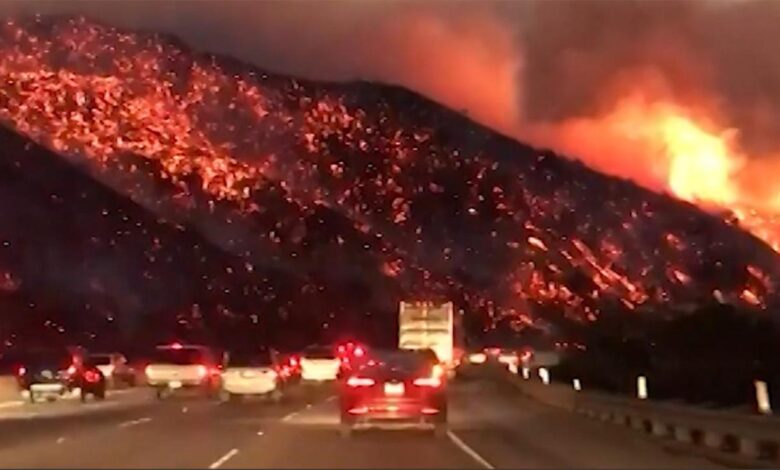
California Destinations Inform Where Fires Burn
California destinations inform where fires burn, revealing crucial insights into the interplay of geography, history, climate change, human activity, and wildfire response strategies. Understanding these factors is essential for mitigating future risks and ensuring community preparedness.
This exploration delves into the complex relationship between California’s diverse landscapes, past fire patterns, and the escalating impact of climate change on fire risk. We’ll examine specific destinations like Yosemite and Malibu, analyzing their unique characteristics and historical fire trends. The discussion will also cover human factors, such as the role of campfires and power lines in igniting fires, and the crucial mitigation strategies employed by authorities and communities.
Geographic Factors Influencing Fire Patterns
California’s breathtaking landscapes, a tapestry of mountains, valleys, and coastlines, are unfortunately vulnerable to devastating wildfires. Understanding the intricate interplay of geography and vegetation is crucial to comprehending the fire patterns that plague the state. These factors, from the steep slopes of the Sierra Nevada to the dry chaparral of Southern California, significantly influence fire behavior, intensity, and risk.California’s diverse geography plays a pivotal role in shaping fire patterns.
The state’s topography, characterized by towering mountain ranges, deep valleys, and a dramatic coastline, creates unique microclimates and fuel conditions. These variations are critical factors in determining the intensity and spread of wildfires.
California’s Topography and Vegetation
California’s topography, encompassing diverse elevations and slopes, profoundly impacts fire behavior. The state’s mountain ranges, such as the Sierra Nevada and the Coast Ranges, often create steep slopes that facilitate rapid fire spread. High elevations, with their specific vegetation types and drier conditions, contribute to fire intensity and longevity. Conversely, valleys can trap smoke and create conditions for intense fire activity.
California’s diverse landscapes, from the dry chaparral to the forested mountains, significantly influence where wildfires ignite. It’s fascinating how the geography plays a role. Similar to how certain destinations in California dictate fire patterns, exploring the Rhine River with Disney offers ample activities, like ample activities rhine cruise with disney , that can be just as captivating and offer a different kind of beauty.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between location and fire risk is crucial for effective fire prevention in California.
Influence of Vegetation Types
California’s vegetation is a crucial factor in determining fire patterns. Different regions exhibit varying vegetation types, which directly affect fire spread and intensity. Chaparral, a dense, low-lying shrubland prevalent in Southern California, is highly flammable, creating a readily ignitable landscape. Forests, particularly in the Sierra Nevada, provide abundant fuel, contributing to large and intense wildfires. Coastal areas, with their unique mix of vegetation, also present specific fire challenges.
Proximity to Urban Areas
The proximity of urban areas to fire-prone regions directly impacts fire risk and response. The presence of homes and infrastructure in areas susceptible to wildfires necessitates proactive fire prevention measures and robust emergency response strategies. Planning for evacuation routes and community preparedness are essential elements in minimizing the impact of wildfires on populated areas. For instance, the 2018 Camp Fire, which ravaged Paradise, California, highlighted the devastating consequences of proximity between urban areas and fire-prone forests.
