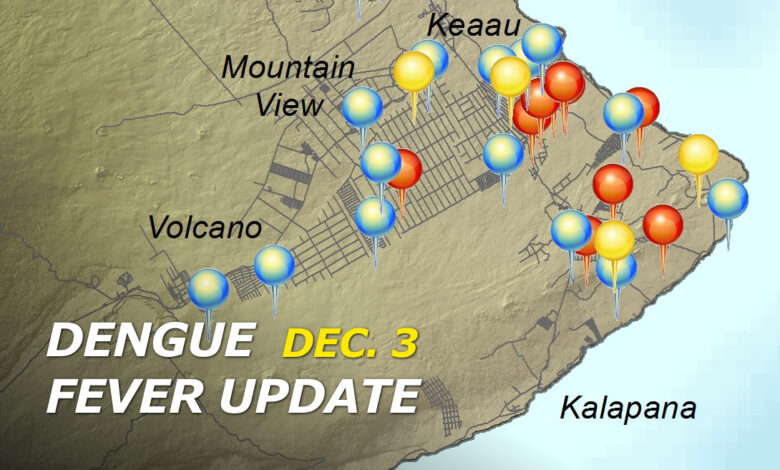
Big Island Dengue Cases Near 80
Big Island approaches 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, highlighting the urgent need for proactive measures to combat this escalating public health crisis. The concerning number underscores the severity of the situation and the potential impact on the island’s residents and economy. Understanding the disease’s characteristics, transmission vectors, and the effectiveness of current response strategies is critical for effectively managing this outbreak.
Dengue fever, a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes, presents a significant threat to public health. Symptoms, ranging from mild fever to severe complications, emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment. The island’s unique environment and recent weather patterns might have contributed to the outbreak’s rapid spread. Comparing this current outbreak to previous ones on the Big Island is vital for identifying trends and developing tailored strategies for this particular context.
Overview of Dengue Fever Outbreak
The Big Island is currently experiencing an outbreak of dengue fever, with 80 confirmed cases. This situation underscores the importance of public health awareness and preventative measures. The recent surge in cases demands a comprehensive understanding of the disease and its potential impact on the community.Dengue fever is a viral infection transmitted primarily through the bite of infected mosquitoes.
It is a significant public health concern globally, and understanding its characteristics is crucial for effective prevention and control.
Key Characteristics of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is characterized by a range of symptoms, including high fever, severe headache, muscle and joint pain, and a characteristic rash. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize complications.
The Big Island is unfortunately approaching 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, a concerning health issue. Meanwhile, a new development in the tourism sector is that Alamo has opened a second Waikiki location, alamo opens second waikiki location , which might provide some relief for visitors needing car rentals. This new location could potentially lessen the impact of the dengue fever situation on the travel industry, hopefully providing much-needed respite for the Big Island’s tourism sector.
- Symptoms: The initial symptoms often resemble the flu, with fever, headache, muscle and joint pain, and sometimes a rash. More severe forms can lead to dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS), which involve severe bleeding, low blood pressure, and organ damage.
- Transmission: The primary mode of transmission is the bite of an infected
-Aedes* species mosquito. These mosquitoes typically breed in stagnant water, making proper sanitation crucial for prevention. - Potential Complications: While most cases resolve without significant complications, severe forms, like DHF and DSS, can lead to serious health issues, including internal bleeding, organ damage, and even death. Prompt medical attention is vital in these situations.
Significance of 80 Confirmed Cases
Eighty confirmed cases represent a notable increase in dengue fever cases on the Big Island. This signifies a need for heightened vigilance and proactive interventions to prevent further spread. The scale of the outbreak demands a coordinated response involving public health officials, healthcare providers, and community members.
Comparison with Previous Outbreaks
Unfortunately, without detailed historical data on previous dengue fever outbreaks on the Big Island, a direct comparison is not possible. Such data would allow for a clearer understanding of trends, patterns, and potential correlations. Future data collection efforts are essential to inform future prevention and control strategies.
| Characteristic | Potential Comparison (Hypothetical Example) |
|---|---|
| Year | 2023 |
| Confirmed Cases | 80 |
| Severity | Moderate (Based on symptoms reported and available information) |
| Intervention Strategies | Increased mosquito control efforts, public awareness campaigns, and improved healthcare access |
Impact and Consequences

The recent surge in dengue fever cases on the Big Island, approaching 80 confirmed infections, necessitates a careful assessment of the potential ramifications. Beyond the immediate health concerns, the outbreak poses significant challenges to the local economy and public well-being. Understanding these consequences is crucial for effective mitigation and long-term prevention strategies.The economic impact of a public health crisis like this can be substantial.
Businesses, particularly those in tourism and hospitality, can experience decreased revenue due to potential travel advisories or cancellations. Lost productivity due to illness among workers and the need for increased healthcare resources further compound the economic burden. The ripple effect of such an outbreak can be felt across various sectors of the local economy.
Potential Impact on Public Health
The escalating number of dengue fever cases highlights the vulnerability of the population to vector-borne illnesses. Increased transmission rates can lead to a surge in hospitalizations and strain healthcare resources, potentially impacting access to other essential medical services. The health authorities are working to address these concerns by increasing surveillance, implementing control measures, and educating the public. Early detection and treatment are critical to preventing severe complications.
Measures Taken by Health Authorities
The Big Island’s health authorities are employing a multi-faceted approach to combat the dengue fever outbreak. These measures include: enhanced vector control efforts, such as increased spraying and fogging in affected areas; increased public awareness campaigns focused on prevention strategies, such as mosquito breeding control and personal protective measures; rapid diagnosis and treatment protocols; and strengthened surveillance systems to monitor the spread and identify high-risk areas.
These combined efforts aim to contain the outbreak and minimize its impact.
Potential Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of the dengue fever outbreak could include the development of resistance to existing treatment methods. It is also possible that the virus could adapt to new vectors or geographical areas, increasing its potential to spread. Furthermore, there may be a lasting impact on public health infrastructure and preparedness. The outbreak could lead to improved infrastructure for vector control, stronger public health surveillance systems, and a greater emphasis on preventative measures.
Effectiveness of Public Health Responses
The effectiveness of the public health responses to the dengue fever outbreak is still being assessed. Currently, there is no definitive data to evaluate the success of each specific measure. However, ongoing monitoring and evaluation of these measures are crucial for refining strategies and improving future responses.
| Public Health Response | Potential Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Enhanced vector control | High potential, contingent on consistent and comprehensive implementation |
| Public awareness campaigns | High potential, dependent on engagement and accurate messaging |
| Rapid diagnosis and treatment | High potential, dependent on timely access to care |
| Strengthened surveillance systems | High potential, enabling proactive interventions and tracking of the spread |
Transmission and Risk Factors

Dengue fever, a mosquito-borne viral illness, is spreading rapidly across the Big Island. Understanding the transmission routes and risk factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies. Effective control relies on recognizing the factors contributing to the spread and the specific mosquito species involved.The primary mode of transmission is the bite of an infected mosquito. The virus multiplies within the mosquito and is then transmitted to humans during a blood meal.
The Big Island is approaching 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, highlighting the need for proactive health measures. With the rising concern, it’s worth considering how changes in the travel industry might impact the situation. For instance, the trend of “all inclusive resorts go small” ( all inclusive resorts go small ) might lead to improved hygiene practices and potentially reduced transmission risks, although further research is needed.
This development, alongside other preventative measures, could help mitigate the spread of dengue on the Big Island.
This highlights the critical role of mosquito control in preventing further infections.
Modes of Transmission
Dengue fever is transmitted primarily through the bite of infected female mosquitoes. These mosquitoes, belonging to specific species, feed on the blood of infected individuals and then transmit the virus to other humans during subsequent blood meals. This cyclical process underscores the importance of breaking the transmission chain.
Risk Factors in the Affected Area
Several factors contribute to increased risk of dengue infection on the Big Island. High population density, coupled with inadequate waste management and stagnant water sources, creates breeding grounds for mosquitoes. These conditions provide ideal environments for mosquito proliferation, significantly increasing the risk of transmission. The presence of unused tires, discarded containers, and even flower pots can serve as breeding grounds.