Correlation Between Regions and Fire Patterns
| Region | Vegetation | Topography | Typical Fire Season | Fire Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern California | Chaparral, grasslands | Rolling hills, steep slopes, coastal areas | Fall, spring | High |
| Sierra Nevada | Coniferous forests, mixed vegetation | High mountains, steep slopes | Summer, fall | Very high |
| Central Valley | Grasslands, agricultural fields | Flat terrain, occasional hills | Summer, fall | Moderate |
| Coastal Areas | Mixed vegetation, chaparral, redwood forests | Coastal mountains, valleys, flat plains | Fall, spring | Moderate to high |
The table above demonstrates a correlation between specific regions and their typical fire patterns, illustrating how geographic features contribute to fire risk and behavior. The interplay of vegetation, topography, and proximity to urban areas shapes the fire dynamics in each region, creating distinct fire challenges.
Historical Fire Trends in California Destinations
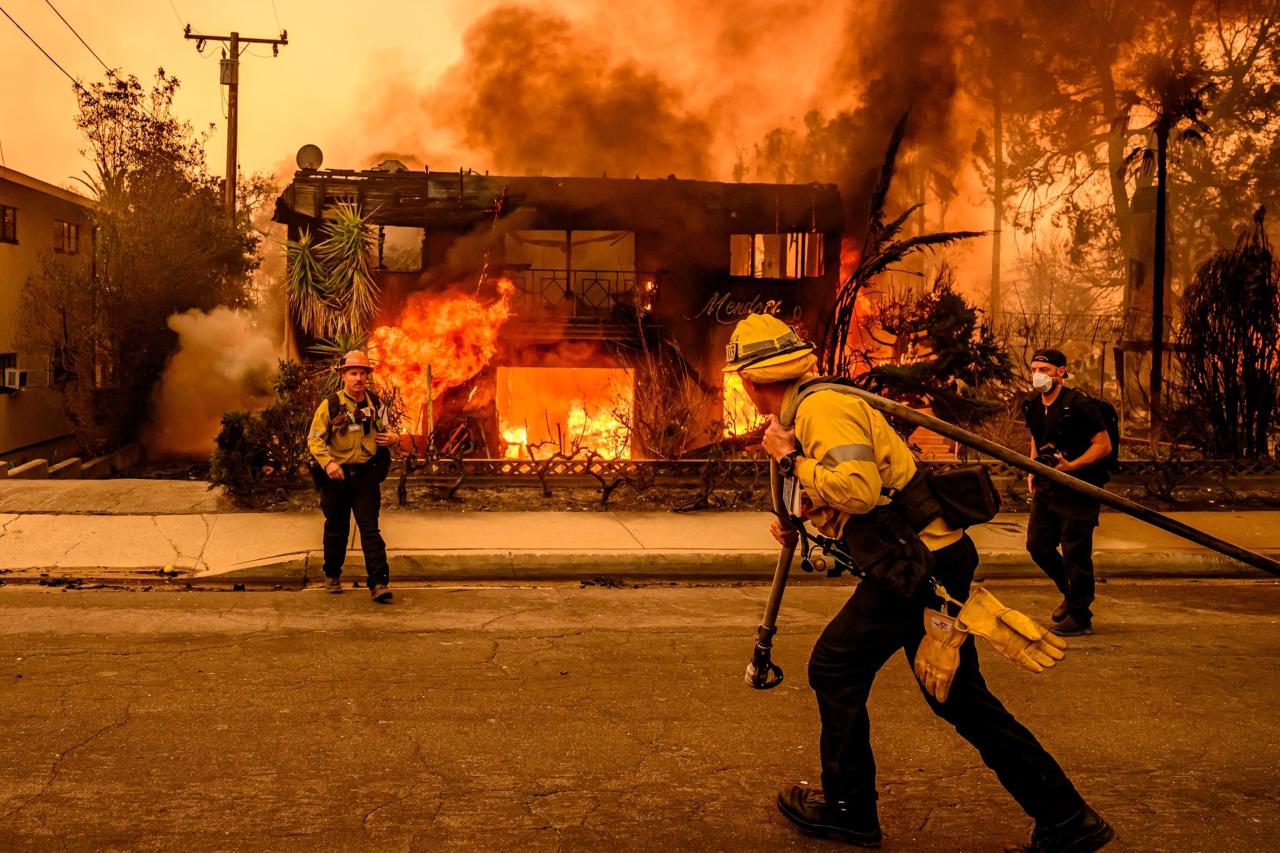

California’s stunning landscapes are tragically vulnerable to wildfires. Understanding past fire patterns is crucial for predicting future risks and developing effective mitigation strategies. Historical records provide valuable insights into the frequency, severity, and potential causes of these devastating events. Analyzing trends across decades can highlight potential links to long-term environmental changes, such as climate change.Historical fire data reveals recurring cycles of intense wildfire activity in California.