Furthermore, recent rainfall patterns have likely contributed to the increase in standing water. All of these environmental conditions facilitate the rapid spread of the disease.
Role of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a pivotal role in the spread of dengue fever. Stagnant water, particularly in areas with poor sanitation, provides breeding grounds for mosquitoes. Accumulation of water in discarded containers, flower pots, and even in small depressions in the landscape provides ideal breeding sites. The presence of unused tires and other debris also creates favorable environments.
The recent increase in rainfall has likely created more standing water, leading to an increased mosquito population.
Mosquito Species and Distribution
| Mosquito Species | Distribution on the Big Island |
|---|---|
| Aedes aegypti | Widely distributed throughout the island, particularly in urban and suburban areas. This species is known for its preference for breeding in containers and other artificial water sources. |
| Aedes albopictus | Found throughout the island, but its distribution varies depending on environmental factors. This species is known for its ability to breed in a wider range of water sources, including tree holes and flower pots. |
| Aedes polynesiensis | Potentially present but not definitively confirmed as a significant vector on the Big Island. More research is needed to determine its prevalence and role in dengue transmission in the area. |
The table above highlights the primary mosquito species known to transmit dengue fever on the Big Island. Understanding their specific breeding preferences is critical for targeted control measures.
Public Health Measures and Preparedness
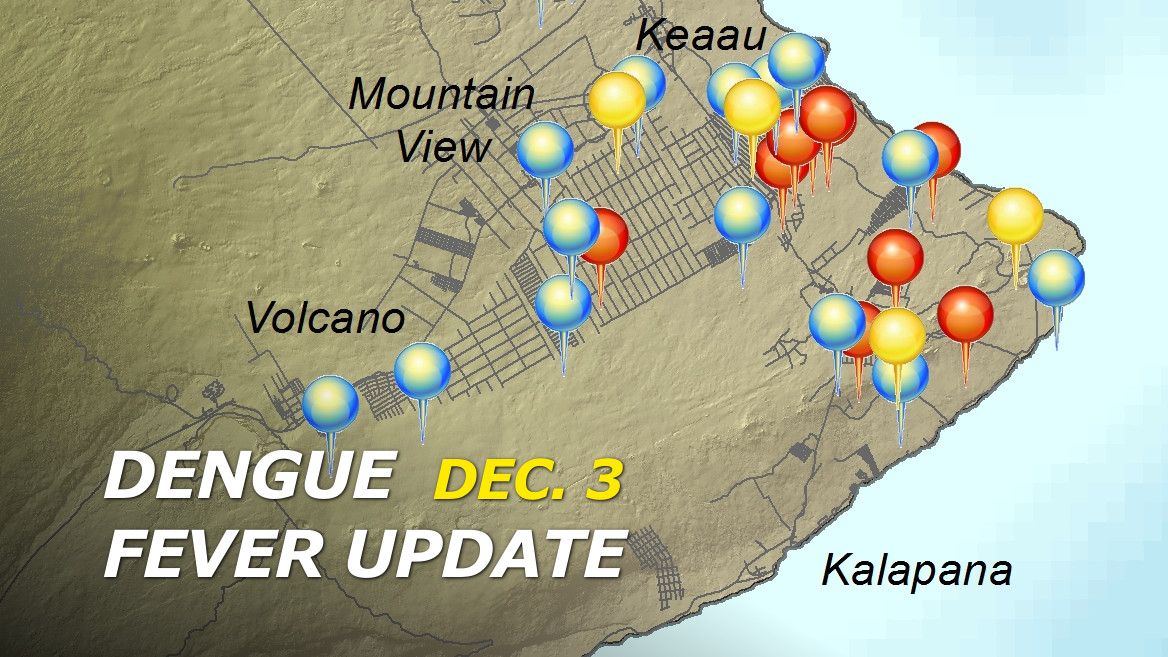
The recent surge in dengue fever cases on the Big Island necessitates a robust public health response. Effective strategies are crucial not only for controlling the current outbreak but also for preventing future outbreaks. This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing community engagement, vector control, and individual precautions. The focus must be on empowering individuals and organizations to take proactive steps towards preventing the spread of the disease.Public health strategies are implemented to interrupt the dengue transmission cycle and to support those affected.
These strategies must encompass both immediate actions and long-term preventive measures to effectively combat the spread of the disease. This multifaceted approach will not only curb the current outbreak but also contribute to the long-term health of the community.
Public Health Strategies Implemented
Comprehensive public health strategies are essential to effectively manage and contain dengue fever outbreaks. These strategies involve a combination of vector control, surveillance, and community engagement initiatives. A key element is the swift identification and isolation of infected individuals to prevent further transmission.
The Big Island is approaching 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, highlighting the importance of preventative measures. While this situation is concerning, perhaps a quick escape to a bite size sailing experience could offer a welcome distraction. A shorter, more manageable sailing trip, like a bite size sailing experience , might be just the thing to soothe anxieties and offer a refreshing change of pace.
Still, the dengue fever situation warrants continued vigilance and proactive health measures on the Big Island.
- Vector Control: Targeted mosquito control measures are implemented to reduce mosquito breeding sites. This includes spraying insecticides, fogging, and community-led efforts to eliminate standing water in containers, flowerpots, and other potential breeding grounds. For example, distributing larvicide tablets for community use and educating residents on proper water storage is crucial.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Close monitoring of the outbreak’s progression is essential to understanding the spread of the disease. This includes tracking the number of confirmed cases, identifying affected areas, and analyzing patterns in transmission. Local health officials actively monitor reported cases, conduct epidemiological investigations, and share data to guide the response. By analyzing trends and geographic patterns, they can effectively deploy resources to high-risk areas.
- Community Engagement: Public awareness campaigns are launched to educate residents about dengue fever symptoms, transmission routes, and preventive measures. Community health workers play a crucial role in disseminating information and encouraging residents to take preventative actions. For instance, holding community health fairs and workshops can be highly effective.
Preventive Measures for Individuals
Individual precautions play a critical role in mitigating the risk of dengue fever. Personal hygiene and proactive measures can significantly reduce the chances of contracting the disease.
- Protection from Mosquito Bites: Using insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, and using mosquito nets are vital. Individuals should apply repellent consistently, especially during peak mosquito activity hours.
- Elimination of Breeding Sites: Promptly emptying and cleaning containers that can hold water, such as flowerpots, buckets, and discarded tires, will significantly reduce mosquito breeding grounds. This effort involves regular inspection of potential breeding sites and prompt removal of standing water.
- Early Detection of Symptoms: Recognizing the early symptoms of dengue fever, such as fever, headache, muscle and joint pain, rash, and nausea, is critical for seeking prompt medical attention. Early intervention significantly increases the chances of favorable outcomes.
Roles and Responsibilities of Organizations
A coordinated effort from various organizations is vital in managing the outbreak effectively. Clear roles and responsibilities will ensure efficient resource allocation and execution of tasks.
| Organization | Roles and Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Ministry of Health | Oversees the overall response, coordinates resources, develops policies, and provides medical support. |
| Local Health Departments | Implement strategies at the local level, monitor cases, and provide community-based support. |
| Hospitals and Clinics | Provide treatment and care to infected individuals, and manage potential surges in patients. |
| Community Organizations | Organize community awareness campaigns, support vector control efforts, and connect individuals with resources. |
| Environmental Agencies | Support vector control measures, identify and eliminate breeding grounds, and provide technical support. |
Community Engagement Initiatives
Engaging the community is critical to successful dengue fever control. Participation and collaboration are vital to achieving long-term results.
- Community Awareness Campaigns: Disseminating information through local media outlets, community meetings, and public service announcements is vital. The focus should be on providing clear and actionable information about dengue prevention.
- Community Health Fairs: Organizing health fairs to provide education, screenings, and information about preventive measures is crucial. These fairs are an excellent platform for direct interaction with residents and fostering a collaborative spirit.