Understanding these cycles is vital for informed decision-making regarding fire prevention, preparedness, and response. Analysis of past events helps us anticipate and mitigate future risks.
Historical Fire Records for Yosemite National Park
Yosemite National Park, a treasured destination, has a long history intertwined with wildfire. Past fires have shaped the park’s ecosystem and contributed to its unique character. Analyzing historical records provides a framework for understanding the patterns of these events.
- The frequency of fires in Yosemite has varied significantly throughout the decades. Some decades experienced a higher number of fires than others, influenced by factors such as drought conditions and human intervention.
- The severity of past fires in Yosemite has ranged from relatively minor blazes to large, destructive conflagrations. The impact of each fire depends on factors like weather conditions, vegetation density, and the proximity of human settlements.
Historical Fire Records for Malibu
Malibu, known for its stunning coastal beauty, has faced a concerning trend of increasingly severe wildfires. Understanding the history of these events is critical for future preparedness and risk mitigation.
- Malibu’s historical fire records show a notable increase in fire frequency and severity in recent decades. This increase coincides with observed changes in climate patterns, suggesting a potential link.
- The close proximity of homes to natural vegetation has heightened the risk of wildfires spreading quickly and intensely, posing a threat to human life and property. This is a crucial factor to consider.
Historical Fire Records for San Diego
San Diego, a popular tourist destination, has a complex history of wildfire activity. Understanding the patterns and potential causes of these events is important for future risk management.
- Historical records reveal that San Diego has experienced a mix of small and large-scale wildfires over the years. Variations in the frequency and severity of these fires are influenced by a combination of factors.
- The impact of past fires on the region’s ecology and the human communities has shaped the landscape and the understanding of fire’s role in the ecosystem. Analysis of these impacts provides a baseline for future planning and response efforts.
Timeline of Major Fires in Yosemite National Park (Past 50 Years)
A visual representation of major fires within Yosemite National Park over the last 50 years provides valuable insights. A timeline is presented to illustrate these events.
| Year | Fire Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | The 2000 Fire | A moderate-sized fire that burned through a portion of the park. It caused minimal damage and was quickly contained. |
| 2015 | The 2015 Fire | A significant fire, larger than the 2000 fire, that required significant resources for containment. It impacted a larger portion of the park and caused damage to some trails. |
| 2022 | The 2022 Fire | A large and intense fire that burned for several days. The fire destroyed numerous structures and required a significant response from local and federal agencies. |
Climate Change Impacts on Fire Risk
California’s breathtaking landscapes, renowned for their vibrant ecosystems, are increasingly vulnerable to devastating wildfires. The state’s unique fire ecology, intricately intertwined with its climate, is undergoing profound transformations due to the impacts of climate change. This shift is not just altering the frequency and intensity of fires; it’s fundamentally reshaping the very nature of California’s fire regime.Climate change is significantly amplifying the risk of wildfires in California by altering fundamental atmospheric conditions and impacting the health of vegetation.
Rising temperatures, coupled with shifts in precipitation patterns, are creating a perfect storm of conditions that increase the likelihood and severity of wildfires. This intricate interplay has far-reaching consequences for the state’s ecosystems, communities, and economy.
Rising Temperatures and Altered Precipitation Patterns
Increasing global temperatures are a primary driver of increased fire risk. Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, making it more flammable and prone to ignition. Simultaneously, altered precipitation patterns, characterized by longer and more intense droughts, exacerbate the dryness. These combined effects create a tinderbox of conditions, where even small sparks can rapidly escalate into catastrophic wildfires. For example, the 2020 California wildfires were fueled by record-breaking heat and prolonged drought, resulting in widespread devastation.
Drought Conditions and Vegetation Health
Prolonged drought periods directly impact the health and flammability of California’s vegetation. Trees and other plants experience stress and reduced water availability, leading to increased susceptibility to insect infestations and disease. This weakened state makes them more prone to ignition and rapid spread of fire. For instance, the severity of the 2018 Camp Fire was exacerbated by the pre-existing drought conditions, which had weakened the forest canopy, making it highly susceptible to fire.
Extreme Weather Events and Fire Outbreaks
Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, lightning storms, and strong winds, frequently coincide with and exacerbate fire outbreaks. These events act as ignition triggers, rapidly spreading fire across large areas. The combination of high temperatures, dry vegetation, and strong winds creates conditions ideal for rapid fire growth and propagation. For example, the 2017 Northern California wildfires were heavily influenced by the confluence of extreme heat and strong winds.
California’s diverse landscapes, from sprawling vineyards to towering redwoods, heavily influence where wildfires ignite. Understanding these destinations is key to comprehending fire patterns. This knowledge is crucial, especially when planning an exceptional tour traced to its roots, like the one detailed in an exceptional tour traced to its roots. Ultimately, understanding the interplay between nature and human activity in California’s various locations is vital for effective fire prevention and management.
Comparative Analysis of Historical Temperature Data and Fire Occurrences
Historical temperature data provides crucial insights into the connection between rising temperatures and increased fire risk. A comparison of temperature records from specific regions in California, such as the Sierra Nevada or the Central Valley, demonstrates a clear correlation between rising average temperatures and the frequency and intensity of fire events. Studies analyzing decades of data reveal a discernible upward trend in both temperature and fire occurrence, supporting the conclusion that climate change is a significant factor in escalating fire risk.