- Volunteer Programs: Engaging volunteers in community-based vector control efforts, such as removing standing water and distributing larvicide, significantly increases the impact of these measures. Volunteer groups provide a powerful mechanism for amplifying the reach and impact of prevention efforts.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Tracking the spread of dengue fever requires robust surveillance systems. Effective monitoring helps public health officials understand disease patterns, identify high-risk areas, and implement targeted interventions. This allows for a proactive response, potentially preventing further outbreaks and minimizing the impact on communities. Without comprehensive surveillance, predicting future trends and tailoring prevention strategies becomes challenging.Accurate and timely data collection is crucial for effective disease surveillance.
Early detection of outbreaks enables swift response, limiting the spread of the disease and preventing severe health consequences. Information gathered from surveillance programs informs decisions on resource allocation, vector control strategies, and public health campaigns. This data-driven approach is essential for optimizing the use of resources and ensuring the most effective interventions are deployed.
Current Surveillance Methods, Big island approaches 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever
Surveillance methods for dengue fever encompass a range of approaches, from passive reporting systems to active surveillance strategies. Passive surveillance relies on routine reporting from healthcare facilities, while active surveillance involves direct investigation of suspected cases and potentially exposed individuals. A combination of these approaches is often the most effective strategy, leveraging the strengths of each method.
Importance of Accurate and Timely Data Collection
Accurate and timely data collection is paramount for effective disease surveillance. Inaccurate or delayed reporting can hinder the ability to identify emerging outbreaks and implement timely interventions. This is particularly critical in rapidly spreading outbreaks, where rapid action can significantly reduce the impact of the disease. For instance, delays in reporting a dengue outbreak in a specific region could lead to a larger number of infected individuals, escalating the need for resources and potentially causing significant morbidity.
Challenges in Surveillance and Monitoring
Several challenges hinder the effective surveillance and monitoring of dengue fever. Limited resources, including funding, personnel, and infrastructure, can hinder the capacity to implement and maintain robust surveillance systems. Data quality issues, such as incomplete or inconsistent reporting, can also significantly impact the reliability of surveillance data. Cultural and language barriers, and challenges in accessing remote or marginalized communities can also affect the effectiveness of surveillance efforts.
Comparison of Surveillance Strategies
| Surveillance Strategy | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Surveillance | Relies on routine reporting from healthcare facilities. | Simple to implement, low cost. | Underestimation of true incidence, delayed detection of outbreaks. |
| Active Surveillance | Direct investigation of suspected cases and potentially exposed individuals. | More accurate estimation of incidence, rapid detection of outbreaks. | More resource-intensive, may not be feasible in all settings. |
| Sentinel Surveillance | Focuses on specific locations or populations to monitor for early signs of an outbreak. | Early warning system for outbreaks, targeted intervention. | May not represent the entire population, requires careful selection of sentinel sites. |
| Syndromic Surveillance | Uses non-specific symptoms or clinical presentations to detect outbreaks. | Early detection of outbreaks, less reliance on laboratory confirmation. | Requires sophisticated data analysis, may lead to false alarms. |
Prevention and Control Strategies
The recent surge in dengue fever cases on the Big Island necessitates a robust and multifaceted approach to prevention and control. Effective strategies must address vector control, public awareness, and targeted interventions to curb the spread of this viral illness. A proactive and community-driven approach is crucial to mitigating the impact of the outbreak and protecting public health.Effective prevention strategies are vital to controlling the dengue fever outbreak and preventing future occurrences.
By understanding the methods used for mosquito control and the importance of public awareness, communities can take proactive steps to protect themselves.
Vector Control Measures
Vector control plays a pivotal role in dengue prevention. Mosquitoes are the primary vectors responsible for transmitting the virus, and controlling their populations is paramount. A multi-pronged approach to vector control, incorporating various methods, is essential for effective intervention.
- Larviciding:
- Larviciding involves the use of larvicides to eliminate mosquito larvae in breeding sites. These sites can include stagnant water in containers, flowerpots, and even discarded tires. Targeted larviciding strategies, such as identifying and treating specific breeding grounds, are essential to effectively control mosquito populations.