Human Activities and Fire Ignition
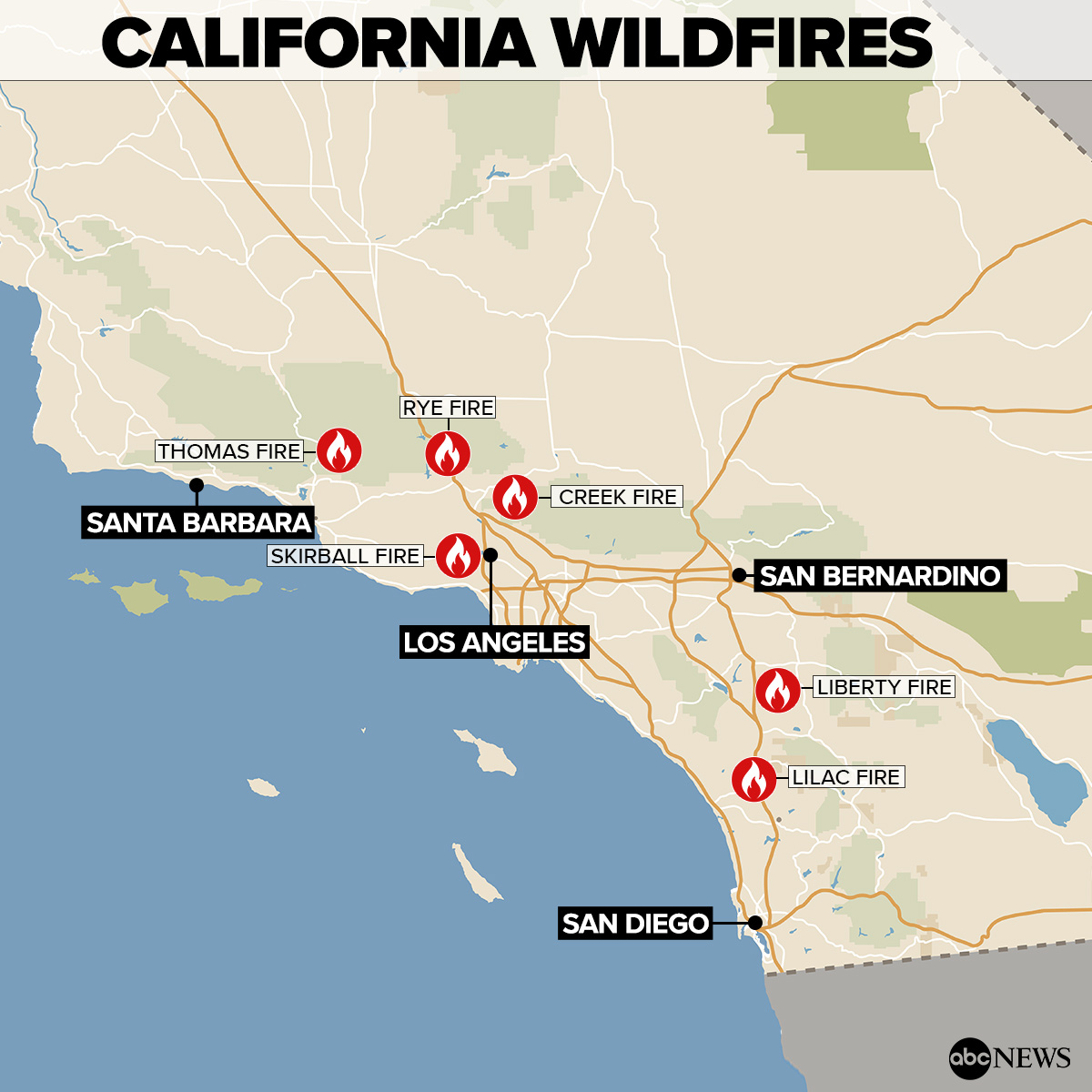
California’s breathtaking landscapes, while beautiful, are also highly susceptible to wildfires. A significant contributor to these devastating events is human activity, often in the form of careless actions or unfortunate circumstances. Understanding these factors is crucial to developing effective preventative measures and promoting responsible behavior in fire-prone areas.
Human Activities Contributing to Fire Ignitions
Human actions are a primary cause of wildfires in California. From carelessly discarded cigarettes to faulty power lines, numerous activities can spark a fire, quickly escalating into a major conflagration if conditions are favorable. The consequences can be catastrophic, impacting both human lives and the environment.
California’s diverse landscapes, from the dry chaparral to the dense forests, heavily influence where wildfires ignite. This year’s patterns, however, are a reminder of how crucial specific locations are in determining fire risk. Interestingly, while we’re focused on the latest California fire updates, the Big Island is also brewing up big things for coffee enthusiasts with its annual coffee fest, showcasing unique local roasts and experiences.
big island brews up big things for coffee fest. Ultimately, understanding the interplay between geography and climate is key to comprehending the wildfire situation across California.
Role of Campfires
Campfires, a cherished part of outdoor recreation, pose a considerable risk if not managed properly. Dry brush and high winds can easily transform a seemingly innocuous campfire into a raging wildfire. Proper campfire safety measures, such as clearing the area of flammable debris, maintaining a sufficient water supply, and extinguishing the fire completely, are paramount. Authorities frequently issue warnings about campfire restrictions during high-fire-risk periods.
Role of Power Lines
Power lines, essential for modern life, can be a source of ignition in dry conditions. Damaged or overloaded lines, coupled with dry vegetation, create a volatile situation. Frequent maintenance and proactive measures to mitigate the risk of sparks are vital. For example, during the 2020 California wildfires, several large fires were initially sparked by downed power lines.
Impact of Human Development on Fire Risk and Spread
Human development, including urbanization and the construction of homes and infrastructure, significantly impacts fire risk and spread. The presence of homes and buildings in wildland areas increases the potential for fire to spread rapidly. Dense vegetation around structures can exacerbate the problem. This underscores the need for defensible space around homes and businesses, along with effective fire prevention measures.
California’s landscapes heavily influence where wildfires rage, dictating fire patterns based on the terrain and vegetation. This geographical impact is a key factor in fire management strategies. Interestingly, companies like aqua expeditions to upgrade both amazon vessels are also adapting to their environments, demonstrating a similar principle of adapting to changing conditions. Ultimately, understanding these environmental influences is crucial for both fire prevention and response efforts in California.
Measures Taken by Authorities to Mitigate Fire Risk from Human Activities
Authorities implement various measures to mitigate fire risk from human activities. These include public awareness campaigns, fire restrictions, and increased monitoring of high-risk areas. Regular inspections of power lines and stricter regulations for campfire use are also crucial components of these strategies. Education programs aimed at educating the public about fire safety are essential in preventing wildfires.
Table: Causes of Wildfires in California Destinations
| Destination | Cause | Frequency | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yosemite National Park | Campfires, discarded cigarettes, lightning | Moderate | Campfire restrictions, increased ranger patrols, public awareness campaigns |
| Southern California (e.g., Los Angeles) | Power lines, arson, campfires | High | Power line inspections, arson task forces, strict campfire regulations, public awareness campaigns |
| Northern California (e.g., Shasta-Trinity) | Lightning, dry vegetation, campfires | Moderate to High | Fire-resistant building codes, defensible space requirements, pre-emptive vegetation management, public education |
Wildfire Response and Mitigation Strategies
California’s history with wildfires is deeply intertwined with its landscape and climate. The state’s response to these devastating events has evolved over time, reflecting a growing understanding of the complex interplay of factors contributing to fire risk and severity. From initial firefighting efforts to proactive mitigation strategies, the approach to wildfire management is constantly adapting to meet the challenges posed by increasingly frequent and intense blazes.Effective wildfire response and mitigation requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses immediate response, long-term prevention, and community preparedness.
This involves not only the heroic efforts of firefighters but also the crucial role played by individuals and communities in safeguarding their homes and livelihoods. The strategies discussed below highlight the critical elements of this multifaceted approach.
Wildfire Response Strategies Employed in California, California destinations inform where fires burn
California’s wildfire response is spearheaded by a network of firefighting agencies, encompassing state, local, and federal entities. These agencies work in concert, leveraging advanced technologies and strategies to contain and extinguish fires. The response often involves rapid deployment of personnel, equipment, and resources to the affected areas. Air support plays a crucial role, enabling rapid assessments, fire suppression, and water delivery.
Advanced fire-fighting technologies and strategies are consistently refined to improve response times and efficiency.
Roles of Firefighting Agencies and Community Preparedness
Firefighting agencies, including the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire), play a vital role in responding to wildfires. They are responsible for coordinating resources, deploying personnel and equipment, and implementing fire suppression tactics. The effectiveness of their response is often enhanced by the preparedness and cooperation of local communities. Community preparedness initiatives, such as evacuation plans and defensible space practices, greatly enhance the ability to minimize damage and casualties.
Community education programs help residents understand the risks associated with wildfires and the proactive steps they can take to protect their homes and property.
Strategies for Preventing and Mitigating Wildfire Risk
Preventing and mitigating wildfire risk necessitates a comprehensive strategy that combines proactive measures with robust response capabilities. These strategies are focused on reducing the fuel load, enhancing defensible space around structures, and improving community preparedness. These measures are vital in preventing the escalation of fires and minimizing their impact. Strategies include fuel reduction projects, which involve controlled burns to remove flammable vegetation.
Developing defensible space around homes involves clearing vegetation and creating firebreaks. This helps prevent fires from spreading to structures.
Examples of Proactive Measures to Reduce Fire Risk in Different Areas
Numerous proactive measures are implemented in different areas to reduce wildfire risk. In areas with high fire danger, fuel reduction projects are commonly undertaken, involving controlled burns to remove accumulated vegetation. These controlled burns are designed to reduce the overall fuel load and make the landscape less susceptible to large-scale fires. In urban-wildland interface zones, implementing defensible space standards is crucial.
This involves clearing vegetation around homes, creating firebreaks, and establishing clear guidelines for landscaping practices. These measures aim to create a buffer zone between homes and the surrounding wildland areas.