- Adulticiding:
- Adulticiding involves the use of insecticides to eliminate adult mosquitoes. This method focuses on reducing the flying mosquito population in the affected areas. The selection of insecticides should consider their efficacy against the prevalent mosquito species and their environmental impact.
- Environmental Management:
- Environmental management strategies are crucial in preventing mosquito breeding. These include eliminating potential breeding sites, such as standing water, and promoting proper water storage practices. Community participation in identifying and eliminating breeding grounds is essential for the success of vector control initiatives.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are crucial for educating communities about dengue fever transmission, risk factors, and preventive measures. Effective communication strategies are vital to ensuring that the message reaches all segments of the population.
- Community Education Programs:
- Community education programs can educate individuals about the importance of eliminating potential mosquito breeding sites in and around their homes. These programs should cover the different types of mosquitoes that transmit dengue fever, the life cycle of the mosquito, and the steps to take to eliminate breeding grounds.
- Mass Media Outreach:
- Using various mass media channels, such as radio, television, and social media, is crucial to reach a broader audience and raise awareness about dengue fever prevention. Clear and concise messages should be disseminated to provide accurate information and dispel misinformation.
- Community Engagement:
- Community engagement is crucial for long-term success in dengue prevention. Involving community leaders and organizations in awareness campaigns can enhance the impact and ensure the message resonates with the local population. This often involves local language support and cultural relevance in the messaging.
Methods for Mosquito Control in the Affected Area
Effective mosquito control methods in the affected area should be tailored to the specific circumstances. A comprehensive approach that considers local environmental conditions and mosquito species is crucial.
- Targeted Surveillance:
- Identifying and monitoring mosquito breeding sites is essential for effective control. This involves regular surveillance of potential breeding areas, identifying the prevalent mosquito species, and assessing the effectiveness of control measures. This also includes ongoing monitoring of vector density to evaluate the effectiveness of control measures.
- Integrated Pest Management:
- An integrated pest management approach is a sustainable method that combines various techniques to manage mosquito populations. This involves using a combination of larviciding, adulticiding, and environmental management strategies to minimize the environmental impact while effectively controlling the mosquito population.
Potential Future Scenarios
The Big Island dengue fever outbreak presents a complex situation, and its trajectory hinges heavily on the effectiveness of implemented control measures. Failure to address the outbreak swiftly and comprehensively could lead to severe consequences, impacting not only public health but also the island’s vital tourism sector. Understanding potential outcomes and comparing different forecasting models is crucial for proactive planning and resource allocation.The current situation underscores the importance of proactive public health strategies.
Ignoring the early warning signs and not acting decisively could result in a significant escalation of the outbreak, with potentially severe health implications for the population. A delayed response could lead to a wider geographic spread of the disease, straining healthcare resources and potentially hindering economic recovery.
Possible Outcomes if Effective Measures are Not Taken
The lack of swift and effective interventions could lead to a prolonged outbreak, resulting in a higher number of infected individuals. This could overwhelm local healthcare facilities, leading to potential shortages of medical supplies and personnel. The increasing number of cases could also result in community transmission, with a greater risk of severe complications and potentially fatal outcomes.
Furthermore, the ongoing spread could potentially lead to a resurgence of the outbreak, requiring a more intensive and prolonged response in the future.
The Big Island is approaching 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, highlighting the need for preventative measures. This recent surge in cases, unfortunately, contrasts sharply with the recent, impressive allure of the seas refurbishment. The ship’s new amenities and features, however, won’t negate the need for careful consideration of mosquito-borne illnesses when visiting the Big Island. It’s a timely reminder of the importance of travel precautions, even with exciting new additions like those on the allure of the seas refurbishment.
Comparison of Forecasting Models for Disease Outbreaks
Various mathematical models are employed to predict disease outbreaks, each with its strengths and limitations. Epidemiological models, for instance, analyze historical data on disease patterns and transmission rates to project future trends. These models often rely on factors like population density, environmental conditions, and socioeconomic indicators. Agent-based models, on the other hand, simulate the behavior of individual agents (in this case, infected individuals and vectors) to understand how interactions and movement patterns influence disease spread.