Resources Available to Communities to Prepare for Wildfires
Communities can access various resources to prepare for wildfires. The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire) website provides valuable information about wildfire safety, evacuation procedures, and preparedness tips. Local fire departments offer community workshops and educational programs to inform residents about wildfire risks and safety measures. Local government agencies often publish resources on evacuation plans, emergency preparedness, and defensible space requirements.
Many organizations offer assistance to those impacted by wildfires, including financial aid and volunteer support.
- Cal Fire: Provides a wealth of information on wildfire safety, prevention, and preparedness.
- Local Fire Departments: Offer community workshops and educational programs.
- Local Government Agencies: Publish resources on evacuation plans, emergency preparedness, and defensible space requirements.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Provide assistance to those impacted by wildfires.
Future Projections and Mitigation Planning
California’s wildfire landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by a complex interplay of climate change, human activity, and geographic factors. Understanding future projections and developing proactive mitigation strategies are crucial to protecting communities and natural resources. The severity and frequency of fires are anticipated to escalate, demanding a comprehensive approach to wildfire management.Predicting future fire risk requires sophisticated modeling and data analysis, taking into account historical trends, climate projections, and potential human influences.
These models can help pinpoint areas with heightened vulnerability, allowing for targeted interventions and resource allocation.
California’s landscapes, with their dry brush and sprawling forests, heavily influence where wildfires ignite. It’s a sobering reminder that the beauty of our destinations often intertwines with the risk of these devastating fires. Luckily, for those seeking a different kind of adventure, Avalon has christened two new river cruise ships, offering a serene escape from the often-raging blazes.
These luxurious cruises provide a refreshing contrast to the landscape-driven fires, highlighting the beautiful and varied destinations across the US. Ultimately, understanding the connection between California’s geography and fire risk is crucial for both preparedness and appreciating the diverse destinations our state holds.
Projected Fire Risk in California Destinations
California’s diverse geography and climate create varying fire risks across different regions. Southern California, with its dry vegetation and high temperatures, is projected to experience an increase in fire frequency and intensity. Coastal areas, while potentially less susceptible to extreme heat, may face heightened risks from strong winds and dry conditions. Northern California, though sometimes experiencing less extreme temperatures, can still experience prolonged dry periods and rapid fire spread, especially in mountainous regions.
Anticipated Challenges in Managing Wildfires
Managing wildfires in the future will be challenging due to several factors. Resource limitations, including personnel, equipment, and funding, may hinder effective response and mitigation efforts. Increased fire frequency and intensity can overwhelm existing infrastructure and response capabilities. Evacuation procedures will need to adapt to the faster spread of fires, and community resilience planning must be prioritized.
Long-Term Strategies to Mitigate Wildfire Risk
Implementing long-term strategies for wildfire mitigation requires a multi-pronged approach. Improved forest management practices, including controlled burns and thinning, can reduce fuel loads and limit the spread of fires. Developing early detection systems, such as advanced sensor networks and aerial surveillance, is crucial for rapid response. Implementing strict regulations on fire-prone activities and creating defensible space around homes are vital for protecting communities.
Examples of Proactive Community Planning for Wildfire Preparedness
Communities can take proactive steps to prepare for wildfires. Creating evacuation plans, including designated assembly points and routes, is essential. Developing defensible space around homes, removing flammable vegetation, and implementing fire-resistant building materials are critical strategies. Investing in community education programs to raise awareness about wildfire safety is essential. For example, the city of Santa Barbara has developed a comprehensive wildfire preparedness plan that includes detailed evacuation maps and community outreach programs.
Comprehensive Wildfire Mitigation Plan
The following flowchart illustrates a comprehensive wildfire mitigation plan:
→ Assessment
→ Risk Analysis
→ Community Engagement
→ Mitigation Strategies (Fuel Management, Defensible Space, Building Codes)
→ Early Warning Systems
→ Emergency Response Plans
→ Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Note: This is a simplified representation. A comprehensive plan would include detailed sub-steps and interconnections between each phase.