Their complexity allows for a more nuanced understanding of the outbreak dynamics. The choice of model depends on the specific characteristics of the outbreak and the available data. For example, a simple SIR model (Susceptible-Infected-Recovered) might be sufficient for initial projections, while more complex models might be necessary for detailed predictions and targeted interventions.
The Big Island is unfortunately approaching 80 confirmed cases of dengue fever, a serious public health concern. While this is a worrying trend, it’s important to remember the incredible feats of engineering underway, like the ambitious salvage project to raise the Concordia. This effort, detailed in this article on attempt to raise concordia is ambitious salvage project , showcases human ingenuity and the drive to overcome seemingly insurmountable challenges.
Hopefully, similar determination can help combat the dengue fever outbreak on the Big Island.
Potential Impact on the Island’s Tourism Sector
The outbreak’s impact on tourism is a significant concern. Dengue fever, being a mosquito-borne illness, is often perceived as a health risk by potential tourists. A perception of heightened risk, even if not fully justified by the data, can deter tourists from visiting the island. This could lead to a decline in visitor numbers, affecting local businesses that rely on tourism for their revenue.
For example, the 2018 outbreak in another island nation had a noticeable impact on tourism, with reported decreases in visitor arrivals in the affected regions. This underlines the need for transparent communication and proactive measures to assure visitors of the safety and health of the island.
Potential Scenarios and Associated Risks
| Scenario | Description | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Controlled Outbreak | Effective public health measures successfully contain the spread of dengue fever within a reasonable timeframe. | Low risk of significant economic or social disruption. |
| Scenario 2: Moderate Outbreak | The outbreak persists for a longer period, affecting a larger portion of the population. Public health measures are implemented, but some challenges are encountered. | Moderate risk of economic disruption, especially in the tourism sector. Potential strain on healthcare resources. |
| Scenario 3: Uncontrolled Outbreak | Public health measures are inadequate or delayed, leading to widespread transmission and severe consequences. | High risk of significant economic and social disruption, including severe damage to the tourism sector. Potential strain on healthcare infrastructure, with possible shortages of resources. |
International Comparisons
Looking beyond the Big Island’s dengue outbreak, understanding how other regions are tackling this disease offers valuable insights. Global comparisons highlight successful prevention strategies and the varying impacts of dengue fever across different countries and climates. Examining past outbreaks and their management provides crucial lessons for the Big Island’s ongoing response.Comparing dengue outbreaks globally reveals common threads but also diverse challenges.
Factors such as socioeconomic conditions, healthcare infrastructure, and mosquito vector control programs all play a significant role in determining the severity and duration of an outbreak. This comparison helps to tailor the Big Island’s response, drawing upon successful interventions in other areas.
Similar Dengue Outbreaks in Other Regions
Numerous countries worldwide have experienced significant dengue outbreaks, often with overlapping challenges. Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean are particularly vulnerable due to climate and population density. These outbreaks frequently involve rapid spread within communities, underscoring the importance of prompt public health interventions. For instance, outbreaks in the Philippines have demonstrated the rapid spread potential of dengue in densely populated urban areas.
Successful Prevention and Control Strategies
Several regions have successfully implemented strategies to mitigate dengue outbreaks. Vector control, including targeted mosquito eradication programs and public awareness campaigns, often plays a crucial role. Effective communication strategies that educate the public about preventive measures and encourage participation are essential for success. Singapore, for example, has implemented comprehensive mosquito control programs that include community engagement, larviciding, and environmental modification to limit mosquito breeding grounds.
These measures highlight the multifaceted approach required to manage dengue.
Impact of Dengue Fever on Different Countries
The impact of dengue fever varies greatly across countries. Factors such as healthcare access, economic conditions, and the presence of pre-existing health issues contribute to the differing outcomes. Developing countries often bear a disproportionate burden due to limited resources and infrastructure. The socioeconomic consequences of dengue outbreaks can be severe, including lost productivity and increased healthcare costs.
This underscores the need for proactive prevention and control measures to minimize the impact on communities.
Global Prevalence of Dengue
| Region | Dengue Prevalence (Estimated) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | High | High population density and favorable climate conditions for mosquito breeding. |
| Latin America | High | Similar to Southeast Asia, favorable conditions for mosquito breeding. |
| Caribbean | Moderate to High | Climate conditions contribute to mosquito breeding and transmission. |
| Africa | Increasing | Changing climate patterns and increased human movement contribute to the spread. |
| North America | Low | More temperate climate and mosquito control measures contribute to lower prevalence. |
This table provides a general overview. Specific prevalence figures can vary depending on the year and the specific region or country being assessed. Ongoing surveillance is essential for tracking the disease’s spread and informing targeted interventions.
Illustrative Cases
The recent surge in dengue fever cases on the Big Island underscores the urgent need for proactive public health measures. Understanding the impact of this illness on individuals and families is crucial for effective community response and prevention strategies. This section presents illustrative cases to highlight the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Individual Impacts
The illness varies in severity, impacting individuals differently. Some experience mild symptoms, while others require hospitalization. The effects extend beyond physical discomfort; the disease often disrupts daily routines, impacting work, school, and family responsibilities. The financial burden associated with medical expenses, lost wages, and potential caregiving needs can be significant. Recovery time can vary greatly depending on the severity of the illness and the individual’s overall health.
Family Impacts
Dengue fever’s impact on families is multifaceted. Caregivers may face increased responsibilities, juggling work and home life while caring for an ill family member. The emotional toll on families is substantial, particularly when facing uncertainty about the severity of the illness and the recovery process. Financial strain due to medical costs and lost income can further complicate family dynamics.
Case 1: A Young Professional
A 28-year-old software engineer experienced a sudden onset of high fever, severe headache, and muscle pain. The symptoms progressively worsened, leading to vomiting and fatigue. Delayed diagnosis initially hampered effective treatment, resulting in a prolonged recovery period. The experience underscored the importance of promptly seeking medical attention when experiencing these symptoms. The impact extended to lost workdays and increased financial burden.
Case 2: A Senior Citizen
An 82-year-old retiree experienced a similar symptom presentation but exhibited a slower progression. The individual’s pre-existing health conditions complicated the recovery process, highlighting the need for prompt medical intervention, especially for vulnerable populations. The family’s strain was substantial due to the need for constant care and the emotional toll of uncertainty.
Case 3: A Young Child
A 6-year-old child experienced a rapid escalation of symptoms, including high fever, rash, and severe abdominal pain. Early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention were critical in preventing potential complications and ensuring a positive outcome. The experience emphasized the need for heightened awareness and immediate action when observing concerning symptoms in children.
“The fever was relentless, and the pain in my muscles felt like someone was twisting them. I couldn’t eat or sleep. I was worried about my family and the financial impact of this.”
Patient Testimonial (redacted for privacy)
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing dengue fever. Prompt medical intervention can prevent severe complications and significantly reduce the duration of illness. This includes recognizing the early warning signs, such as fever, headache, and muscle pain, and seeking immediate medical attention. This proactive approach can greatly reduce the impact on individuals and families.
Summary
The situation regarding dengue fever on the Big Island demands immediate attention. The increasing number of confirmed cases, combined with the potential economic and social repercussions, underscores the need for effective public health measures. By understanding the transmission pathways, implementing preventive measures, and enhancing surveillance efforts, the community can work together to mitigate the spread and protect the well-being of the island’s population.
Continued monitoring and adaptation of strategies will be crucial to managing the long-term impact of this health crisis.
Q&A: Big Island Approaches 80 Confirmed Cases Of Dengue Fever
What are the typical symptoms of dengue fever?
Symptoms can range from mild fever and headache to more severe complications like severe bleeding or organ damage. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
How can individuals protect themselves from dengue fever?
Avoiding mosquito bites is paramount. Using mosquito repellent, wearing long sleeves and pants, and eliminating standing water around homes are essential preventive measures.
What are the long-term effects of a dengue fever infection?
While most recover fully, some individuals experience lingering health issues, highlighting the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment.
How effective are the current mosquito control measures on the Big Island?
Information about the effectiveness of current mosquito control measures should be included in the full report. Evaluating the success of these programs is vital for tailoring future strategies.