Final Thoughts
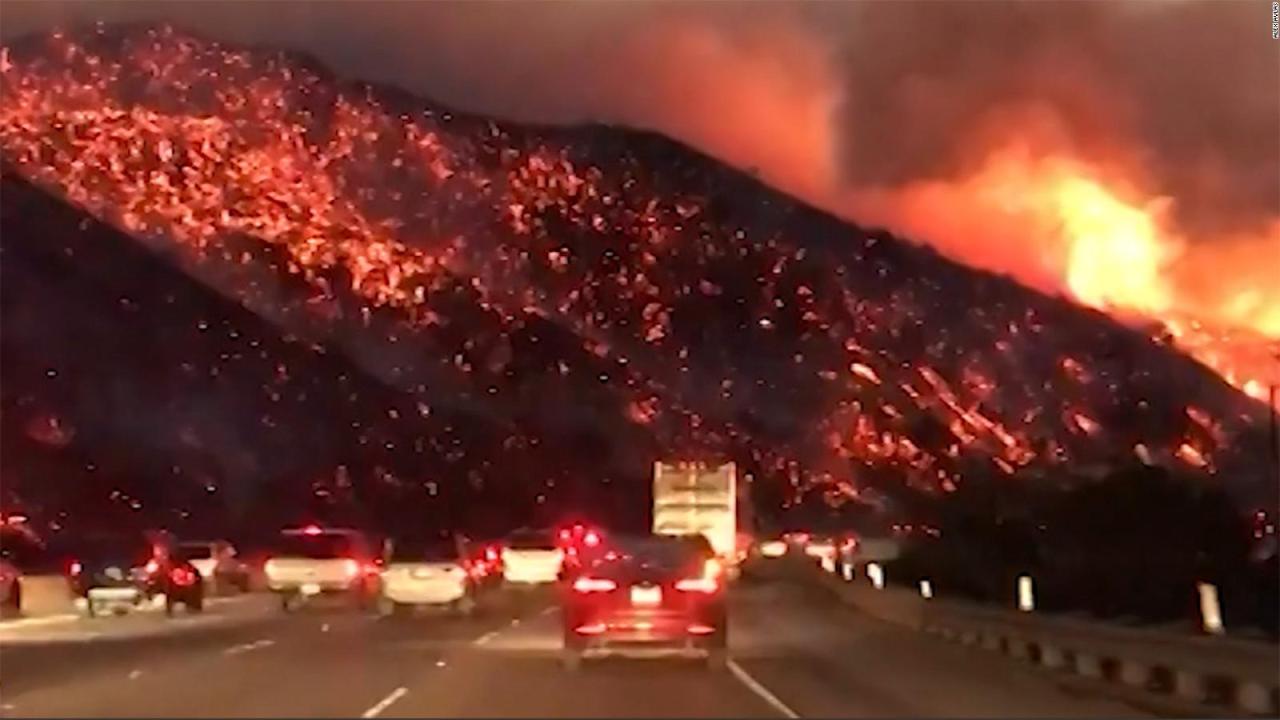

In conclusion, California’s fire patterns are a complex interplay of geographical factors, historical trends, climate change impacts, human activities, and effective response strategies. Understanding these interconnected elements is vital for proactive wildfire mitigation and community preparedness. Future projections highlight the need for sustained efforts in preventing and responding to these devastating events. Ultimately, by learning from the past and adapting to the future, California communities can better protect themselves from the threat of wildfires.
FAQ Corner: California Destinations Inform Where Fires Burn
What is the role of vegetation in fire spread?
Different vegetation types, such as chaparral and forests, have varying flammability. The density and type of vegetation in a specific area significantly influence how quickly and intensely a fire spreads.
How does topography affect fire behavior?
Topography, including slopes and elevation, plays a crucial role in fire behavior. Steep slopes can accelerate fire spread, while higher elevations may experience different fire patterns due to varying weather conditions.
What are some common causes of wildfires in California?
Common causes include campfires, power lines, lightning strikes, and human carelessness. Understanding the frequency of these causes helps prioritize mitigation strategies.
What resources are available to communities for wildfire preparedness?
Local fire agencies, community groups, and government websites often provide valuable resources and information on wildfire preparedness, including evacuation plans, safety guidelines, and community workshops.